Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose:
B cells are central to SLE. Signaling through the B cell receptor (BCR) controls critical processes at various stages of B cell development. Murine BCR manipulation and human genomic studies have implicated the BCR pathway in SLE, but few studies have assessed this pathway in patients.
Methods:
Ethics committee approval was obtained. Blood lymphocytes were isolated from patients with SLE and other autoimmunities, and normal controls; cells were frozen in liquid nitrogen. Detailed clinical parameters were obtained. 100 000 B cells were stimulated with 20 ug/mL anti-IgM and anti-IgG for 0 or 5 minutes, and a 10-color flow cytometry panel was used to identify the following B cell subsets: naïve mature, transitional, IgM memory, IgG memory, IgG B1 and IgM B1. We assayed surface BCR levels, pSyk (early signaling), pPLC-γ2 (mid-point), pERK1/2 (late) and carboxy-pLyn (regulation). Triplicates of each assay, daily bead-based voltage adjustment, and replication of all experiments on separate days ensured signal stability.
Results:
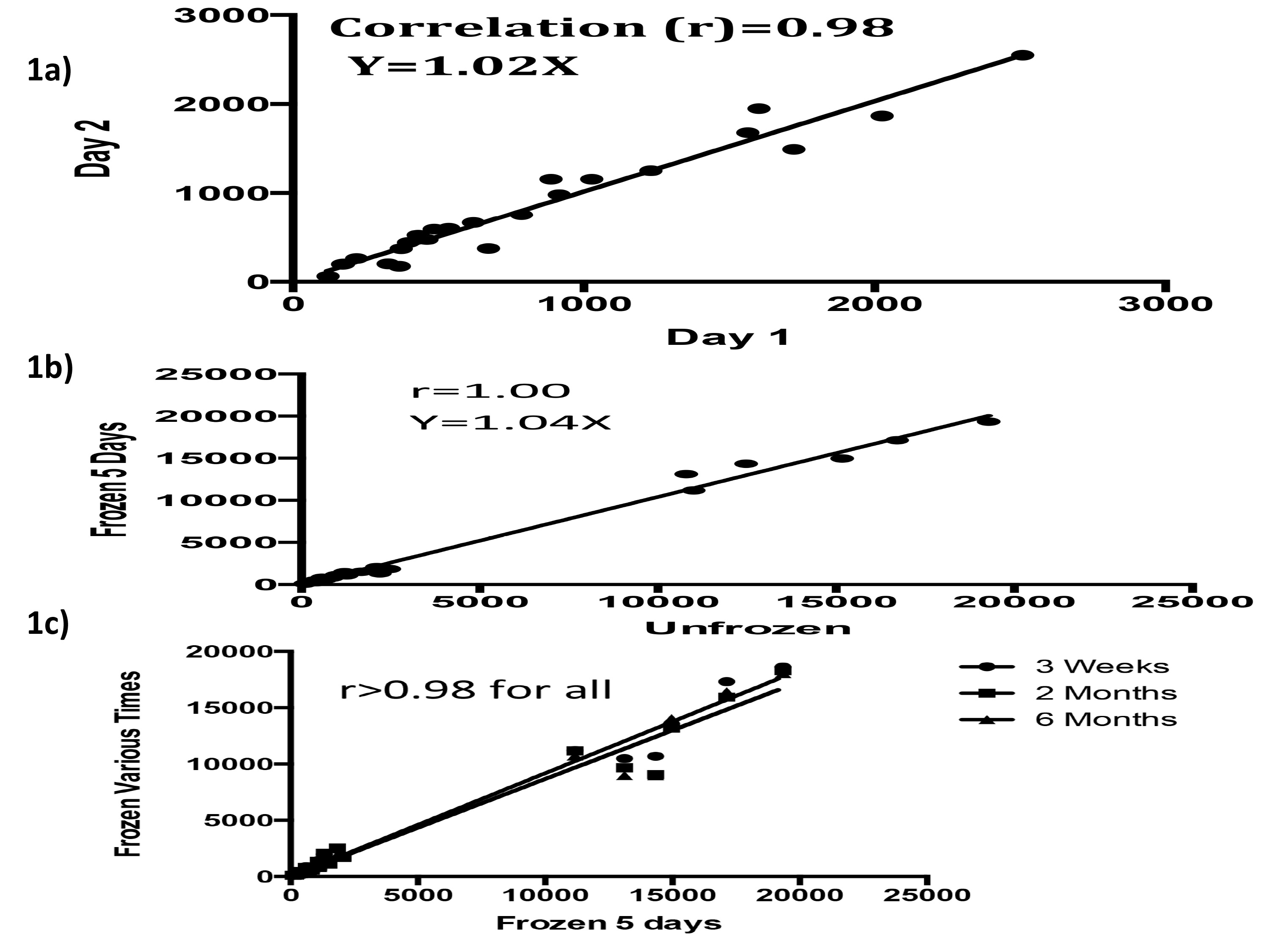
Fig 1: Stability of BCR signal. We found consistently high correlation between assays run on separate days (1a), between frozen and unfrozen cells (1b) and cells obtained at various times from the same person (1c). Each dot represents the fluorescence of one signaling parameter in a specific B cell subset.
