Session Information
Date: Monday, October 27, 2025
Title: (1434–1466) Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster II
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab, a dual IL-17 A and F blocker, has recently been added in the therapeutic rheumatologist’s armamentarium of PsA, but real-world evidence is lacking. Phase 3 trials have suggested that its efficacy between TNFi-naïve and TNFi experienced patients is not significantly different. In this nationwide study we aimed to comparatively examine the efficacy of bimekizumab in biologic(b)/ targeted synthetic(ts)-DMARD-naive and IL-17Ai-experienced PsA patients.
Methods: Consecutive PsA patients, either b/ts-DMARD-naïve (Group 1) or IL-17Ai- experienced (Group 2) followed up from October 2024 – January 2025 were prospectively included and assessed at time-0 (commencement of bimekizumab) and at month-3. There were no exclusion criteria. The following characteristics were recorded: demographics, clinical features (peripheral arthritis, axial involvement, dactylitis, enthesitis, psoriasis, nail-, eye- and bowel- involvement) present throughout the disease , as well as laboratory parameters, clinical features and disease activity scores at time-0 and at month-3. Treatment characteristics (concurrent conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs, previous bDMARDs treatment if any and reason for bimekizumab discontinuation, if so) were also recorded. Difference between scores was expressed as Delta (Δ) (score at time-0 minus score at month-3).
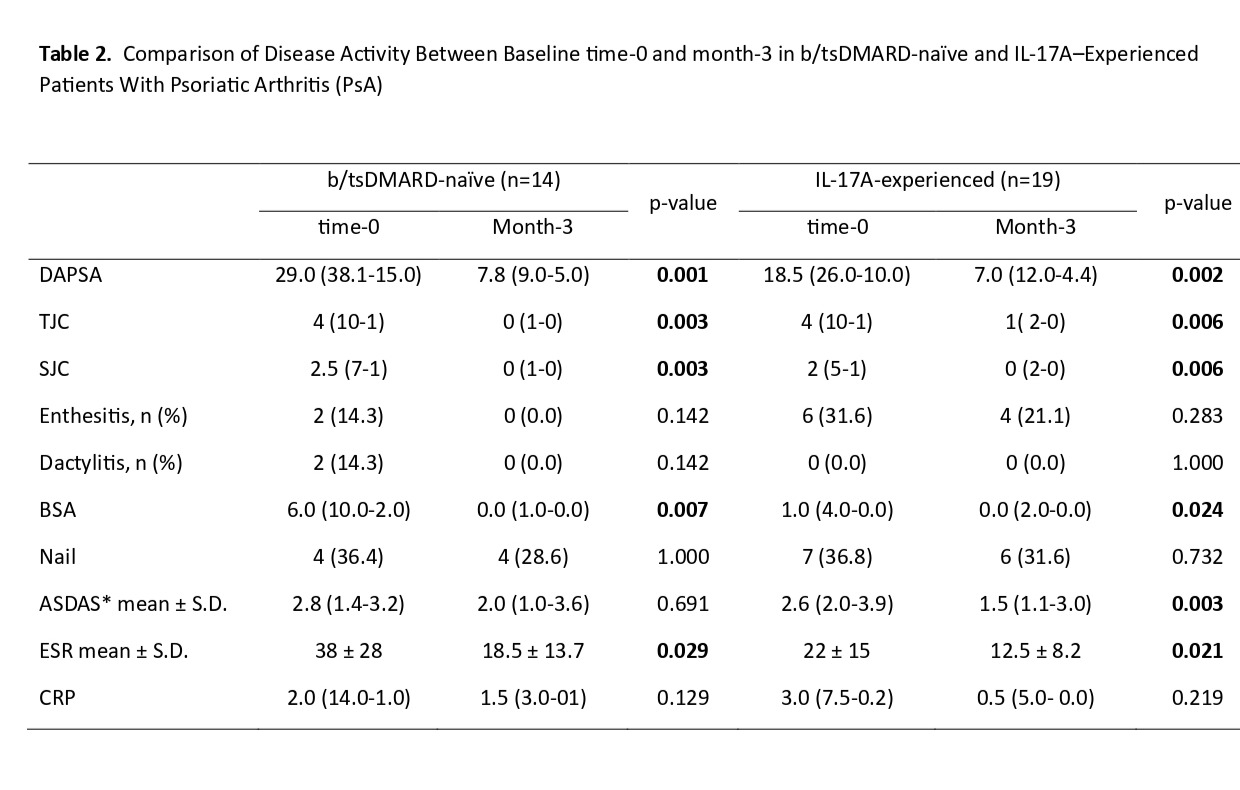
Results: In total 33 patients were enrolled. Fourteen patients were b/tsDMARD-naïve (Group 1) and 19 were IL-17Ai-experienced (Group 2). csDMARDs were co-administered in 50% and 42.1% of patients, respectively. In Group 2, 7 were switched directly from another IL-17Ai to bimekizumab, while 12 received other b/tsDMARDs in-between. Of note, 42.1% of patients in Group 2 had failed in two different IL-17A-inhibitors. No significant differences were detected in the characteristics between the two groups apart from enthesitis and nail disease which were slightly more common in the latter (Table-1). At month 3, Disease Activity index for PsA (DAPSA) was significantly improved in both groups (Group 1; p=0.001, Group 2; p=0.002) (Table-2), while ΔDAPSA was comparable (Group 1; 10.8±14.6, Group 2; 15.5 ±13.1, p=0.258). Number of tender count joints (TJC)/ swollen count joints (SJC), as well as Body Surface Area (BSA) and