Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster IV: Lifespan of a Disease
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In clinical practice, drug treatment decisions must account for the expected benefit from a drug along with its potential risks. Evaluating the number needed to treat (NNT) and the number needed to harm (NNH), together, is one approach to inform about the benefit-risk profile of a drug. The objective of this analysis is to report the NNT and NNH of Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors approved in the US, baricitinib 2 mg/day (BARI), tofacitinib 5 mg twice daily (TOFA), and upadacitinib 15 mg/day (UPA), in RA patients who have an inadequate response to TNF inhibitors (TNFi-IR).
Methods: Data were from published Phase 3 randomized, double-blind clinical trials (RCTs) in TNFi-IR RA patients. In the BARI and UPA RCTs, patients were required to have an RA diagnosis defined by the 2010 ACR classification criteria,1,2 whereas patients in the TOFA RCT were required to have an RA diagnosis based on the 1987 ACR criteria.3 The respective treatment and placebo (PBO) sample sizes included 174 and 176 BARI and PBO patients,1 133 and 132 TOFA and PBO patients,2 and 164 and 169 UPA and PBO patients.3 Endpoints were evaluated at 12 weeks and included the reported proportion of patients who achieved American College of Rheumatology 20%, 50%, or 70% response (ACR20, ACR50, ACR70, respectively) for NNT and percentage of patients who experienced adverse events (AEs) leading to study discontinuation or serious AEs (SAEs) for NNH. NNT and NNH were calculated as 100 / difference (95% CI) of response or event rate between treatment and PBO.
Results: Across trials, patient age ranged from an average of 54 to 58 years (yrs) and 99-100% of patients had prior use of at least one biologic DMARD or TNFi, specifically. The duration of disease ranged from 11-15 yrs. The percentage of patients experiencing the given endpoints with treatment vs. PBO and the associated NNT or NNH are presented in the Table by study. The NNTs were < 10 for BARI, TOFA, and UPA with ACR20 and ACR50. The NNH values varied by JAK inhibitor and by event type.
Conclusion: There is no methodology that can be considered a gold-standard to evaluate the benefit and risk profile of a drug in a specific population. Across different studies of patients with refractory RA, JAK inhibitors have a favorable benefit and risk profile. Each drug delivers benefits with an associated level of risk, and these are not the same from drug to drug. NNT and NNH is one strategy for clinicians to standardize the benefit-risk assessment across different clinical programs that can be useful to support better informed decision making in clinical practice.
References: 1Genovese, et al. NEJM 2016; 374:1243-1252; 2Genovese, et al. Lancet 2018; 391: 2513-24; 3Burmester, Lancet 2013; 381:451-60
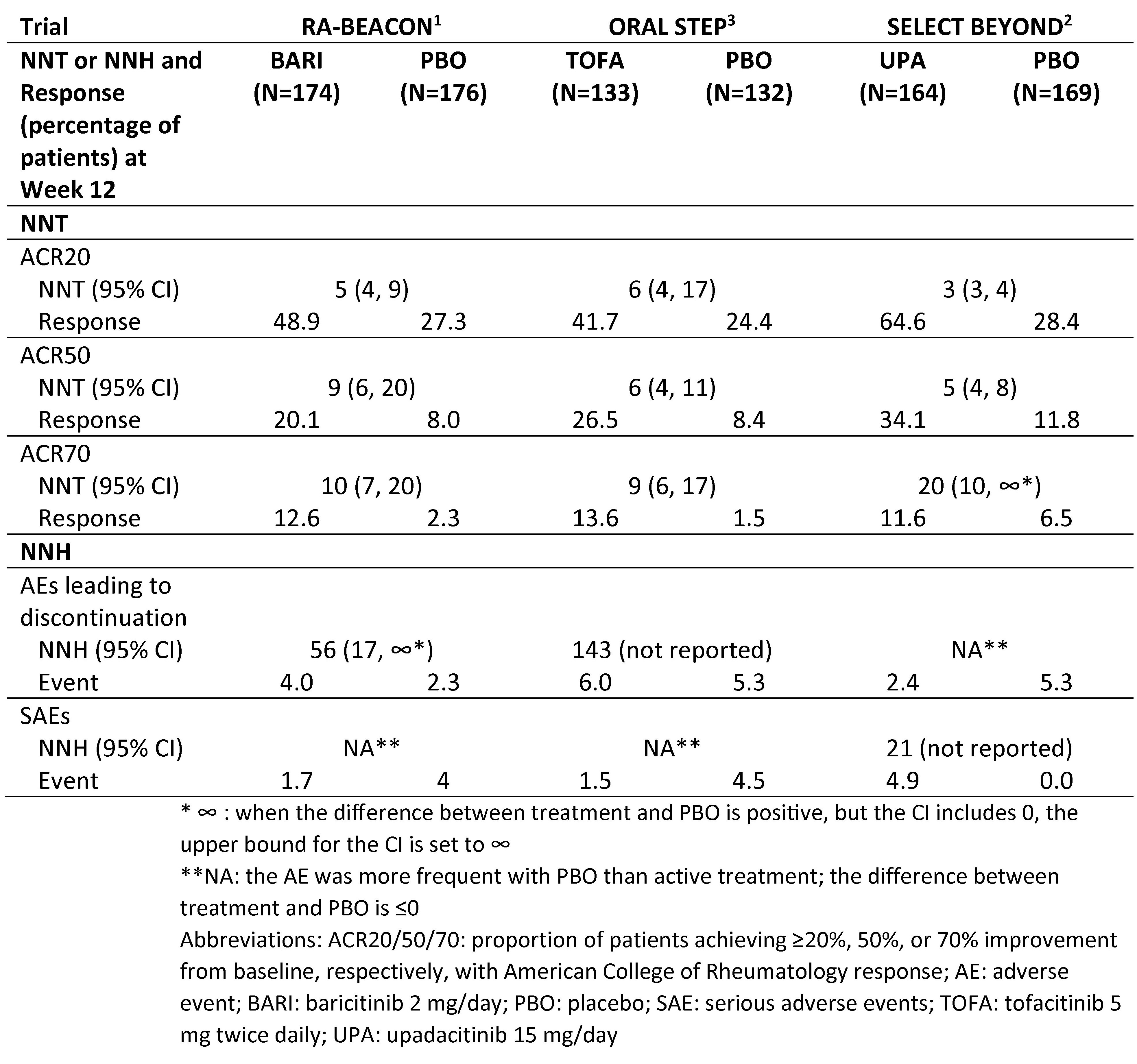 Number needed to treat and number needed to harm at Week 12 for baricitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib
Number needed to treat and number needed to harm at Week 12 for baricitinib, tofacitinib, and upadacitinib
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wells A, Griffing K, Quebe A, Sun L, Zhang H, Reis P. Benefit and Risk Profiles of Janus Kinase Inhibitors Approved in the US for the Treatment of RA [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/benefit-and-risk-profiles-of-janus-kinase-inhibitors-approved-in-the-us-for-the-treatment-of-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/benefit-and-risk-profiles-of-janus-kinase-inhibitors-approved-in-the-us-for-the-treatment-of-ra/
