Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: During the last two decades we’ve witnessed the rising use of biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (bDMARDs) in the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA), leaving a questionable place of methotrexate (MTX) use in treatment strategies. Long-term therapy is impaired by treatment discontinuation and loss of effectiveness. Combination therapy with MTX have proven to improve drug survival in rheumatic diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis. This article reviews the available data on bDMARD drug survival when used combined with MTX in PsA.
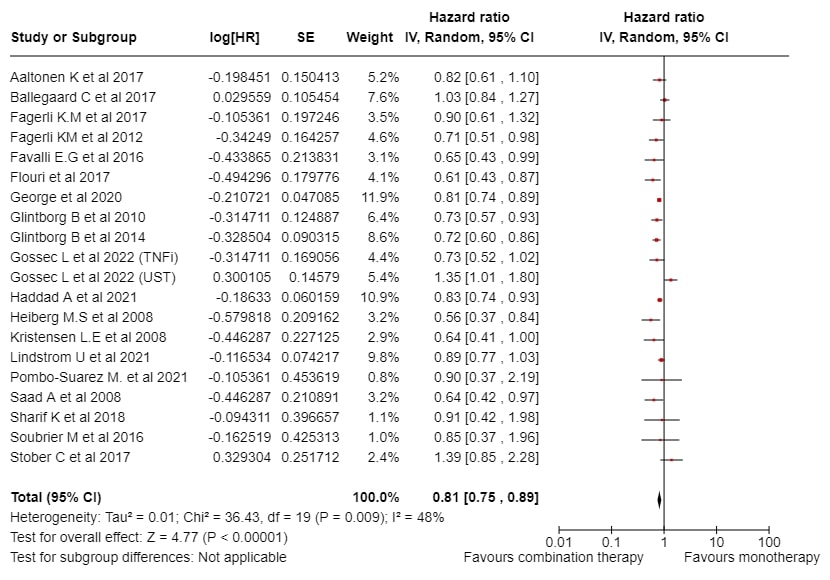
Methods: We identified studies answering our research question through a comprehensive, systematic literature search using predefined search criteria. All databases (PubMed, Embase, Cochrane) were thus searched to identify all pertinent articles up till December 2023. Studies were screened by title and abstract then further by full‐text review. Hazard ratio (HR) data were extracted. Where applicable, HRs values were estimated directly from published Kaplan–Meier drug survival curves using the method of Parmar et al. study (1) 1998, Stats in Med 2815-2834). We considered HRs > 1.0 to be in favour of monotherapy, and HRs < 1.0 to be in favour of combination therapy. Meta-analyses were completed using Review Manager 5.4 with a random-effect model and inverse-variance method. Sensitivity analyses were conducted using a leave-one-out method to determine the effect of each study on the reliability of overall pooled effect sizes.
Results: 542 records were identified through database searching. Nineteen studies were included, with a total of 28,340 patients with PsA. All studies were observational. Only two studies involved bDMARDs other than TNF inhibitors (TNFi). PsA diagnosis were based on CASPAR criteria or left to clinician discretion. Combination therapy with MTX was found to be associated with a superior drug survival (HR = 0.81 [IC95%, 0.75, 0.89], p-value < 0.00001, I2=48%) When the two studies evaluating drug survival of non TNFi bDMARDs were excluded, our finding remains in favour of combination therapy with MTX (HR=0.79 [IC95%, 0.73, 0.86], p-value < 0.00001, I2=30%). All studies were at an overall moderate risk of bias given the methodological similarities.
Conclusion: This meta-analysis suggests the positive impact of MTX on bDMARD drug survival, especially with TNFi. Further studies are needed to confirm this hypothesis with robust evidence such as randomised controlled trials.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
HANNA ABDELMASSIH S, DUJARDIN T, BAILLET A, GAUDIN P, ROMAND X. bDMARD Drug Survival in Combination Therapy with Methotrexate in Psoriatic Arthritis: A Systematic Literature Review and Meta-analysis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bdmard-drug-survival-in-combination-therapy-with-methotrexate-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-literature-review-and-meta-analysis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/bdmard-drug-survival-in-combination-therapy-with-methotrexate-in-psoriatic-arthritis-a-systematic-literature-review-and-meta-analysis/