ESR were also significantly improved for both groups (Table-2). ΔESR (Group 1; 12.0±12.5, Group 2; 16.6 ±28.8, p=0.813), as well as ΔTJC (Group 1; 4.2±6.0, Group 2; 4.8±4.8, p=0.741) and ΔSJC (Group 1; 2.3±3.7, Group 2; 3.5±3.6, p=0.338) were comparable between groups. ΔBSA was significantly higher for the Group 1 (Group 1; 5.6±4.2, Group 2; 2.6±6.5, p=0.007). Finally, in the whole cohort, Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score was also significantly improved (time-0; 2.64±0.75, month-3; 1.95±0.96, p=0.01), This was also evident when Group 2 was analyzed separately, as Group 1 included only 3 patients with axial disease (Table-2). Two patients (6.1%) developed oral candidiasis.
Conclusion: In this real-world prospective study, we found that at 3 months bimekizumab is equally effective in b/tsDMARDs and IL-17A-experienced patients in almost all aspects of PsA. Also, bimekizumab was found to be effective for axial-PsA.
 b/tsDMARD: biologic/target synthetic DMARD; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease
b/tsDMARD: biologic/target synthetic DMARD; IBD: Inflammatory bowel disease
.jpg) Values are presented as median (Q3–Q1) unless otherwise indicated. p-value in bold indicates statistically significant difference (p < 0.05)
Values are presented as median (Q3–Q1) unless otherwise indicated. p-value in bold indicates statistically significant difference (p < 0.05)
b/tsDMARD: biologic/target synthetic DMARD; DAPSA: Disease Activity in Psoriatic Arthritis; TJC: Tender Joint Count; SJC: Swollen Joint Count; BSA: Body Surface Area affected by psoriasis; ASDAS: Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score
Nail: nail involvement in psoriatic disease.
*ASDAS is calculated based on CRP
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Poulia V, Sampatakaki E, Katsifis-Nezis D, Pappa M, Mole E, Gazi S, Skouvaklidou E, Kougkas N, Polyzou M, Koutsogeorgopoulou L, Xynogalas I, Karamanakos A, Vassilakis K, Papadimitriou E, Papagoras C, Evangelatos G, Gerolymatou N, Voulgari P, Fragoulis G. Bimekizumab in Psoriatic Arthritis. A real-world prospective study. Comparison of its efficacy in bDMARD-naive and IL-17A-experienced patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-real-world-prospective-study-comparison-of-its-efficacy-in-bdmard-naive-and-il-17a-experienced-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-real-world-prospective-study-comparison-of-its-efficacy-in-bdmard-naive-and-il-17a-experienced-patients/
