Session Information
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Beta-2-glycoprotein-I(b2GPI), an apolipoprotein abundant in plasma, is readily expressed in human atherosclerotic plaque. Anti-b2GPI-IgA antibodies (Ab) have been previously reported in both rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and controls;they independently predicted cardiovascular events in general patients. We explored whether a-b2GPI-IgA presence predicted coronary plaque burden, its progression and potential interactions between a-b2GPI-IgA and inflammation on atherosclerosis load increase in RA.
Methods: One hundred-one participants with a baseline coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA) underwent follow-up assessment within 83±3.6 months. Numbers of coronary segments with plaque andcumulative plaque stenosis were recorded.Coronary artery calcium (CAC) was quantified by the Agatston method. Subclasses (IgG, IgM and IgA) of a-b2GPI Ab, anticardiolipin-Ab and lupus anticoagulant were assessed at baseline and confirmed 12-weeks later, if positive. Serum interleukin-6 (IL-6) was measured at baseline, while CRP was assessed on every visit from baseline through follow-up. Multivariable robust linear regression models evaluated the effect of a-b2GPI-IgA presence onbaseline CACandCAC change. Negative binomial regression assessed plaque progression, defined as number of segments with new plaque or increase in stenosis of existing plaque.The effects of interactions between a-b2GPI-IgA and time-averaged CRP or baseline IL-6 on plaque progression were also explored.
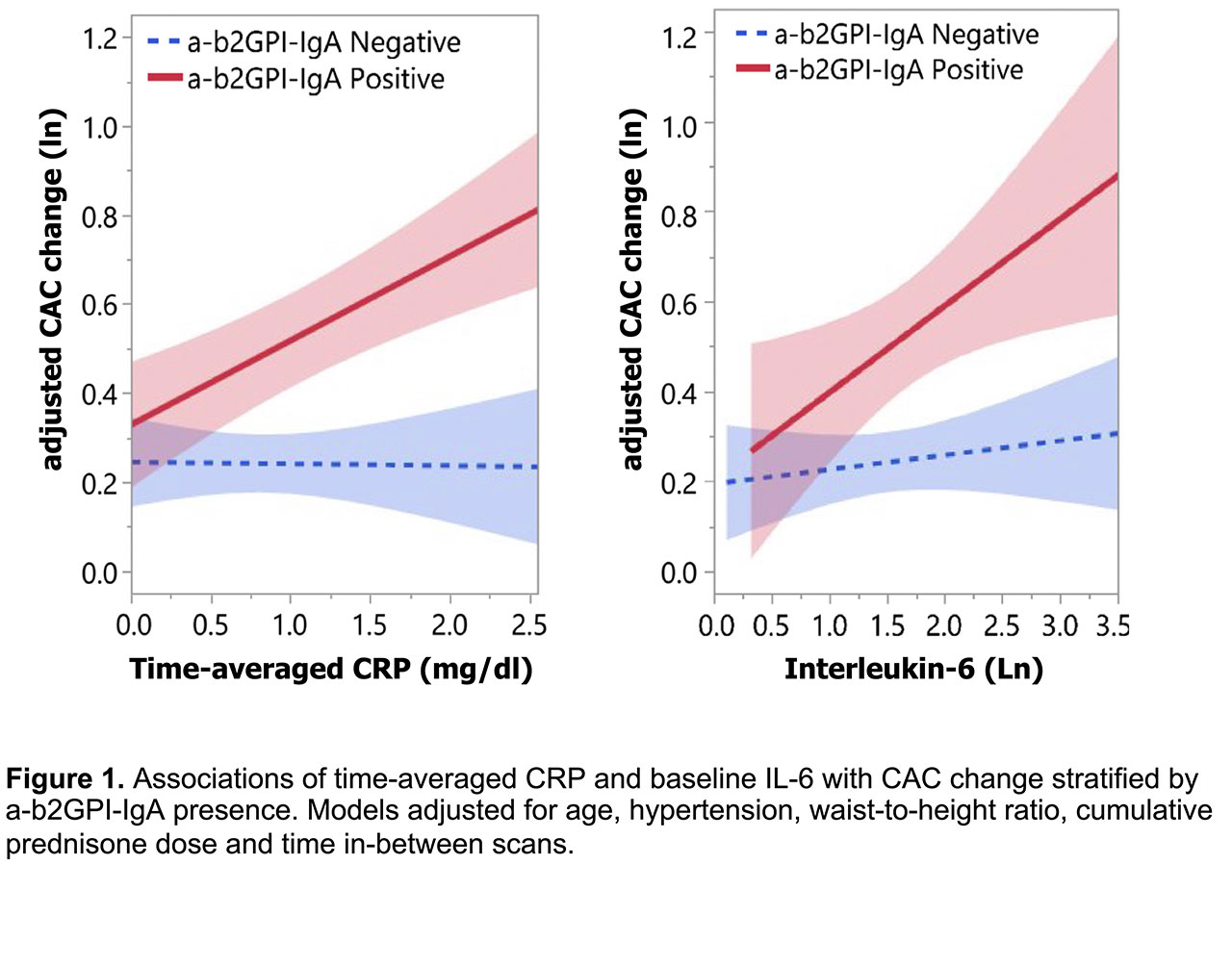
Results: A-b2GPI-IgA was highly prevalent (34.7%) in contrast to other antiphospholipid-Ab subclasses (< 4%). Their presence predicted baseline CAC score independently of age, hypertension, statin use, and CRP [β=0.37 (0.04-0.71), p=0.029]. A-b2GPI-IgA further predicted CAC change [β=0.387 (0.06-0.71), p=0.019] and plaque progression [IRR=1.62 (1.03-2.56), p=0.039], independently of age, hypertension, time-averaged CRP, cumulative prednisone and methotrexate dose and duration of statin exposure. Similarly, Ab presence predicted incident CAC [OR=5.67 (1.10-29.23), p=0.038] as well as prevalent CAC progression [β=0.64 (0.02-1.26), p=0.044]. Notably, a-b2GPI-IgA moderated the effect of both time-averaged CRP and baseline IL-6 (Figure 1) on CAC change [p-interaction=0.01 and 0.017 respectively]; specifically, higher time-averaged CRP and higher baseline IL-6 promoted CAC progression only in a-b2GPI-IgA positive patients [β =0.47 (0.26-0.67), p< 0.001 and β=0.43 (0.05-0.81), p=0.028, respectively] but not negative ones [β=0.07 (-0.10-0.25), p=0.395 and β=-0.07 (-0.34-0.20), p=0.621, respectively].
Conclusion: A-b2GPI-IgA in RA independently contribute to higher baseline coronary atherosclerosis burden, accelerated plaque progression and remodeling, especially in the context of higher cumulative inflammation.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Karpouzas G, Ormseth S, Hernandez E, Bui V, Budoff M. Beta-2-Glycoprotein-I IgA Antibodies Predict Coronary Plaque Burden, Progression and Moderate the Effect of Inflammation on Atherosclerosis in Rheumatoid Arthritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/beta-2-glycoprotein-i-iga-antibodies-predict-coronary-plaque-burden-progression-and-moderate-the-effect-of-inflammation-on-atherosclerosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/beta-2-glycoprotein-i-iga-antibodies-predict-coronary-plaque-burden-progression-and-moderate-the-effect-of-inflammation-on-atherosclerosis-in-rheumatoid-arthritis/