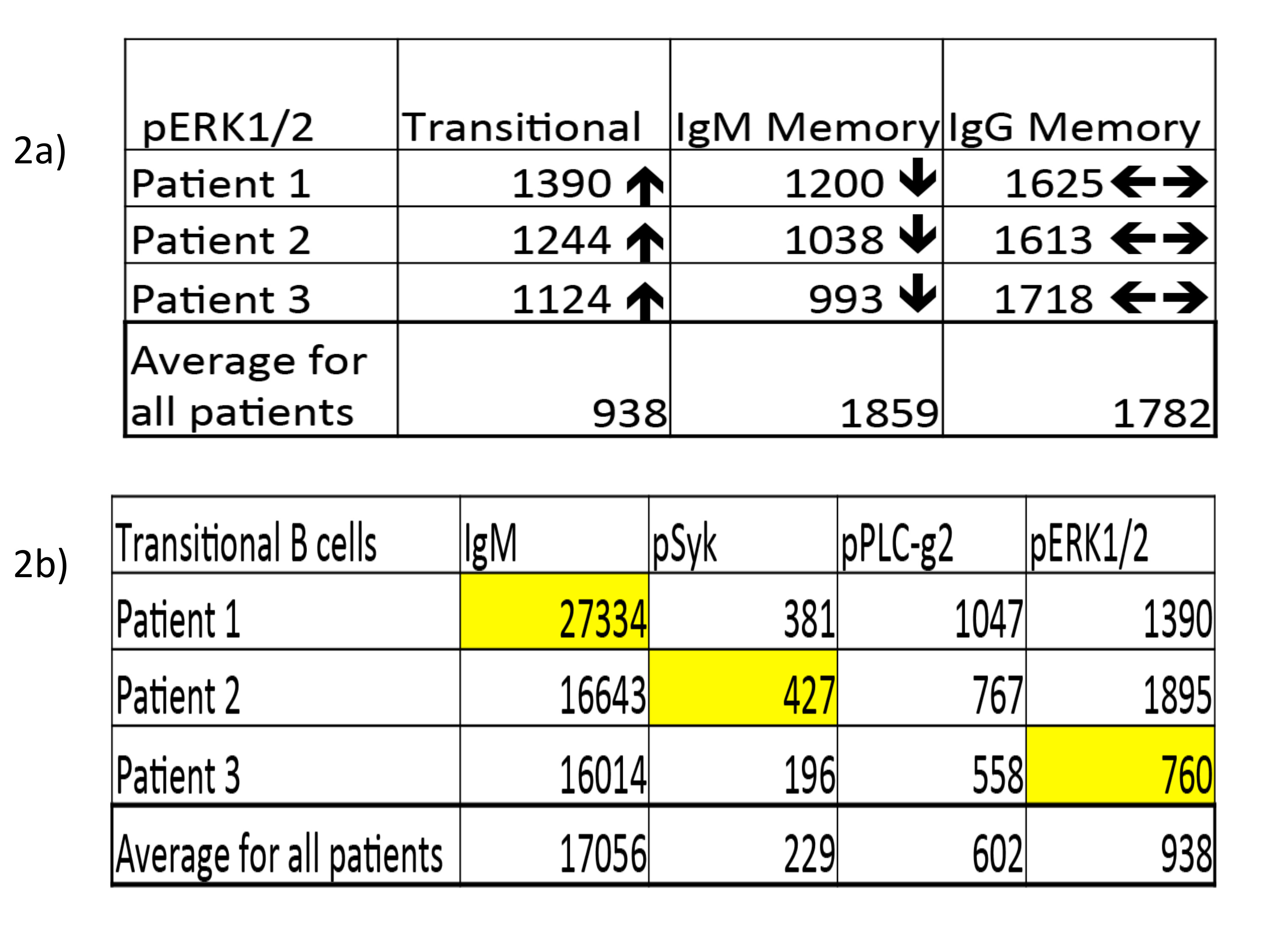
Fig 2: The importance of studying different B cell subsets and BCR stages. Some patients had increased signal in one subset but decreased or normal in other subsets (2a). Signaling deviation can occur at different stages (2b, yellow highlights).
