Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1412–1441) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II: SpA
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: PsA impacts the physical health and functional ability of patients (pts),which can contribute to reduced work productivity.1 Bimekizumab (BKZ) is a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL-17F in addition to IL-17A, and has demonstrated efficacy and tolerability in pts with PsA to 16 weeks (wks), vs placebo (PBO), sustained to 52 wks.2–5Here, we report the impact of BKZ treatment on work productivity up to 1 year using data from two phase 3 studies.
Methods: BE OPTIMAL (NCT03895203; biologic DMARD [bDMARD]‑naïve pts) and BE COMPLETE (NCT03896581; inadequate response or intolerance to TNF‑α inhibitors [TNFi‑IR] pts) were PBO‑controlled phase 3 studies assessing BKZ in pts with active PsA.2,3 Pts in BE OPTIMAL were randomized 3:2:1 to subcutaneous (sc) BKZ 160 mg every 4 wks (Q4W), PBO, or reference (sc adalimumab 40 mg Q2W; not reported here); the study was active treatment-blind to Wk 52, after which pts could enter the ongoing open-label extension BE VITAL (NCT04009499). Pts in BE COMPLETE were randomized 2:1 to sc BKZ 160 mg Q4W or PBO; pts who completed Wk 16 were eligible for BE VITAL. BE COMPLETE plus BE VITAL is referred to as ‘BE COMPLETE’ hereafter. In both BE OPTIMAL and BE COMPLETE, PBO-randomized pts switched to BKZ 160 mg Q4W at Wk 16 (PBO/BKZ). Pt work productivity is derived from the Work Productivity and Activity Impairment Questionnaire – Specific Health Problem v2.0 (WPAI-SHP), adapted for PsA;6 collected to Wk 52 in BE OPTIMAL and Wk 40 in BE COMPLETE. Percentage change from baseline in WPAI-SHP scores are reported for four dimensions: overall work impairment, activity impairment, work time missed (absenteeism), and impairment while working (presenteeism).
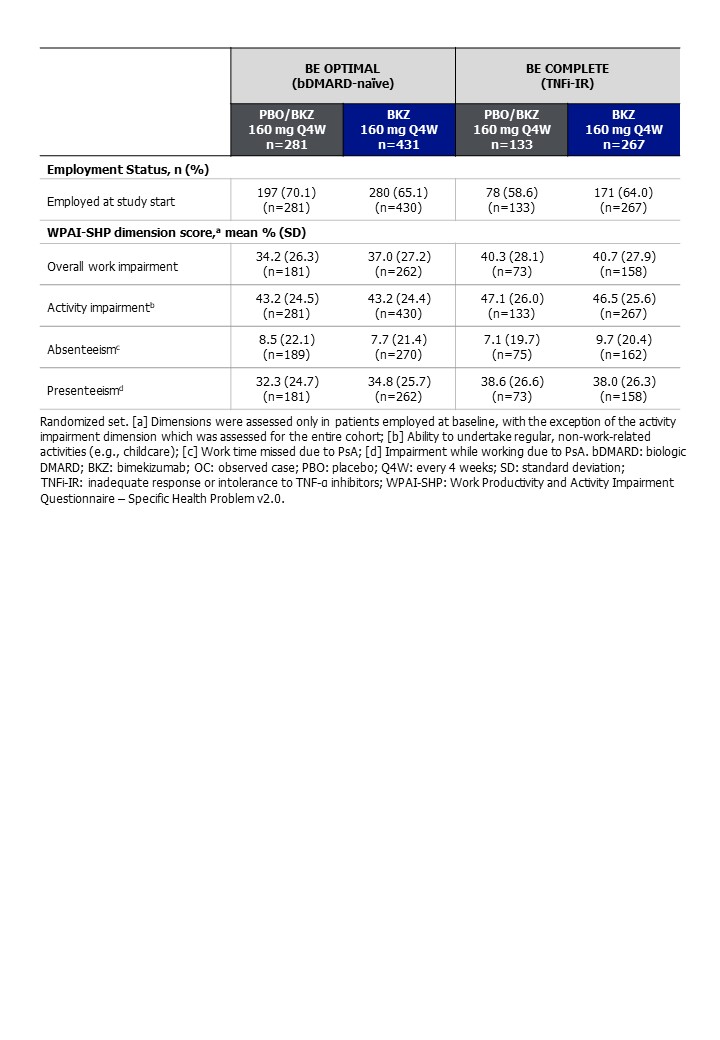
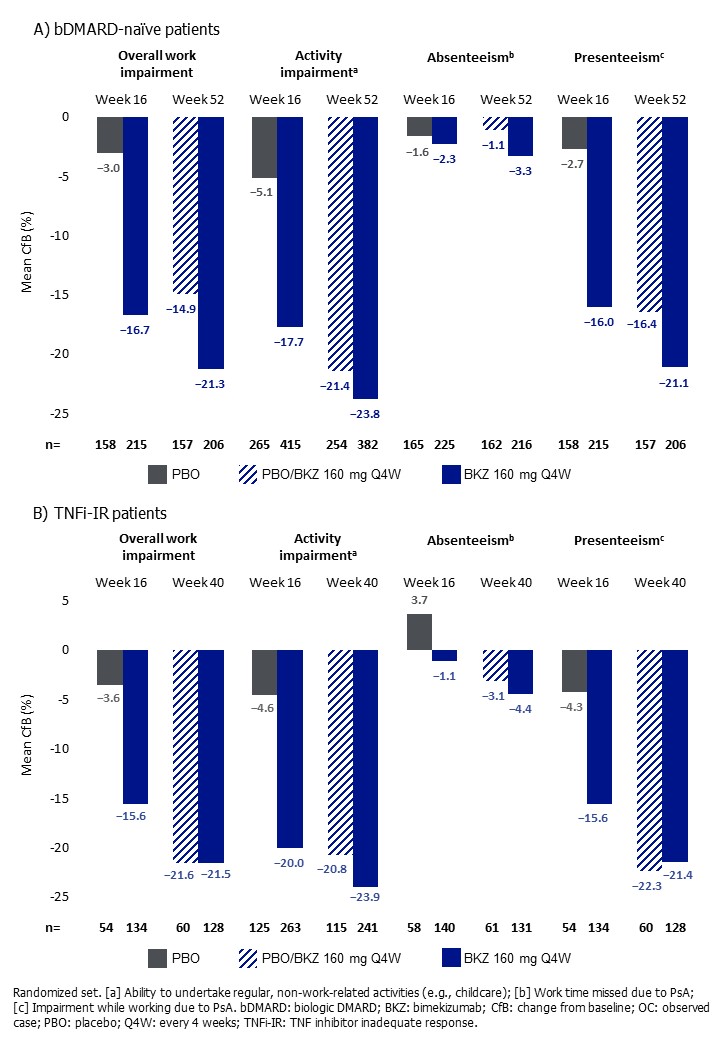
