Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: Patient Outcomes, Preferences, and Attitudes Poster II: Patient Perspectives
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose:
To determine beliefs about methotrexate (MTX) in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) in relation to views obtained from a range of information sources.
Methods:
RA patients, who had completed an online questionnaire on a national RA database within the previous 12 months, n=1010, were invited to participate in an additional online questionnaire (Survey Monkey) regarding their use and views of MTX. Participants who had ever-used MTX were asked about sources consulted for MTX information, and whether positive or negative views were obtained. The Beliefs about Medicine Questionnaire (BMQ), consisting of general medication (overuse and harm) and MTX specific (necessity and concerns) was used to measure patient specific beliefs about MTX. Demographic and clinical information of the survey respondents was obtained by linkage to the national database.
Results:
The survey response rate was 804/1010 (80%). MTX survey data was analysed for 742 RA participants (age 59 years, 76% female, disease duration 19 years, 75% rheumatoid factor positive) who had ever-used MTX, with 494/742 (67%) reporting current use.
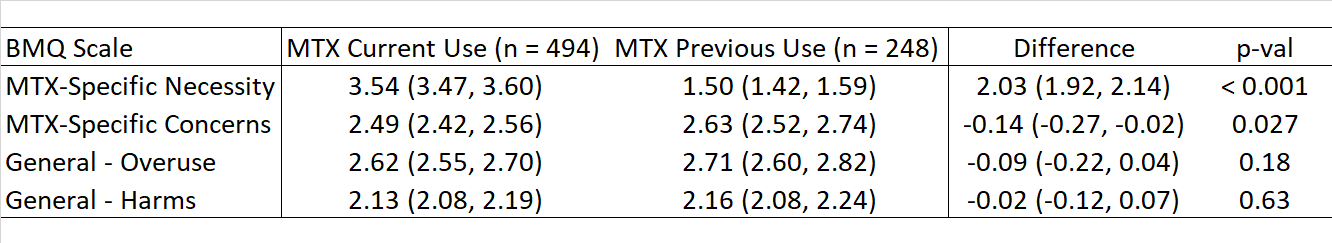
Current MTX users scored substantially higher on the BMQ MTX specific Necessity scale, and slightly lower on the MTX-specific Concerns scale (Table 1).
Table 1. Beliefs about Medicine Questionnaire results by MTX use
Participants consulted multiple information sources (median 3, IQR 1-5), which was associated with younger age, higher education levels, higher MTX-specific concerns and general medication BMQ scores (p<0.05, multiple Poisson regression). Rheumatologists (98%), GPs (55%), internet search engines (39%), educational websites (38%), and Pharmacist (37%) were the most common information sources. When consulted, positive MTX information was most often obtained from rheumatologists (93%), GPs (67%), and educational websites (56%) (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Reported MTX Views by Source
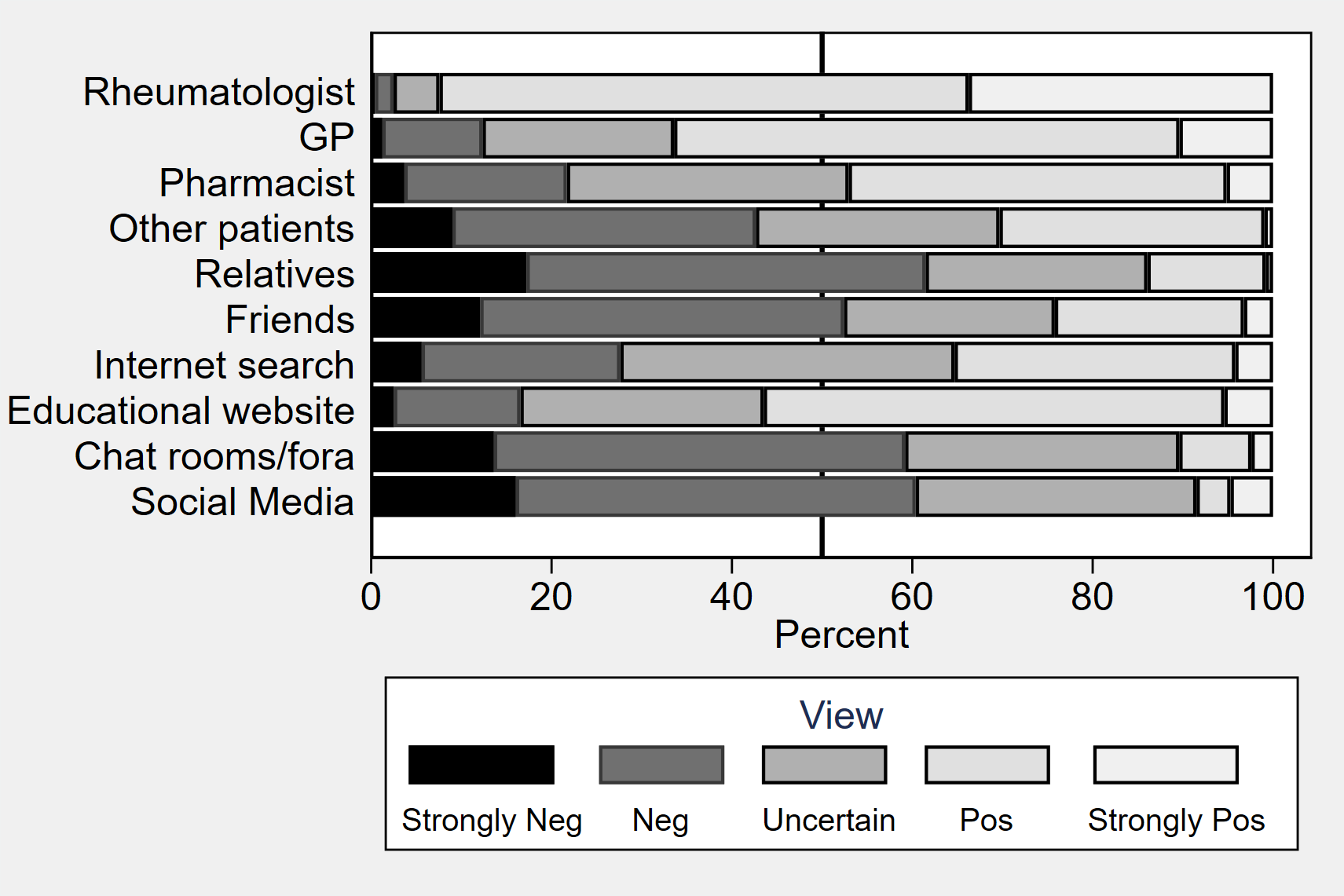
Negative MTX information was most often obtained from relatives, social media, internet chat rooms, and friends. Positive information from Rheumatologists (p<0.001) and Educational websites (p= 0.021) was influential on favourable MTX-specific necessity and concerns BMQ scores (MANOVA analysis).
Conclusion:
RA patients have significant concerns regarding MTX and consult a variety of sources for MTX information. However, the patient perception of this information varies widely. Rheumatologists and educational websites are the most important information sources in terms of utilisation, positive information, and influence on the patient’s perception of MTX.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Leonardo N, Lester S, Graham M, Whittle S, Rowett D, Buchbinder R, Hill C. Attitudes and Beliefs Regarding Methotrexate in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from Australian Rheumatology Association Database [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/attitudes-and-beliefs-regarding-methotrexate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-australian-rheumatology-association-database/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/attitudes-and-beliefs-regarding-methotrexate-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-results-from-australian-rheumatology-association-database/
