Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: SLE flares are associated with increased risk of organ damage/mortality; flare prevention is a key treatment goal.1 Initiating treatment earlier has benefits in autoimmune diseases; data are not available for SLE as early disease (EYD) has not been defined. Pooled analyses from belimumab (BEL) clinical trials may provide insights into earlier use of BEL on SLE flares. This analysis used data from BEL clinical trials to evaluate flares in patients (pts) with SLE, treated with BEL or placebo (PBO) plus standard therapy (ST), across subgroups of EYD and established disease (ESD), respectively, based on baseline SLE disease duration (< 2 or ≥2 years), Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index (SDI) score (0 or ≥1), and immunosuppressant (IS) use (no/yes).
Methods: This post hoc analysis integrated data from Phase 3 BEL trials in adults with SLE (BLISS-76, BLISS-52, North East Asia, EMBRACE and BLISS-SC)2–6 randomized to BEL (10 mg/kg/month intravenously or 200 mg/week subcutaneously) or PBO, plus ST. Time to first severe Safety of Estrogens in Lupus Erythematosus National Assessment (SELENA)–SLEDAI flare index (SFI) flare, any SFI flare, and BILAG flare (1A/2B) over 52 weeks was evaluated (EYD [baseline SLE disease duration < 2 years, SDI=0, no IS use] or ESD [baseline SLE disease duration ≥2 years, SDI≥1, IS use]). Hazard ratios (HRs), 95% confidence intervals (CIs), and p-values were from Cox proportional hazards models for BEL vs. PBO adjusting for study and baseline SELENA-SLEDAI score (≤9 vs ≥10).
