Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Belimumab, a B-cell modulator monoclonal antibody that selectively inhibits BLyS and reduces autoreactive B-cells that drive lupus disease activity, has consistently demonstrated improved efficacy compared with standard therapy alone, across diverse groups of adults and children with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). This 2-year, large, ambi-directional, observational cohort study (RELIABLE; funding: GSK214958) conducted across China aimed to assess the real-world effectiveness of belimumab.
Methods: Eligible patients were adults with SLE who were newly prescribed belimumab within 6 months and had ≥1 available assessment of all components for the Lupus Low Disease Activity State (LLDAS) within 3 months before belimumab initiation (index). Patients were followed up retrospectively (up to 6 months after index) and/or prospectively for a total maximum of 24 months. The primary outcome was proportions of patients achieving LLDAS at 12 and 24 months after index. The results for this interim analysis which was conducted after all patients completed baseline visits are reported here, focusing on LLDAS.
Results: From July 08, 2023, to September 29, 2024, 400 patients were enrolled (female, 366 [91.5%]). Mean (standard deviation [SD]) age was 31.0 (12.7) years at SLE diagnosis and 36.3 (12.5) years at index, with a mean gap of 63.7 (SD, 76.2) months (Table 1). At baseline, 273 (68.3%) patients had a SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI) of 0, 156 (39.0%) received ≤1 prior immunosuppressant, 274 (68.5%) received oral steroid ≥7.5 mg/d, 6 (1.5%) had a disease duration of < 2 years, and mean SLEDAI-2K score was 10.2 (SD, 5.9). By data cut-off (October 31, 2024), 76 (19.0%) patients completed a 12-month follow-up and 22 (5.5%) withdrew. Thirty-eight (9.5%) patients received belimumab consecutively for ≥12 months and 249 (62.3%) had a proportion of days covered of ≥0.8. The proportion of patients achieving LLDAS progressively increased from 8.6% (34/394) at baseline (treatment initiation) to 18.6% (50/269) at Month 3 and 36.3% (66/182) at Month 6 following belimumab initiation. At Month 3, 97.2% (138/142) of patients achieved a reduction of ≥4 points in SLEDAI-2K from baseline; this trend continued at Month 6 with a proportion of 96.3% (105/109). The proportion of patients without significant fatigue, i.e., scoring >34 on the Functional Assessment of Chronic Illness Therapy-Fatigue scale (FACIT-F), rose from 72.9% (129/177) at baseline to 78.5% (212/270) at Month 3 and 85.9% (183/213) at Month 6. Improvements in biomarkers were observed after belimumab initiation (Table 2).
Conclusion: The interim results of RELIABLE demonstrated that belimumab reduces disease activity, evidenced by increased rates of LLDAS attainment, along with improved biomarkers and patient-reported outcomes, within 6 months after belimumab initiation among Chinese SLE patients from real-world settings. These findings are clinically important due to the large and diverse patient population from 14 sites across China. Long-term follow-up is expected to further demonstrate enhanced clinical outcomes and improved quality of life following belimumab initiation and to enrich the clinical, real-world, and long-term evidence for belimumab in China.
