Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1052–1081) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Biologic therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM) of TNF-inhibitor drug and anti-drug antibody provides patient-specific pharmacokinetic and immunogenic assessment. In suboptimal response, drug and anti-drug antibody concentrations discern the underlying mechanism of failure as: 1) Pharmacokinetic Insufficiency, not enough drug (low drug) 2) Mechanistic Mismatch, wrong type of drug (as evidenced by sufficiently high drug) or 3) immunogenicity (anti-drug antibodies) As such, biologic TDM informs the very different medication decisions of whether to increase the same biologic or to switch drug, in- or out-of class.
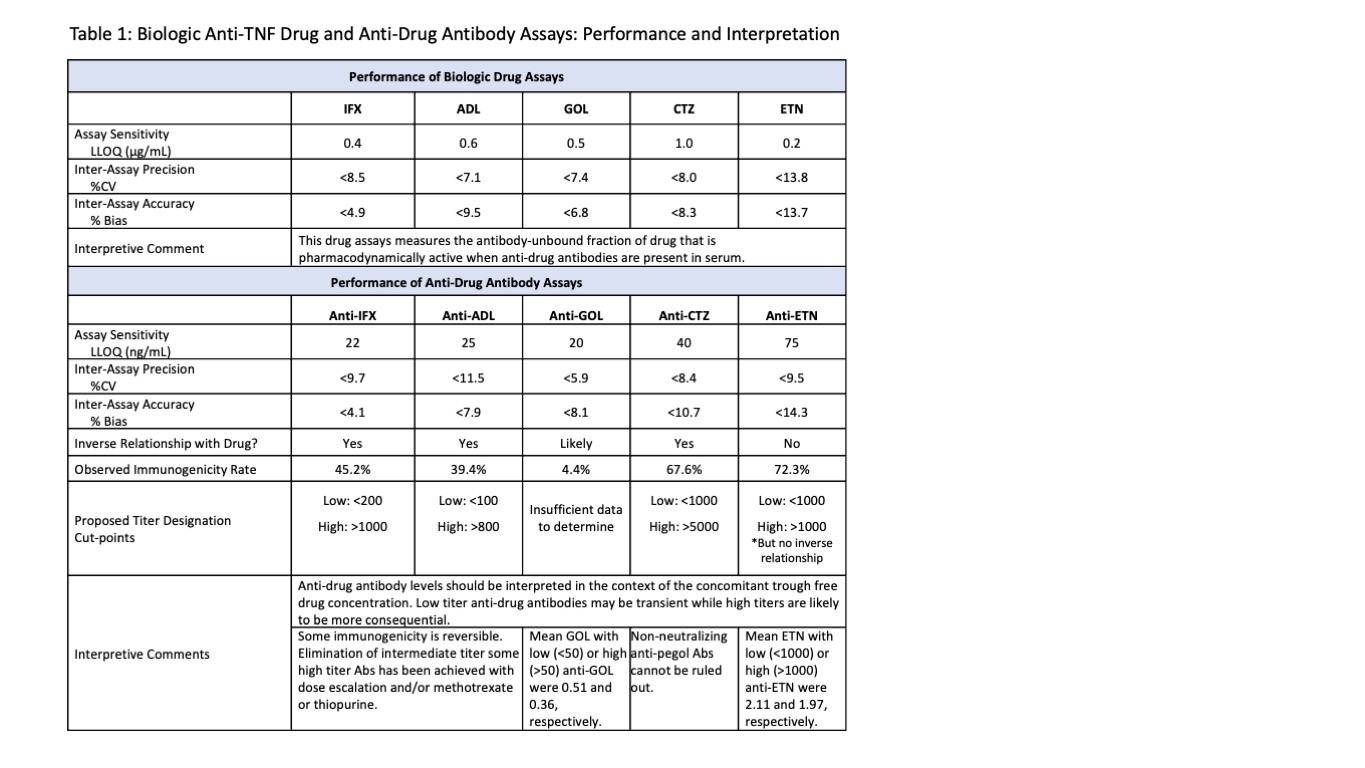
Methods: Drug (in μg/mL) and anti-drug antibody (in ng/mL) were measured by lab developed chemiluminescent immunoassays (Table 1). Of note, all drug assays measure the antibody-unbound fraction of drug when serum anti-drug antibodies are present. All anti-drug antibody assays are drug-tolerant and drug-specific as verified by a confirmatory test. Blood collection just prior to next infusion/injection is recommended because target ranges have been set by studies using trough concentrations.