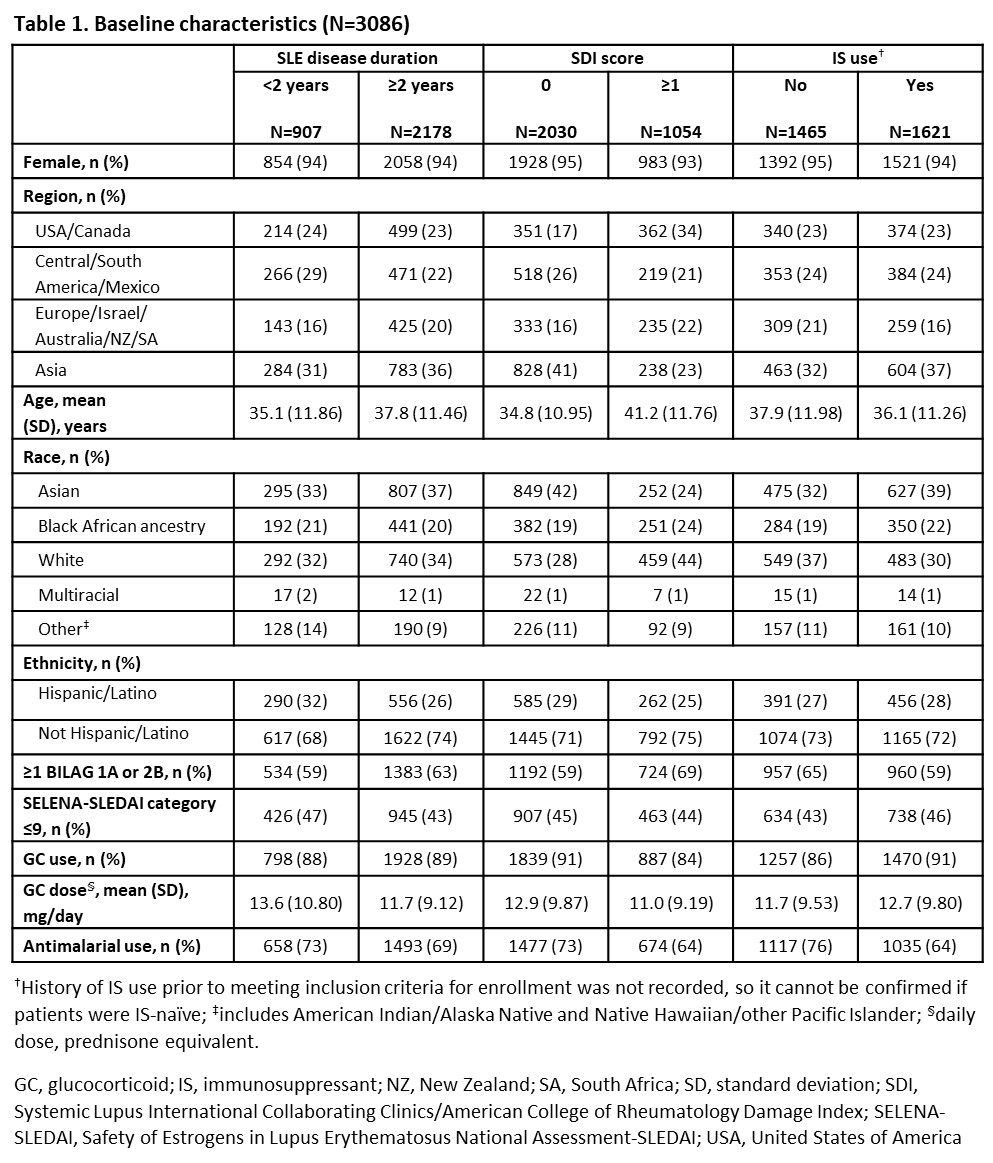
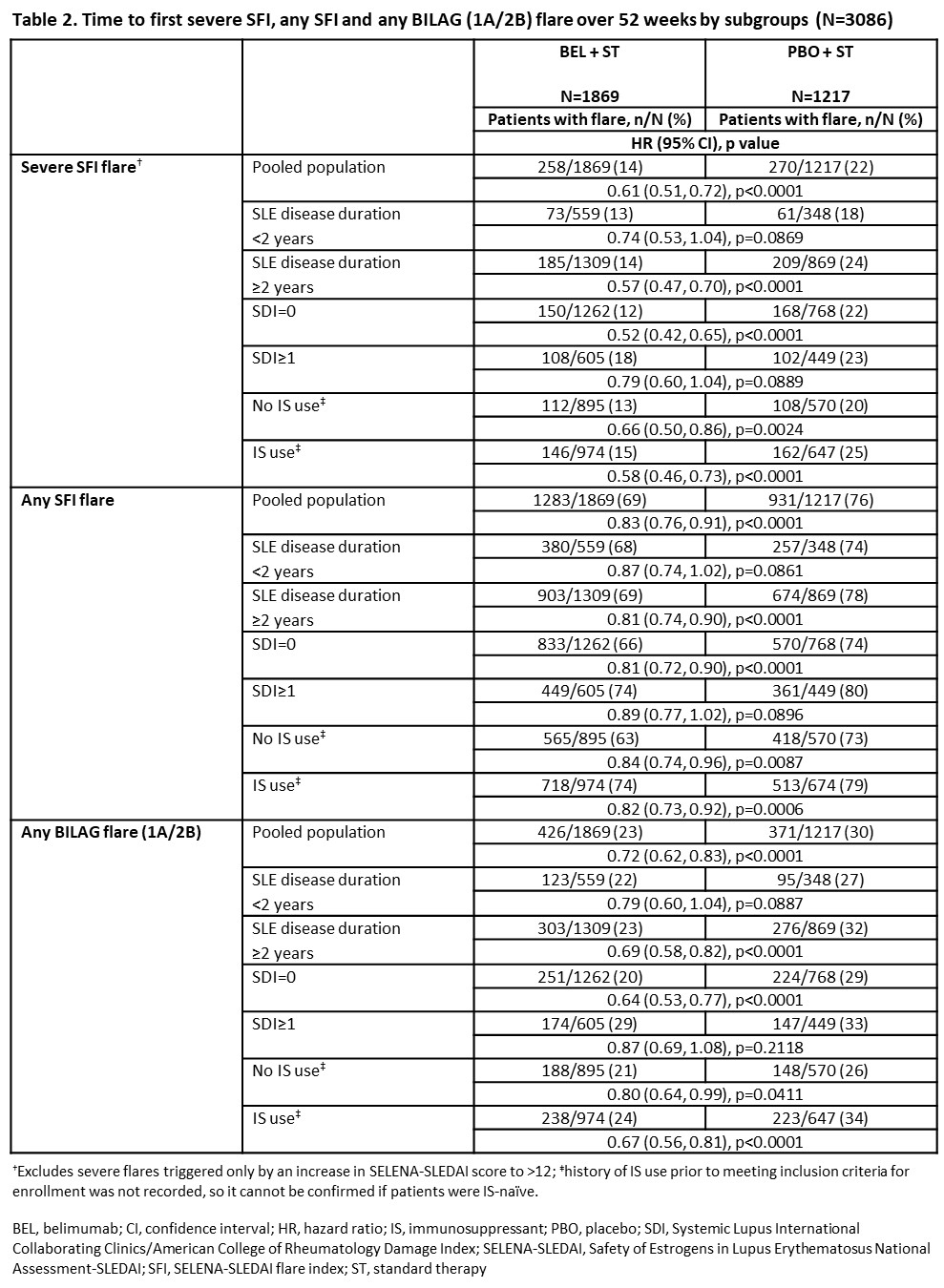
Results: We studied 1869 BEL- and 1217 PBO-treated pts. Differences in baseline characteristics were observed (Table 1). In the pooled population, less pts experienced a severe SFI flare (HR [95% CI]: 0.61 [0.51, 0.72]; p< 0.0001), any SFI flare (0.83 [0.76, 0.91]; p< 0.0001), or BILAG flare (0.72 [0.62, 0.83]; p< 0.0001) over 52 weeks with BEL vs PBO (Table 2). Over 52 weeks, less BEL- vs PBO-treated pts experienced severe/any SFI/BILAG flare in EYD/ESD subgroups. Treatment differences did not reach statistical significance for all comparisons (Table 2). Treatment differences (BEL vs PBO) reached statistical significance for pts with SDI=0 or no IS use at baseline, with more reduction in flares observed in pts with SDI=0 vs. the pooled population and pts with SDI ≥1. Proportion of pts with severe/any SFI/BILAG flare over 52 weeks was lower in the EYD vs ESD subgroups and pooled population for BEL and PBO (Table 2).
Conclusion: Fewer pts had flares with BEL vs PBO in the pooled population and EYD or ESD subgroups, with particular benefit in pts with no baseline organ damage. Proportion of pts with flares were lower in EYD vs ESD, for BEL and PBO. Although original trials were not designed to evaluate flares in these subgroups, findings suggest BEL use in EYD may improve outcomes. Confirmation in longer prospective studies is needed.
References
1. Fanouriakis A et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2024;83:15-29
2. Navarra SV et al. Lancet. 2011;377:721-31
3. Furie R et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63:3918-30
4. Zhang F et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77:355-63
5. Stohl W et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2017;69:1016-17
6. Ginzler E et al. Arthritis Rheum. 2022;74:112-23
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Mosca M, Costenbader K, Merrill J, Quasny H, Henning C, Bloom S, Harris J, O’Shea C, Atsumi T, Van Vollenhoven R. Belimumab Reduces Disease Flares versus Placebo in Adults with Early Active Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Results of a Large Integrated Analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-reduces-disease-flares-versus-placebo-in-adults-with-early-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-of-a-large-integrated-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-reduces-disease-flares-versus-placebo-in-adults-with-early-active-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-results-of-a-large-integrated-analysis/