Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ), a monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively inhibits IL‑17F in addition to IL‑17A, has demonstrated sustained reductions in disease impact of PsA, assessed by the PsA Impact of Disease‑12 (PsAID‑12) questionnaire, up to 1 year (yr) in two phase 3 studies.1 The PsAID-12 questionnaire is a patient (pt)‑reported outcome measure assessing the impact of PsA across 12 physical, social, and psychological domains.2 Here, we report the efficacy of BKZ treatment using the PsAID‑12 questionnaire up to 2 yrs in pts with active PsA.
Methods: BE OPTIMAL (NCT03895203; biologic DMARD [bDMARD]-naïve) and BE COMPLETE (NCT03896581; TNF inhibitor inadequate response/intolerance [TNFi‑IR]) assessed subcutaneous (sc) BKZ 160 mg every 4 weeks (Q4W) in pts with PsA; both were placebo (PBO)-controlled to Week (Wk) 16.1 At Wk 16, PBO pts switched to BKZ (PBO/BKZ). BE OPTIMAL included a reference arm (sc adalimumab [ADA] 40 mg Q2W); these pts switched to BKZ at Wk 52 (ADA/BKZ) with no washout between treatments. BE OPTIMAL Wk 52 and BE COMPLETE Wk 16 completers were eligible for BE VITAL (open‑label extension; NCT04009499).
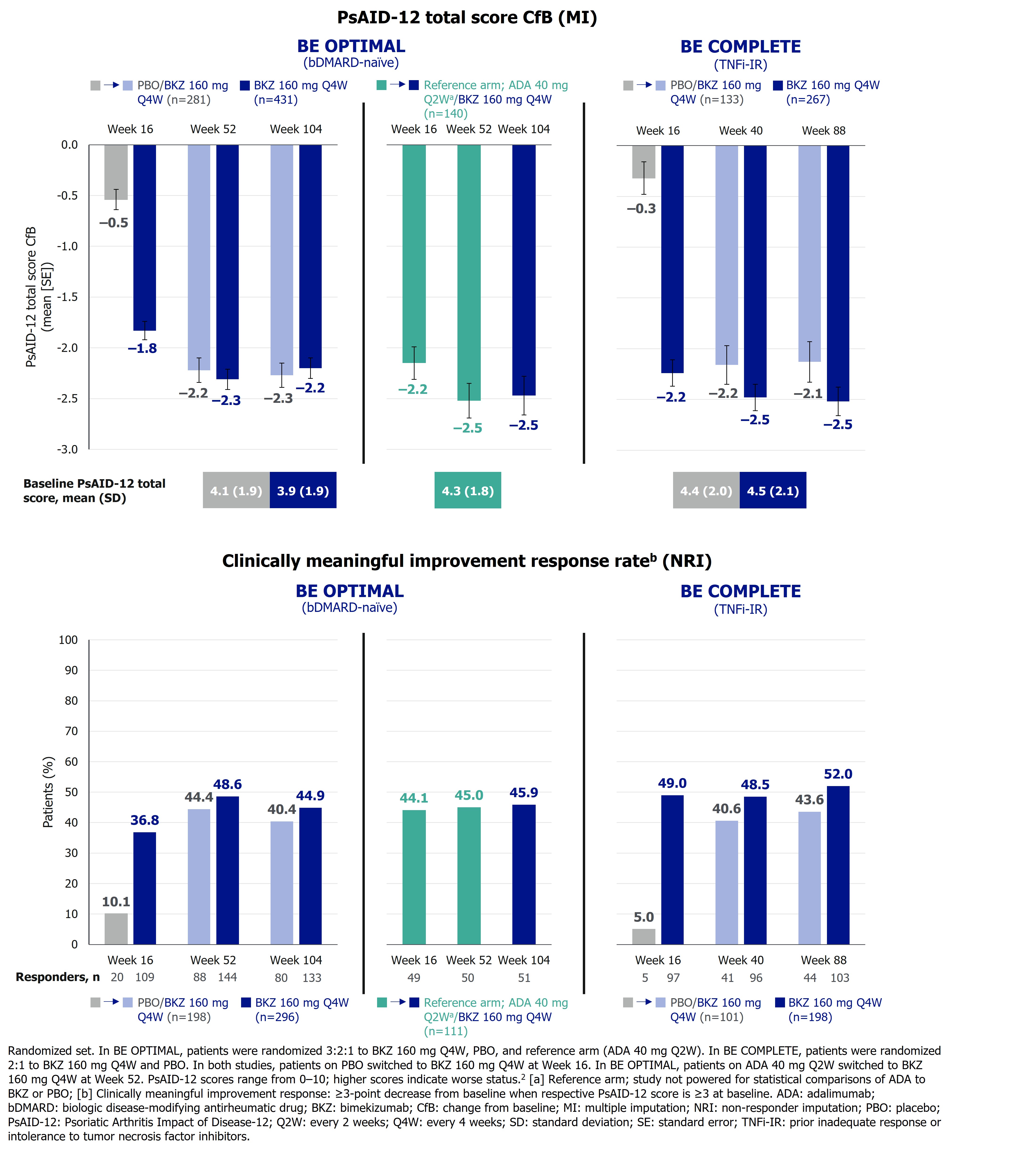
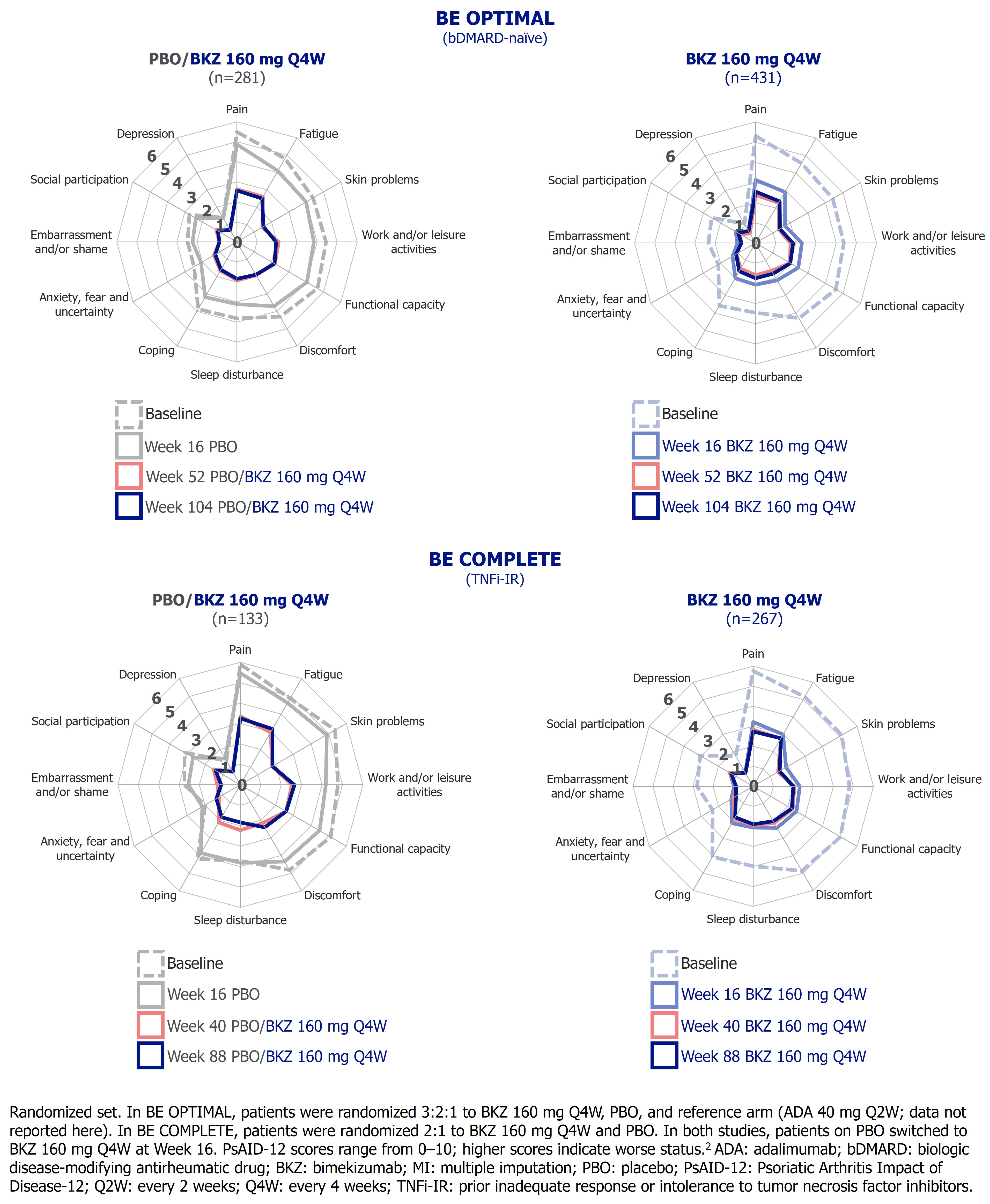
