Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 9, 2021
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster II (1862–1888)
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: Neurobehçet’s disease (NBD) is a severe complication of Behcet’s disease (BD). Despite well-established therapies, with glucocorticoids and conventional immunosuppressants (cIS) a significant proportion of patients are refractory. The aim of this study is to assess efficacy and safety of biologic therapy (BT) in NBD refractory to glucocorticoids and at least one cIS.
Methods: Open-label multicenter study of refractory NBD from 22 different referral Spanish Hospitals. The main outcome variables were safety and clinical response measured at baseline, 6, 12 and 24 months. Other outcome variables were improvement in analytical parameters and corticosteroid-sparing effect of biological therapy.
Results: We studied 42 patients (21 women/21 men; mean age 40.4±10.8 years). HLA B51 was positive in 15 (40.5%) out of 37 patients tested. Non-neurological manifestations were oral ulcers (n=41, 97.6%), genital ulcers (n=31, 73.8%), skin lesions (n=28, 66.7%), arthralgia (n=27, 64.3%), uveitis (n=21, 50.0%), arthritis (n=9, 21.4%), venous thrombosis (n=9, 21.4%) and arterial thrombosis (n=4, 9.5%). The underlying neurologic manifestation were parenchymal (n=34, 81 %) and non-parenchymal (n=17, 40.5%) involvement (TABLE). The first BT used was infliximab (n=20), adalimumab (n=13), golimumab (n=3), tocilizumab (n=3) and etanercept (n=2).
After 58.2±51.4 months since initiation of BT, neurological response was complete (n=27; 64.3%), or partial (11, 26.1%). Only 4 (9.5%) patients did not respond (FIGURE). After 6 months of BT, ESR improved from.31.5±25.6 to 15.3±11.9 mg/L (p=0.005) and CRP from 1.4 [0.2-12.8] to 0.3 [0.1-3] mg/L (p= 0.002). Likewise, a decrease in oral prednisone dose was also achieved from 45.6±17.3 mg/day at baseline to 5.17±2.85 mg/day after 24 months (p< 0.0001).