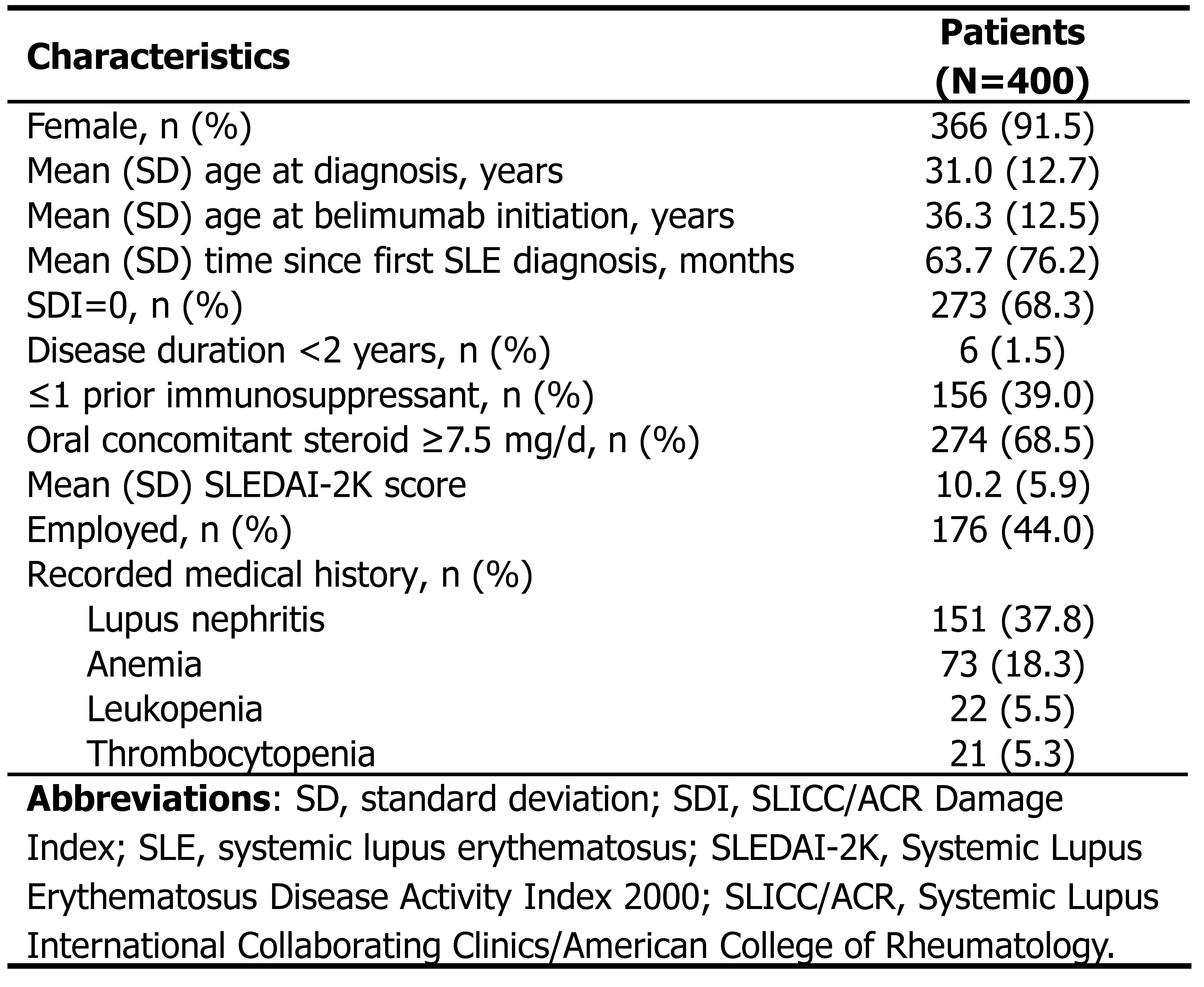 Table 1. Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
Table 1. Demographics and Baseline Characteristics
.jpg) Table 2. Summary of Efficacy Results
Table 2. Summary of Efficacy Results
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhang Z, Liu S, Yang M, Li Y, Yu Q, Duan X, Shu Q, Xie Q, Chen Y, Ou D, He L, Li H, Yang P, Li J, Yan T, He X, Moldaver D, O'Shea C, Fan L. Belimumab Real-World Effectiveness in Chinese Patients with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: Interim Analysis of an Ambidirectional, Observational Cohort Study (RELIABLE) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2025; 77 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-real-world-effectiveness-in-chinese-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-interim-analysis-of-an-ambidirectional-observational-cohort-study-reliable/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2025
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/belimumab-real-world-effectiveness-in-chinese-patients-with-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-interim-analysis-of-an-ambidirectional-observational-cohort-study-reliable/