PsAID‑12 total and single-item domain scores range from 0–10; higher scores indicate worse status.2 The PsAID-12 questionnaire was administered to Wk 104 in BE OPTIMAL and Wk 88 in BE COMPLETE. Change from baseline (BL; CfB) and clinically meaningful improvement response rates (≥3-point decrease from BL when respective PsAID‑12 score is ≥3 at BL) were assessed. Missing data were imputed using multiple (continuous) or non‑responder (binary) imputation.
Results: Overall, 710/852 (83.3%) bDMARD-naïve and 330/400 (82.5%) TNFi-IR pts completed Wk 104/88.
Improvements in PsAID-12 total score were sustained on BKZ, with a mean CfB (standard error) of –2.3 (0.1) at Wk 52 and –2.2 (0.1) at Wk 104 in bDMARD‑naïve pts, and −2.5 (0.1) at both Wk 40 and Wk 88 in TNFi‑IR pts. Pts who switched from ADA to BKZ at Wk 52 demonstrated similar sustained improvements at Wk 104 (Figure 1). Clinically meaningful improvement responses observed at Wk 52/40 in PsAID‑12 total score were sustained to Wk 104/88 in bDMARD‑naïve (40.4% PBO/BKZ, 44.9% BKZ, 45.9% ADA/BKZ) and TNFi‑IR pts (43.6% PBO/BKZ, 52.0% BKZ; Figure 1).
Improvements from BL across all PsAID-12 single‑item domain mean scores observed at Wk 52/40 were sustained or further numerically improved to Wk 104/88 on BKZ (Figure 2). ADA/BKZ pts sustained their improvements across domains from Wk 52 to 104 after switching to BKZ, and further reductions in impact of skin problems were seen. In both studies, the domains with the greatest disease impact at BL (pain, functional capacity, fatigue, and skin problems) were among the domains with the greatest improvements at Wk 52/40, which were sustained to Wk 104/88. Clinically meaningful improvement responses were achieved by around half of BKZ‑treated patients across most single-item domains at Wk 104/88.
Conclusion: BKZ treatment demonstrated sustained reduction in disease impact up to 2 yrs in pts with PsA who were bDMARD-naïve or TNFi-IR. Pts who switched from ADA to BKZ at Wk 52 showed sustained reduction in disease impact up to 2 yrs.
References: 1. Gossec L. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2024;keae277; 2. Gossec L. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1012–9.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Gladman D, Coates L, de Wit M, Ink B, Bajracharya R, Coarse J, Lambert J, Orbai A. Bimekizumab-Treated Patients with Active Psoriatic Arthritis Showed Sustained Reductions in Disease Impact Assessed by the Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease (PsAID)-12 Questionnaire: Up to 2‑Year Results from Two Phase 3 Studies [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treated-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-showed-sustained-reductions-in-disease-impact-assessed-by-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-psaid-12-questionnaire-up-to-2/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-treated-patients-with-active-psoriatic-arthritis-showed-sustained-reductions-in-disease-impact-assessed-by-the-psoriatic-arthritis-impact-of-disease-psaid-12-questionnaire-up-to-2/