Session Information
Date: Friday, November 6, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Bimekizumab (BKZ), a humanized monoclonal IgG1 antibody that selectively neutralizes interleukin (IL)-17A and IL-17F, has shown clinical improvements in joint and skin outcomes and a favorable safety profile in patients (pts) with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA).1 Here we report the impact of BKZ treatment over 48 weeks on two patient-reported outcome (PRO) measures: Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ-DI) and Psoriatic Arthritis Impact of Disease-9 (PsAID-9). The PsAID-9 is a questionnaire specifically developed to assess the impact of PsA on pts’ lives.2, 3 We also examine the association between achieving high disease control states (very low disease activity [VLDA], minimal disease activity [MDA] or Disease Activity in PSoriatic Arthritis [DAPSA] remission) and PsAID-9 score.
Methods: In this phase 2b dose-ranging study (BE ACTIVE; NCT02969525), PsA pts received BKZ or placebo.1 Here we report improvements in PROs over 48 weeks using the proportion of pts who achieved a Minimal Clinically Important Difference (MCID) in the functional score HAQ-DI (≥0.35 decrease from baseline). We also show the rate of pts reporting a PsAID-9 Patient Acceptable Symptom State (PASS), which for the PsAID-9 has been proposed as a score ≤4,2 and examine the association of VLDA/MDA (binary disease control states) or DAPSA (where remission is 0–4, low: 5–14, moderate: 15–28, and high disease activity is >28) with PsAID-9 score at Wk 12. The Full Analysis Set (FAS) is used up to and including Wk 12; the Dose-Blind Set (DBS) is used from Wk 12 to Wk 48.
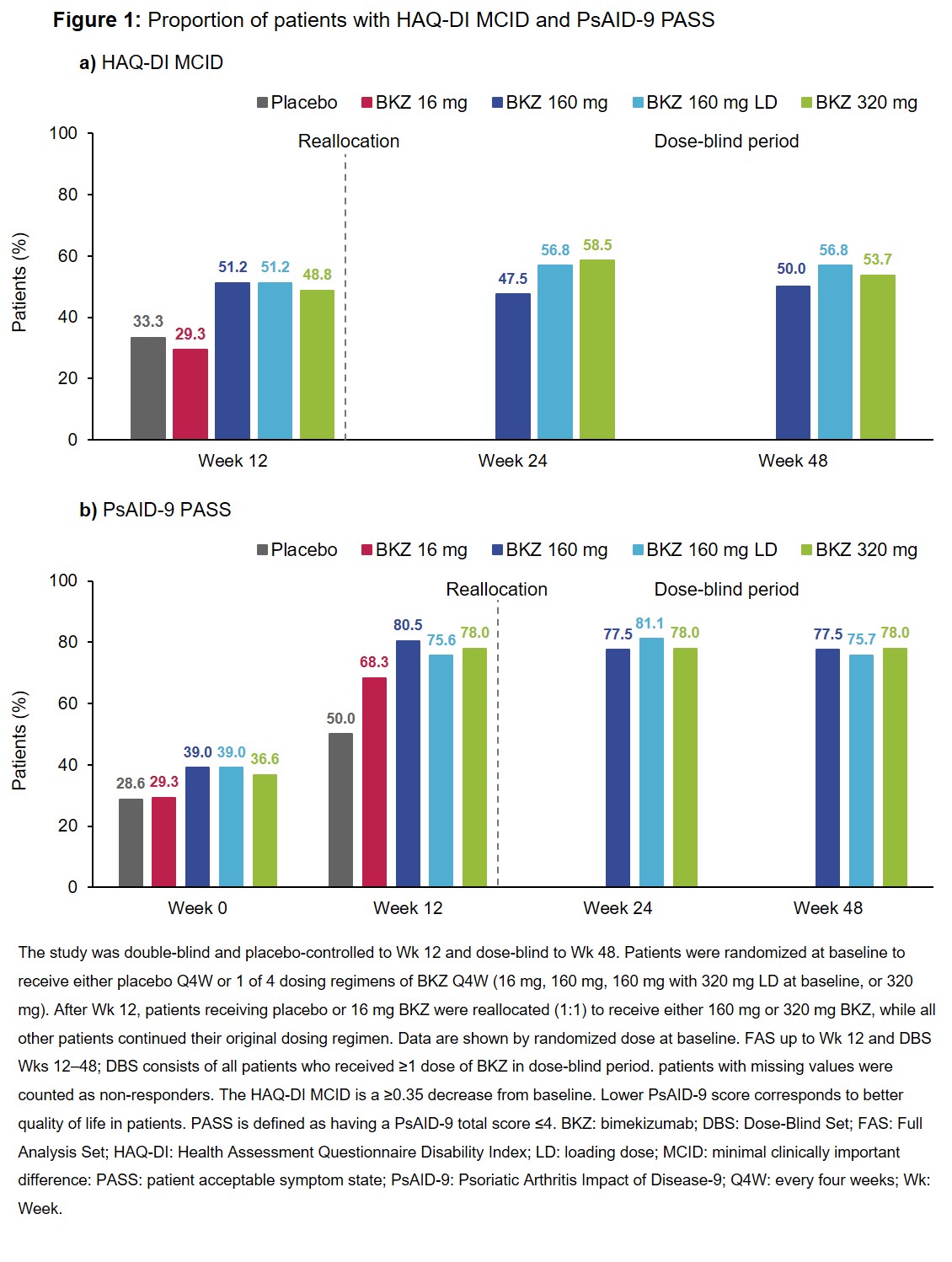
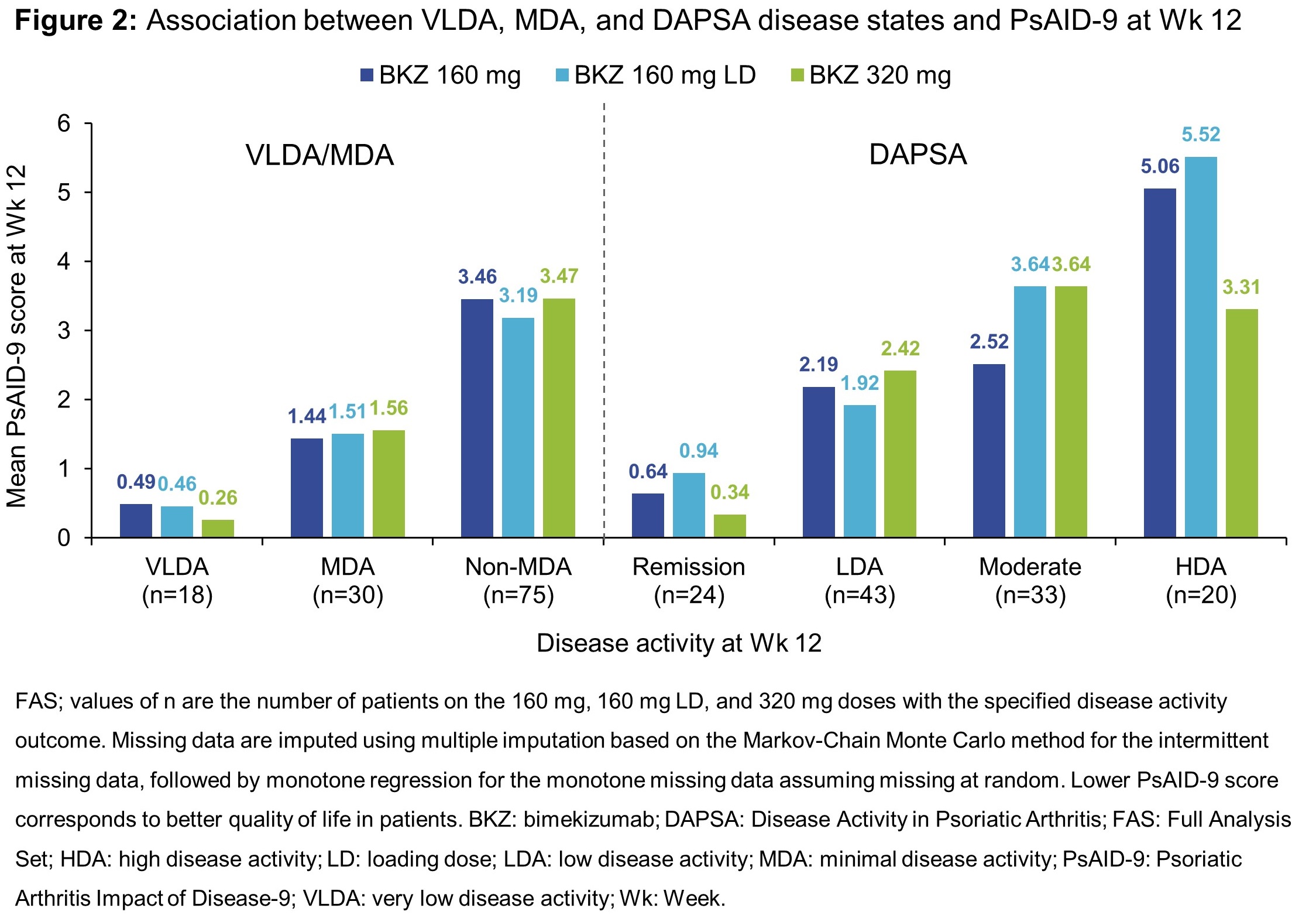
Results: Across 206 randomized pts at baseline, 66.5% had psoriasis body surface area (BSA) ≥3%, 18.9% had prior tumor necrosis factor inhibitor (TNFi) exposure, and 63.6% received concomitant methotrexate. Mean baseline HAQ-DI scores were comparable across all treatment arms (including placebo), ranging from 0.9–1.0; PsAID‑9 scores ranged from 4.3–4.8. The proportion of pts achieving HAQ-DI MCID for BKZ 160 mg, 160 mg plus loading dose (LD), and 320 mg treatment arms was 47.5–58.5% across Wks 12, 24 and 48 (Figure 1a). Additionally, more than 75% of pts receiving BKZ 160/160 LD/320 mg achieved PsAID-9 PASS across Weeks 12, 24 and 48 (Figure 1b). Furthermore, a substantial proportion of pts within these BKZ treatment arms also achieved VLDA, MDA and/or DAPSA remission at Wk 12; this generally increased through to Wk 24 and 48 (Table). PsAID-9 score at Wk 12 was consistently lower for pts with VLDA/MDA or in DAPSA remission (Figure 2).
Conclusion: This patient population with active PsA demonstrated rapid and sustained improvements in patient-reported physical function and psychological wellbeing over 48 weeks of BKZ treatment. Achievement of VLDA/MDA or DAPSA remission was associated with lower mean PsAID-9 scores, reinforcing evidence that achievement of higher disease control in pts with PsA is important for improved quality of life.
References: 1. Ritchlin C. Lancet 2020;395:427–40; 2. Gossec L. Ann Rheum Dis 2014;73:1012–9; 3. Johnson K. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2019;49:241–5.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gossec L, Mease P, Gottlieb A, Assudani D, Coarse J, Ink B, Coates L. Bimekizumab Improves Patient-Reported Outcomes in Psoriatic Arthritis: 48-Week Results from a Phase 2b Study and Association Between Patient-Reported Outcomes and Disease Activity [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-improves-patient-reported-outcomes-in-psoriatic-arthritis-48-week-results-from-a-phase-2b-study-and-association-between-patient-reported-outcomes-and-disease-activity/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bimekizumab-improves-patient-reported-outcomes-in-psoriatic-arthritis-48-week-results-from-a-phase-2b-study-and-association-between-patient-reported-outcomes-and-disease-activity/