Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The pathophysiology of primary Sjögren’s disease involves the interaction of genetic, epigenetic, and environmental factors. With limited treatment options for severe disease, a detailed understanding the proteomic architecture is necessary. Herein, we investigated the associations between circulating proteins on primary Sjögren’s disease using mendelian randomization.
Methods: We selected single nucleotide polymorphisms from protein quantitative trait loci using the genome wide association studies from samples profiled in the UK Biobank Pharma Proteomics Project. Genetic association data for proteins were collected from a study with a sample size of 54,306, and from 3,232 individuals with primary Sjögren’s syndrome and 17,481 controls. Forward and reverse mendelian randomization analyses were conducted. The Wald ratio or inverse variance weighted methods estimated causal effects. We applied colocalization and pleiotropy-robust methods as sensitivity analyses for confounding.
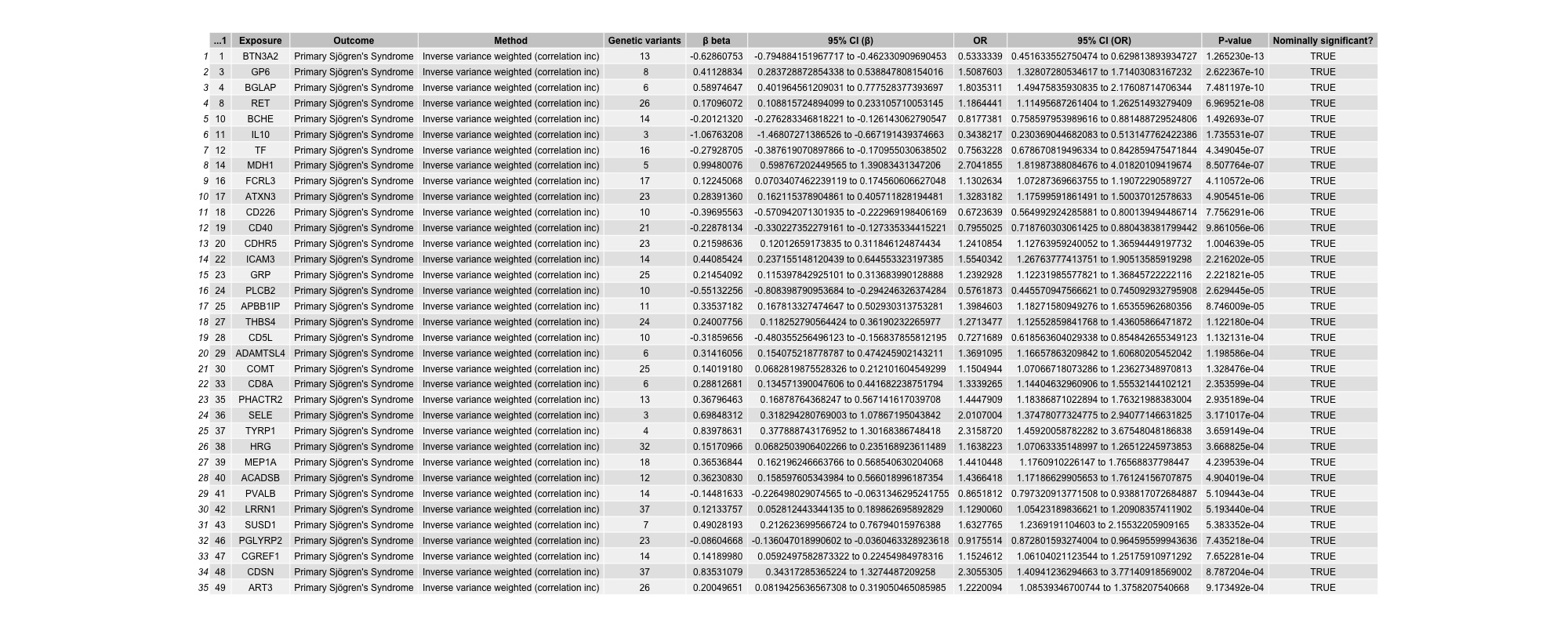
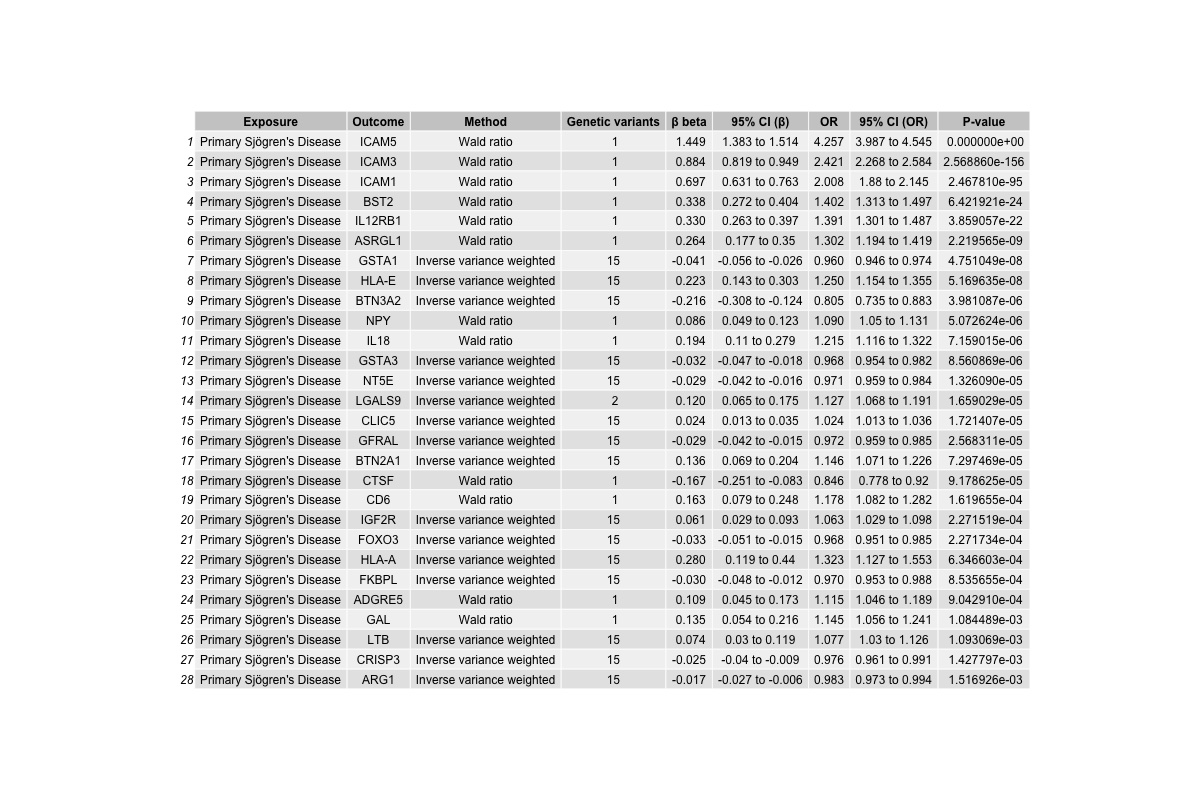
Results: 1,963 of the selected proteins were valid from which 35 survived the mendelian randomization analyses and multiple comparisons assessment, as well as the sensitivity tests (Table 1). Colocalization analyses highlighted that 15 of these proteins had conditional probabilities for a shared causal variant exceeding 80%, suggesting minimal genetic confounding. Notably, our results suggested that CD40 is implicated in primary Sjögren’s disease pathogenesis (odds ratio [OR] 0.80; 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.72-0.88). Reverse mendelian randomization analyses confirmed a causal role for the 15 proteins which survived multiple comparison assessments and identified 28 potential biomarkers for primary Sjögren’s disease (Table 2).
Conclusion: We provided genetic evidence further elucidating the complexity of primary Sjögren’s disease pathogenesis. Additionally, we suggested a genetic causal link between CD40 and primary Sjögren’s disease – supporting the continued investigation of anti-CD40 therapy, such as iscalimab, as a novel treatment for this condition.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zuckerman B, Warwick A, Schuermans a, Gibson M, Karafotias I, Yang Z, moezinia C, Russell M, Wincup C, Galloway J, Zhao S. Associations Between Protein Quantitative Trait Loci and Risk of Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome: A Mendelian Randomization Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-protein-quantitative-trait-loci-and-risk-of-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-a-mendelian-randomization-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-protein-quantitative-trait-loci-and-risk-of-primary-sjogrens-syndrome-a-mendelian-randomization-study/