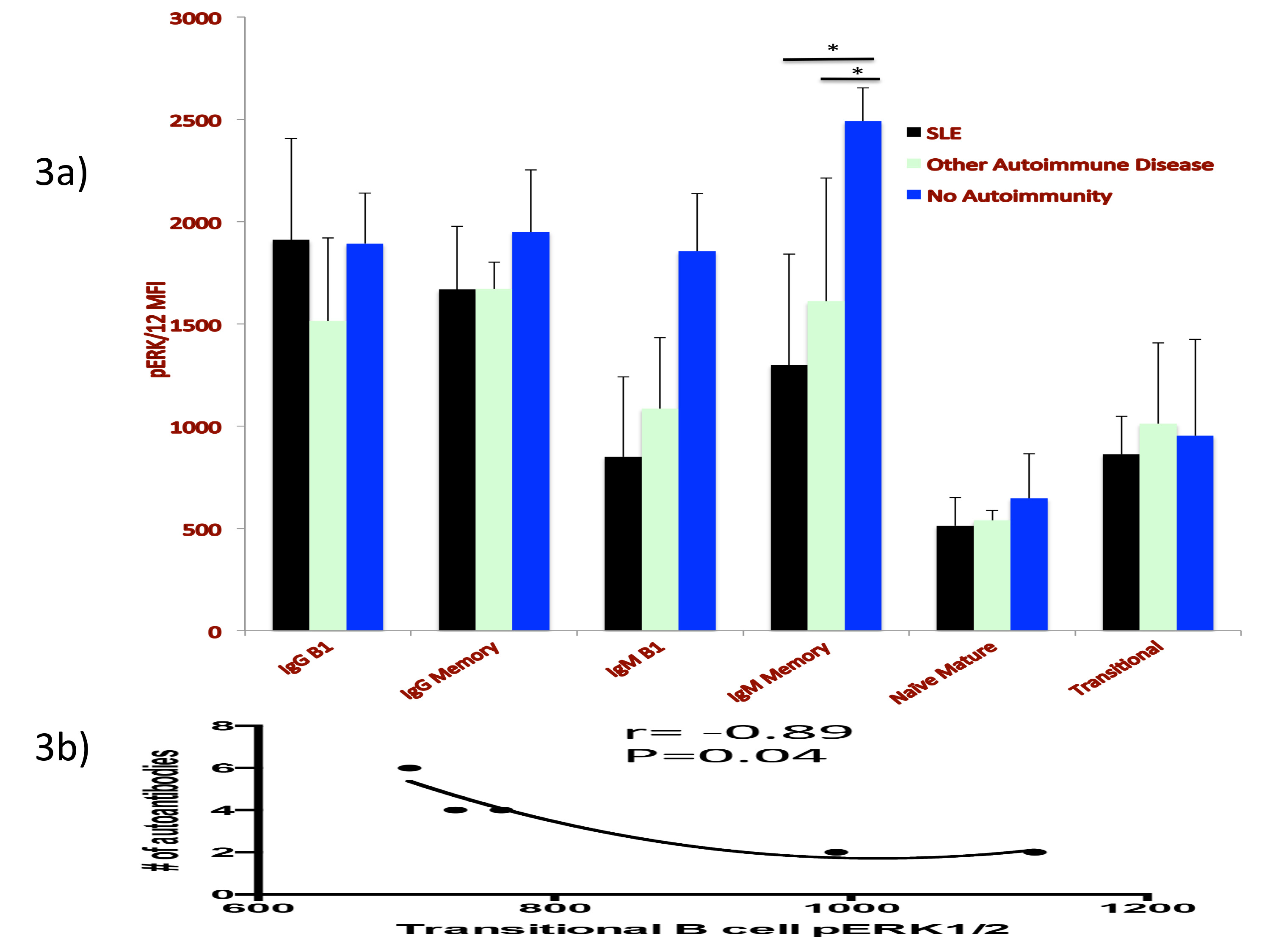
Fig 3: Signaling in 15 patients. Diminished IgM Memory BCR signal was found in SLE and other autoimmunities versus controls (3a). Among SLE patients, diminished signal in transitional B cells correlated with increased number of autoantibody specificities (3b).
Conclusion:
We have optimized a flow cytometry-based technique that allows simultaneous study of BCR signaling in B cell subsets, at various stages of signaling, in a manner that yields stable results over time. We found that diminished BCR signaling in transitional B cells correlates with increased diversity of autoantibodies in SLE patients. We will study 150 patients. Clinical BCR measurement may inform SLE pathogenesis and guide emerging BCR-targeted therapies.
Disclosure:
M. Faludi,
None;
C. A. Pineau,
None;
E. Vinet,
None;
A. E. Clarke,
None;
S. Bernatsky,
None;
J. Rauch,
None;
E. P. Nashi,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/b-cell-receptor-signaling-as-a-potential-clinical-parameter-in-lupus/