Results: Baseline WPAI-SHP scores suggest work productivity was impaired in pts: mean overall work impairment was 34.2%–40.7% across studies, with similar rates of activity impairment and presenteeism between treatment arms (Table). At Wk 16, BKZ‑treated pts in both studies showed numerically greater mean percentage reduction from baseline in overall work impairment compared with PBO‑treated pts; bDMARD-naïve: 16.7% BKZ, 3.0% PBO and TNFi-IR: 15.6% BKZ, 3.6% PBO. Work productivity continued to improve up to 1 year; PBO/BKZ pts demonstrated similar reductions in overall work impairment to BKZ‑randomized pts at Wk 52 for the bDMARD‑naïve population (21.3% BKZ, 14.9% PBO/BKZ) and at Wk 40 for the TNFi-IR population (21.5% BKZ, 21.6% PBO/BKZ). Trends were generally comparable for all dimensions in both studies (Figure).
Conclusion: BKZ demonstrated improvements vs PBO in all WPAI-SHP dimensions to Wk 16 which were clinically meaningful,6 with greatest improvements observed in activity impairment and presenteeism. Work productivity continued to improve with BKZ to 1 year; pts who switched to BKZ at Wk 16 experienced similar levels of improvement to BKZ-randomized pts. Improvements in work productivity were similar in bDMARD-naïve and TNFi-IR pts, demonstrating consistent response.
1. Husni ME. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2017;47:351–60; 2. McInnes IB. Lancet 2023;401:25–37; 3. Merola JF. Lancet 2023;401:38–48; 4.Ritchlin CT. Arthritis Rheumatol 2022;74(S9); 5. Coates L. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82(S1); 6. Tillett W. Rheumatol Ther 2019;6:379–91.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mease P, Gladman D, Gossec L, Nash P, Ink B, Coarse J, Lyris N, Willems D, Tillett W. Bimekizumab Treatment Impact on Work Productivity in Biologic DMARD‑Naïve and TNFi-IR Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis: Results up to 1 Year from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-impact-on-work-productivity-in-biologic-dmard%e2%80%91naive-and-tnfi-ir-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-up-to-1-year-from-two-phase-3-studies/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treatment-impact-on-work-productivity-in-biologic-dmard%e2%80%91naive-and-tnfi-ir-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-results-up-to-1-year-from-two-phase-3-studies/