Primary failure was observed in 16 (38.1%) patients due to inefficacy (n=11, 68.8%) or adverse effects (n=5, 31.3%). Similarly, secondary failure was detected in 6 (14.3%) patients due to inefficacy (n=5, 83.3%) or adverse effects (n=1, 16.7%). No serious adverse effects were observed.
Conclusion: BT, especially monoclonal anti-TNF drugs, seems effective and safe in patients with refractory NBD.
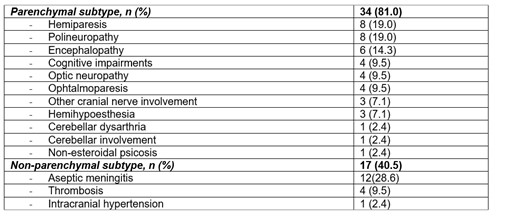 TABLE: Underlying neurologic manifestation of 41 patients with refractory neurobehçet’s disease treated with biologic therapy
TABLE: Underlying neurologic manifestation of 41 patients with refractory neurobehçet’s disease treated with biologic therapy
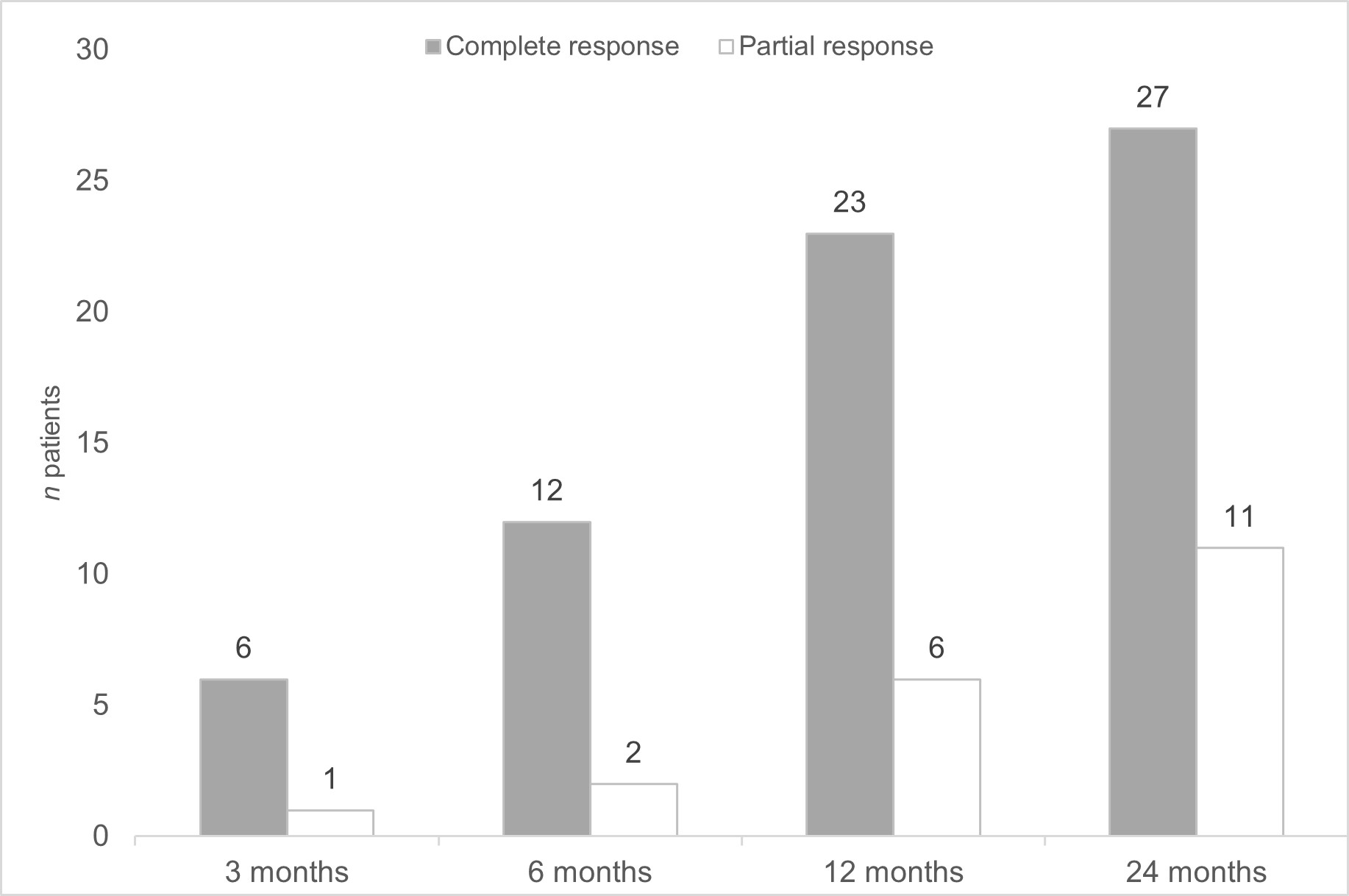 FIGURE: Neurological response after initiation of biological therapy
FIGURE: Neurological response after initiation of biological therapy
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Herrero-Morant A, Martin-Varillas J, Calvo-Río V, Castañeda S, Maíz O, Blanco A, Sánchez J, Ortego N, Raya E, Brandy-Garcia A, Olive-Marques A, Prior-Español A, Moriano C, Díez E, Melero R, Grana Gil J, Seijas-López , Urruticoechea-Arana A, Ramos-Calvo , Delgado-Beltran C, Loredo-Martinez M, Salgado E, Sivera F, Torre I, Narvaez J, Andreu J, Martinez O, Gómez de la Torre R, Fernandez-Aguado S, Romero-Yuste S, Espinosa G, gonzalez-Gay M, Blanco R. Biological Therapy in Refractory Neurobehçet’s Disease. Multicenter Study of 42 Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biological-therapy-in-refractory-neurobehcets-disease-multicenter-study-of-42-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biological-therapy-in-refractory-neurobehcets-disease-multicenter-study-of-42-patients/
