Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A, showed efficacy to Week (Wk) 52 in patients (pts) with non-radiographic and radiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-/r-axSpA) in the phase 3 trials BE MOBILE 1 and 2.1,2 We compare impact of shorter vs longer duration of symptoms (DoS) on BKZ efficacy to 2 years (yrs).
Methods: In BE MOBILE 1 (nr-axSpA; NCT03928704) and 2 (r-axSpA; NCT03928743), pts were randomized to BKZ or placebo (PBO); all received BKZ in Wks 16–52. At Wk 52, pts could enter an ongoing open-label extension (NCT04436640) and receive BKZ. We report outcomes to Wk 104 for pts with DoS ≤2/ >2 yrs (ASAS early axSpA definition),3 and ≤5/ >5 yrs to optimize subgroup sample sizes (BE MOBILE 2 DoS ≤2 n=17). Continuous BKZ pts and PBO/BKZ switchers were pooled within each trial from Wk 52.
We report ASAS40 (non-responder imputation), ASDAS < 2.1 (multiple imputation [MI]), and BASDAI change from baseline (CfB; MI) for pts with DoS ≤5/ >5 (both trials) and DoS ≤2/ >2 (BE MOBILE 1). We report mean MRI sacroiliac joint (SIJ) SPARCC inflammation score (observed case) for MRI sub-study pts with DoS ≤5/ >5 (BE MOBILE 1 only; BE MOBILE 2 MRI sub-study DoS ≤5 n=27).
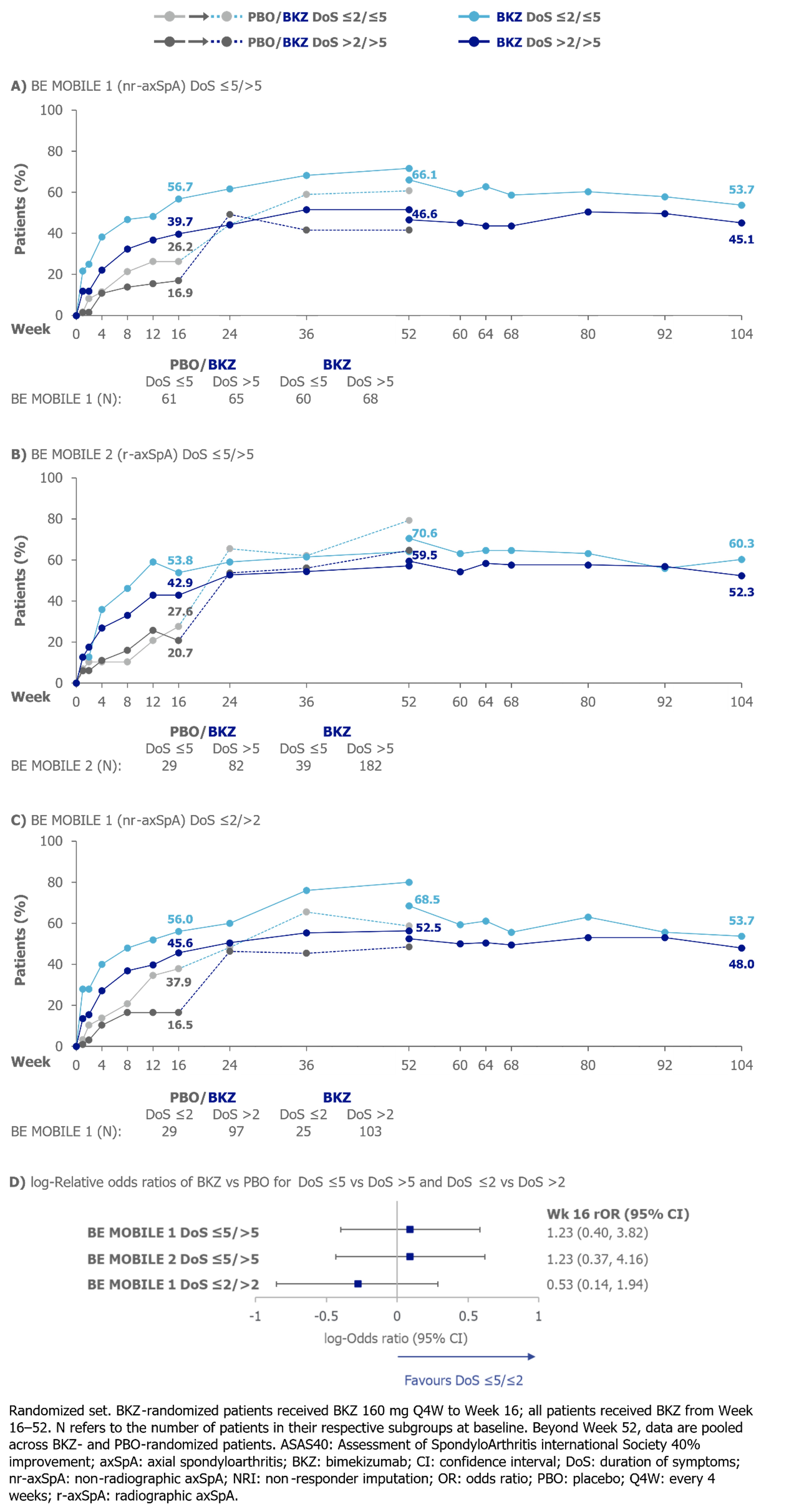
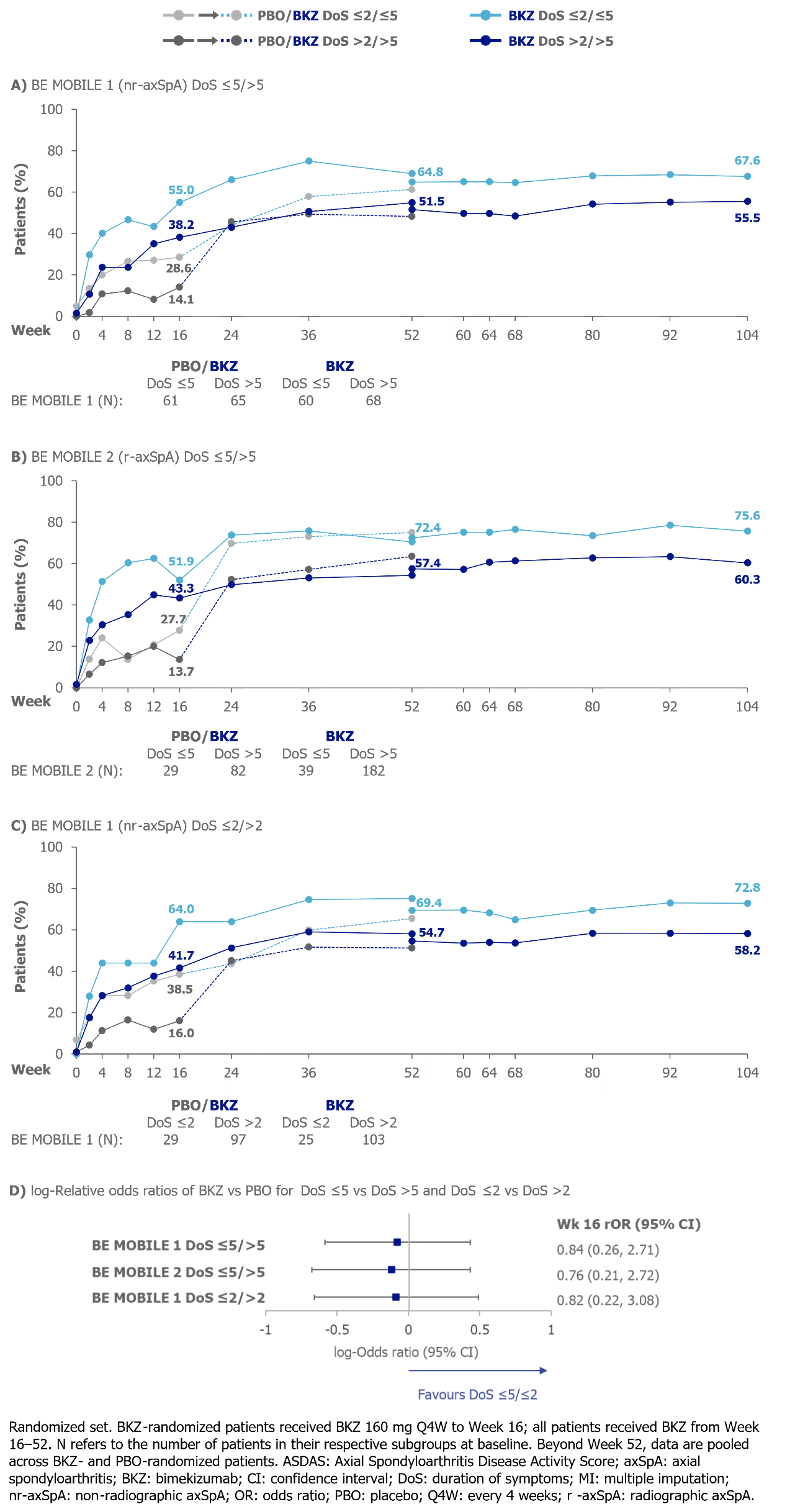
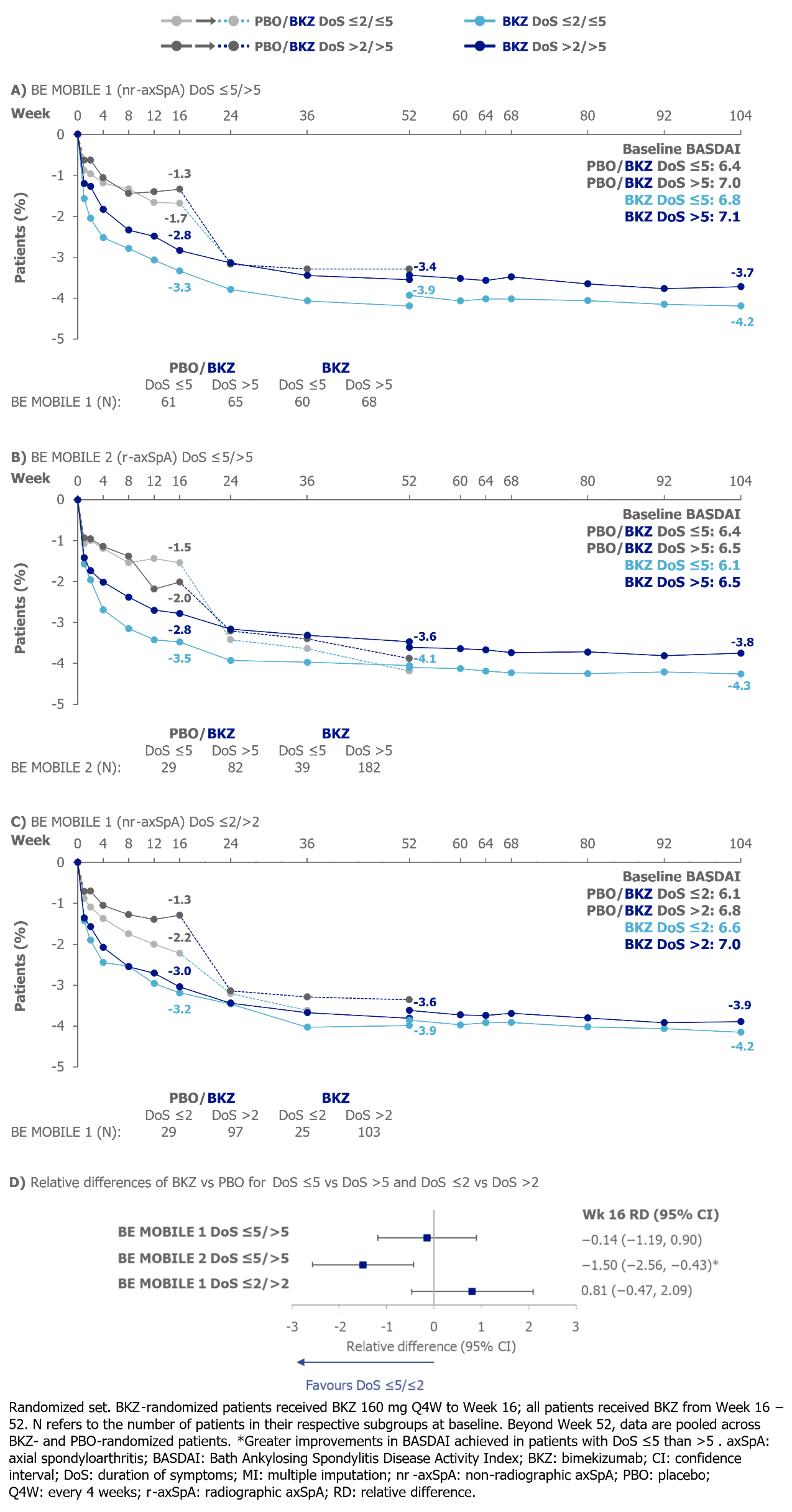
To compare BKZ vs PBO efficacy between DoS subgroups, Wk 16 relative odds ratios (ASAS40, ASDAS < 2.1) and relative differences (BASDAI CfB, MRI SIJ SPARCC) were calculated, sample size permitting. Trials were not powered for post hoc analyses; results should be interpreted as nominal.
Results: Better outcomes were seen with BKZ vs PBO at Wk 16, regardless of DoS. Outcomes were sustained or improved in all DoS subgroups to Wk 104.
At Wk 16, numerically larger proportions of BKZ-treated pts with DoS ≤5/≤2 achieved ASAS40 and ASDAS < 2.1 vs pts with DoS >5/ >2, respectively. No statistically significant difference was detected between DoS ≤5/ >5 (BE MOBILE 1 