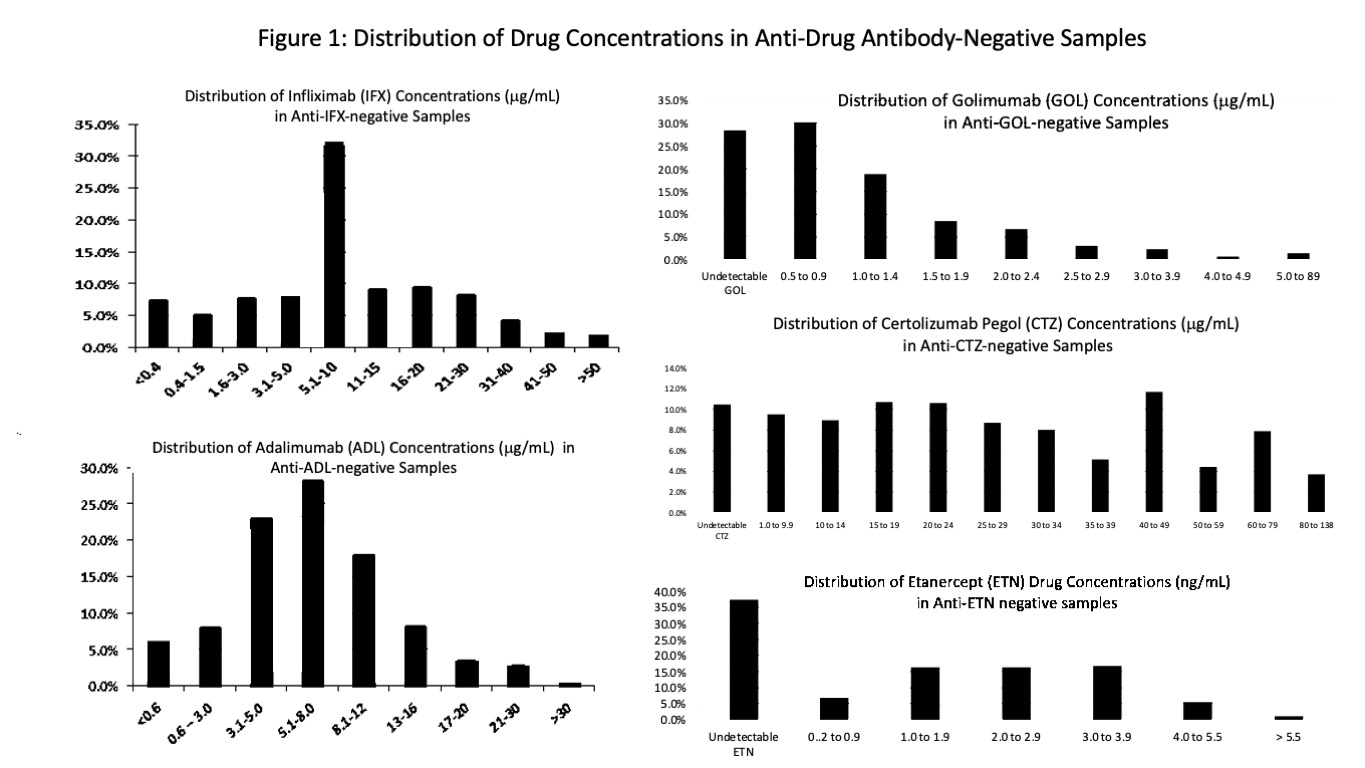
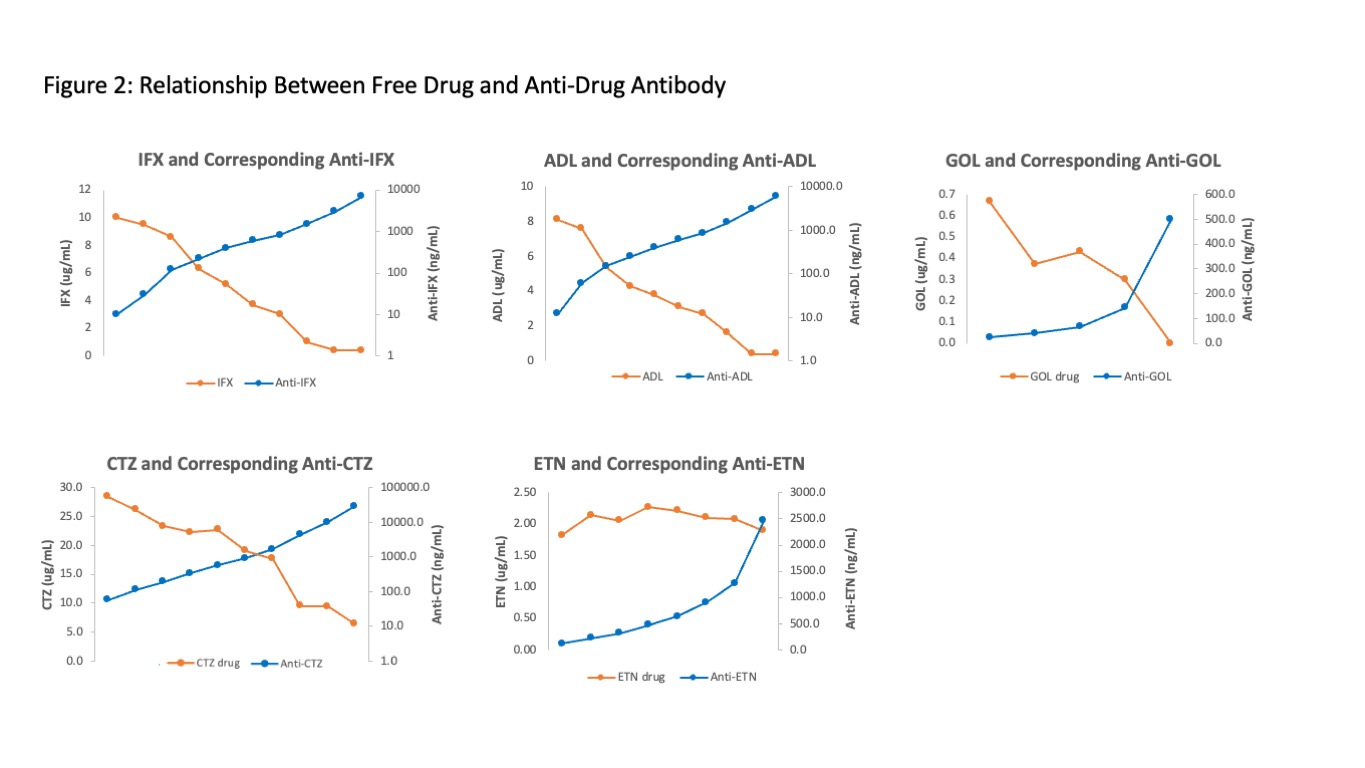
Results: Serum samples from 37,165, 22,412, 1032, 2587, and 734 patients were analyzed for IFX, ADL, GOL, CTZ or ETN and corresponding anti-drug antibodies. Distribution of drug levels (Figure 1) demonstrates that even in the absence of immunogenicity, many patients may be subtherapeutic when using reasonable, if not well-established, therapeutic targets of 3 for IFX, 5 for ADL, 3 for GOL, 20 for CTZ, and 3 for ETN. Immunogenicity rates were 45.2%, 39.4%, 4.4%, 67.6% and 72.3% for IFX, ADL, GOL, CTZ and ETN, respectively (Table 1). High immunogenicity of ETN and CTZ may be explained by their uniqueness as fusion and pegylated molecules, respectively. Figure 2 demonstrates the relationship between free drug and anti-drug antibody. Analysis of this inverse relationship yielded cut-points for titer designations of low, intermediate, and high for anti-IFX, anti-ADL, and anti-CTZ (Table 1). Of note, ETN alone lacked this inverse relationship. Anti-ETN, even in high titer, had no effect on concomitant ETN. Anti-CTZ were the highest numerically, but many may be non-neutralizing antibodies against pegol where only >5000 appears to be impactful. As a good rule, anti-drug antibodies should be interpreted in the context of the concomitant free drug trough concentration.
