Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 8, 2015
Title: Osteoporosis and Metabolic Bone Disease - Clinical Aspects and Pathogenesis Poster
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
are diagnosed with osteoporosis earlier than and those without RA, and are
therefore exposed to Bisphosphonates (BPs) for longer. The long-term BPs treatment
is one of the suggested predisposing factors for atypical
femur fracture (AFF).
Thus the aims of the present study were to examine
the incidence and clinical characteristics of BPs-associated AFF and to identify
predictors of AFF in patients with RA.
Methods: An age-
and sex- matched nested case-control study was conducted based on 7 years of
data collected at Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital, a
tertiary rheumatology center. All patients treated
with BPs met the 2010 RA
classification criteria. AFFs
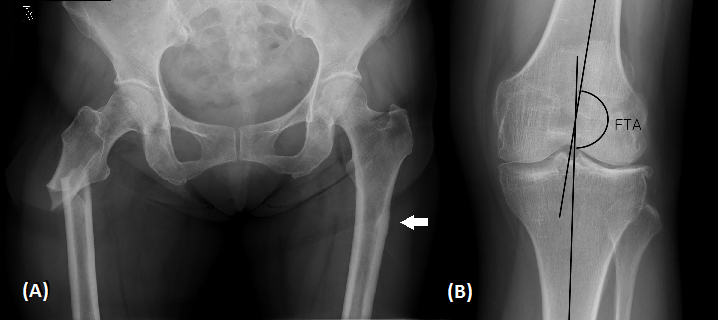
were defined as atraumatic or low-trauma fractures of the subtrochanteric or
femoral shaft (Figure 1A). Ten cases of AFF were
identified by reviewing surgical procedures and
radiographs of the low extremities. The study included
40 age- and sex-matched controls with RA but without AFF. The
femorotibial angle (FTA) was measured on radiographs taken with the patient
standing to examine alignment of the lower limb under weight-bearing conditions
(Figure 1B).
Results: All patients
with AFF were female (age, 66.3±8.7 years) and 90% of cases involved fracture
of the proximal femur. The mean length of BPs exposure for patients with AFF was
7.4±3.2 years. Patients with AFF had longer exposure to BPs and a smaller FTA (P
< 0.001 and 0.010, respectively, Table 1). There were no differences in
RA duration, medications taken during the previous 6 months, and bone mineral
density in the femur and lumbar spine between patients with and without AFF.
Multivariate logistic analyses identified BPs exposure (odds ratio [OR], 2.145;
95% confidence interval [CI], 1.175–4.283) and interestingly a FTA < 175°Æ
(OR, 114.796; 95% CI, 2.263–5821.991) as being associated with an increased
risk of AFF.
Conclusion: RA
patients with a valgus deformity and receiving long-term BPs are at higher risk
of AFF than matched RA control subjects. These patients should be carefully
followed up with X-rays or dual energy bone densiometry.
Figure
1(A) Anteroposterior radiopraph
shows right atypical subtrochanteric fracture and a cortical thickness at the
left lateral cortex (arrow) (B) Measurement of femorotibial angle (FTA) on a
radiograph. The FTA is the lateral angle between the axis of the femoral shaft
and that of the tibial shaft
Table
1. Clinical characteristics of rheumatoid arthritis
patients ever exposed bisphosphonates according to experience atypical femur
fracture
|
|
Non-fracture |
Atypical fracture |
P-value |
|
BMI, kg/m2 |
22.2±2.7 |
23.7±1.9 |
0.090 |
|
RA duration, yrs |
12.7±10.1 |
10.2±5.0 |
0.454 |
|
Total bisphosphonates exposure*, yrs |
3.8±2.3 |
7.4±3.2 |
<0.001 |
|
Drug holiday, n (%) |
18 (45) |
0 |
0.009 |
|
Cumulative oral prednisolone dose, g |
5.2±4.3 |
8.7±12.7 |
0.417 |
*
In case of AFFs, total BPs exposure was computed just before fracture.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Koh J, Ju JH, Chung MK, Kim JH, Jung SM, Lee JY, Lee J, Kwok SK, Park SH. Atypical Femur Fracture in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with Bisphosphonates: A Nested Case-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/atypical-femur-fracture-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-bisphosphonates-a-nested-case-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/atypical-femur-fracture-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-bisphosphonates-a-nested-case-control-study/