and 2) or between DoS ≤2/ >2 (BE MOBILE 1). At Wk 104, numerically larger proportions of pts with DoS ≤5/≤2 achieved ASAS40 and ASDAS < 2.1 (Figures 1−2).
No statistically significant difference was detected in Wk 16 relative differences in mean BASDAI CfB between DoS ≤5/ >5 or DoS ≤2/ >2 in BE MOBILE 1, but larger improvement was found in BASDAI in pts with DoS ≤5 vs >5 in BE MOBILE 2. There were numerically larger reductions (i.e., improvements) from baseline in mean BASDAI for pts with DoS ≤5/≤2 at Wk 104 vs pts with DoS >5/ >2, respectively (Figure 3).
Baseline MRI SIJ SPARCC scores indicated more inflammation in pts with DoS ≤5 vs >5. BKZ treatment led to reduction in mean MRI SIJ SPARCC scores to Wk 16; vs PBO, no statistically significant difference was detected between DoS ≤5/ >5 in BE MOBILE 1 (relative difference [95% CI]: −3.10 [−8.09, 1.90]). Mean MRI SIJ SPARCC scores remained low to Wk 104 (DoS ≤5: 2.03 [n=40], DoS >5: 2.83 [n=55]) and indicated resolution of inflammation, regardless of DoS.
Conclusion: BKZ treatment was efficacious to 2 yrs, regardless of DoS. Overall, no difference in Wk 16 treatment effect of BKZ vs PBO between pts with shorter vs longer DoS was found.
References: 1. van der Heijde D. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(4):515–26; 2. Baraliakos X. Ann Rheum Dis 2024;83:199–213; 3. Navarro-Compán V. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;10.1136/ard-2023-224232.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ramiro S, Proft F, Sengupta R, van Tubergen A, Molto A, Gensler L, Kishimoto M, Taieb V, Voiniciuc D, Massow U, Navarro Compán V. Bimekizumab Treatment Was Efficacious to 2 Years Regardless of Duration of axSpA Symptoms: Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-was-efficacious-to-2-years-regardless-of-duration-of-axspa-symptoms-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-was-efficacious-to-2-years-regardless-of-duration-of-axspa-symptoms-results-from-two-phase-3-studies/