Conclusion: Here, we report TNF-inhibitor and their anti-drug antibody levels in >60,000 patients. Though clinical histories and blood collection timing are not known, Figure 1 showed that many patients may have insufficient drug levels. Observed immunogenicity rates to IFX, ADL, CTZ and ETN were high and all anti-drug antibodies except anti-ETN adversely affect free drug levels. Numeric antibody results should be interpreted with the help of titer designations (low/high) by the laboratory because low titer antibodies have less impact on drug levels and may be transient or reversible whereas high titers with nil or very low drug indicate refractory immunogenicity. In this way, biologic TDM elucidates the mechanism of suboptimal response and should be used to optimize drug efficacy and longevity by informing and expediting adjustments to medication.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chun K, Yang J. Biologic Drug and Anti-Drug Antibody Monitoring: All 5 TNF-Inhibitors, Infliximab, Adalimumab, Golimumab, Etanercept, Certolizumab Pegol, in 63,930 Patient Samples [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biologic-drug-and-anti-drug-antibody-monitoring-all-5-tnf-inhibitors-infliximab-adalimumab-golimumab-etanercept-certolizumab-pegol-in-63930-patient-samples/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/biologic-drug-and-anti-drug-antibody-monitoring-all-5-tnf-inhibitors-infliximab-adalimumab-golimumab-etanercept-certolizumab-pegol-in-63930-patient-samples/