Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Patients (pts) with PsA can develop axial inflammation in the SI joints (SIJs) and/or spine. Although validated classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis exist, established criteria for classifying axial PsA are lacking. STAR (NCT04929210), a Phase 4, multicenter, randomized, controlled trial of biologic-naïve PsA pts with current neck/back/hip (spinal) pain and MRI-confirmed axial inflammation, is prospectively evaluating the efficacy of guselkumab (GUS), IL-23p19-subunit inhibitor, on axial symptoms and objective measures (MRI) of axial inflammation.1 This exploratory analysis of available screening MRI data from STAR compared clinical-characteristics between pts meeting vs not meeting STAR MRI eligibility criteria.
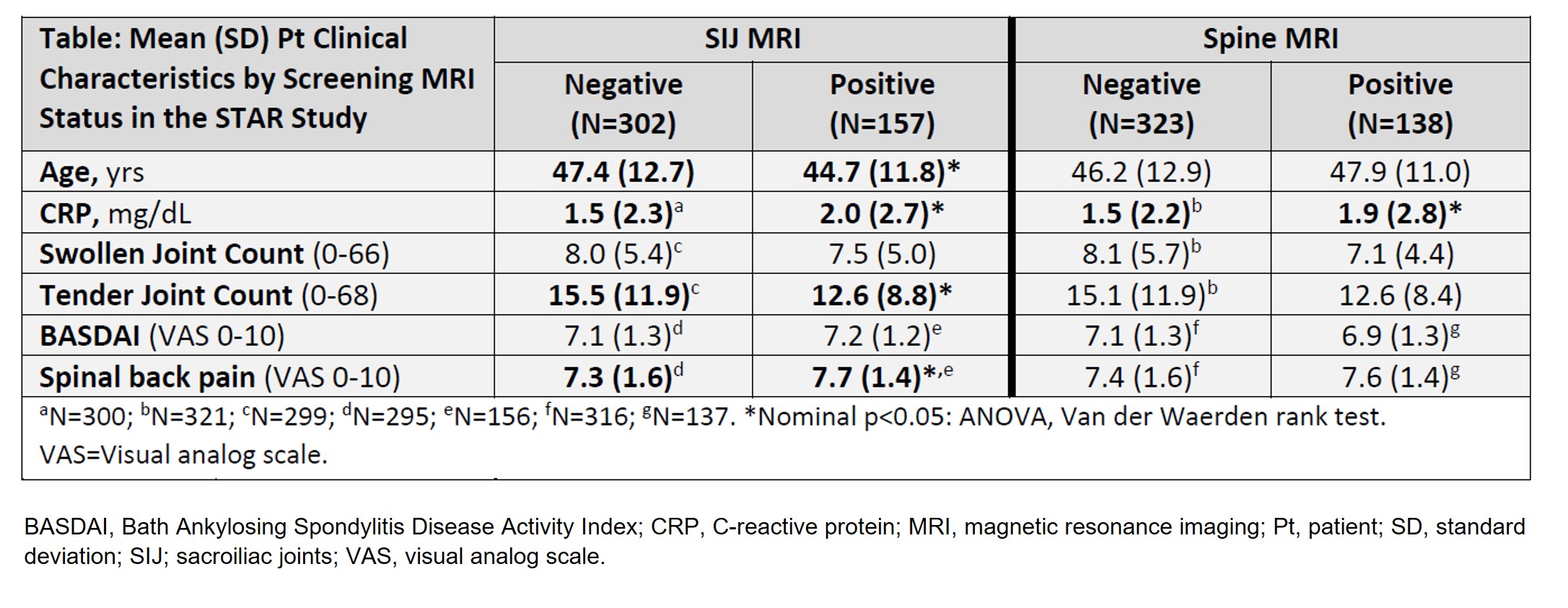
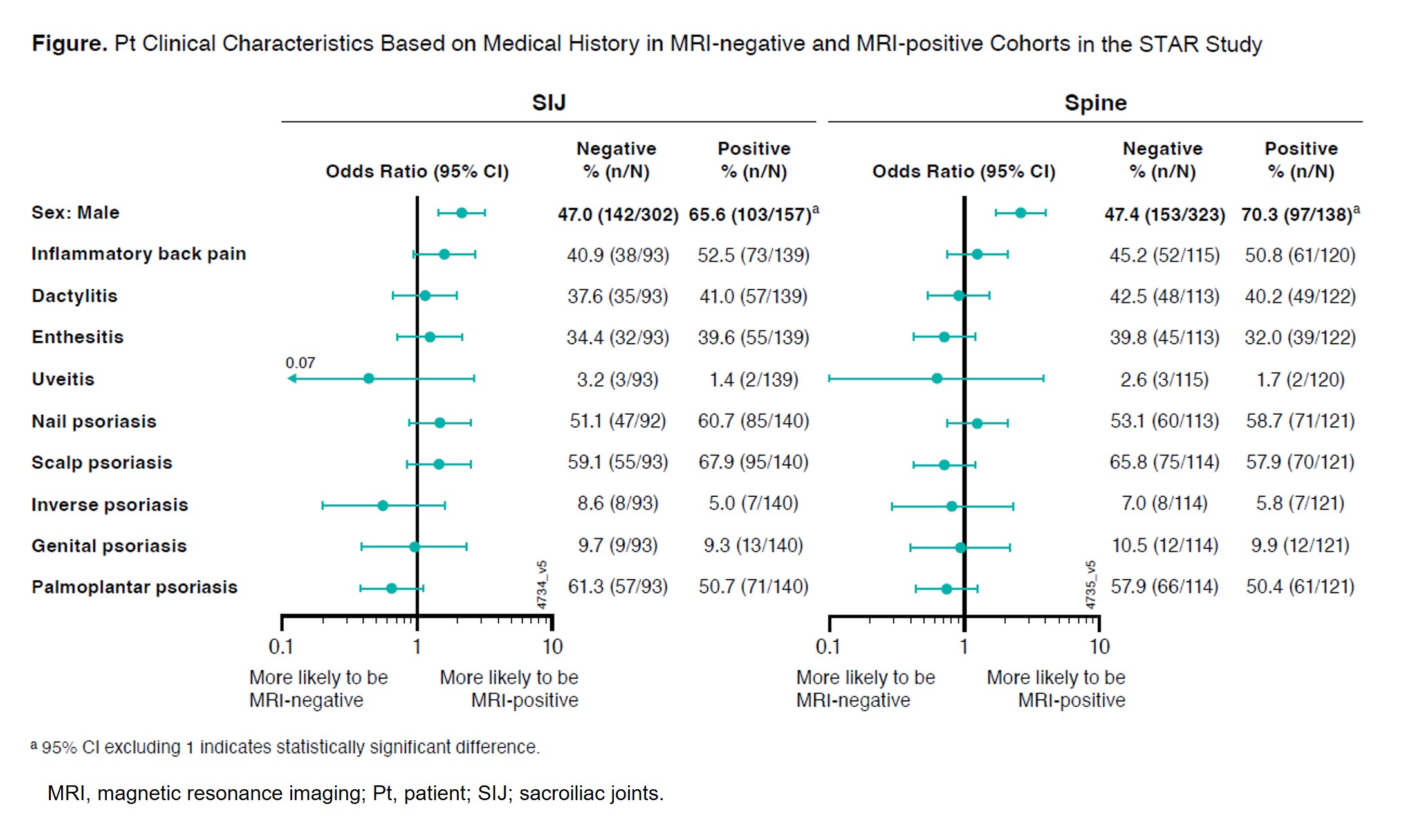
Methods: STAR is designed to randomize (1:1:1) 405 pts to GUS every 4 weeks (Q4W); GUS at W0, W4, then Q8W; or placebo→GUS Q8W at W24. Eligibility criteria include active PsA (≥3 swollen and ≥3 tender joints, CRP ≥0.3 mg/dL) despite non-biologic DMARDs, apremilast, and/or NSAIDs. Eligible pts are naïve to biologics/Janus kinase inhibitors and have BASDI ≥4, BASDI spinal pain score ≥4, and screening MRI-confirmed axial involvement (positive spine and/or SIJ MRI defined by blinded, centrally-read Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada score ≥3). SI Joint/Spine MRI reading involves 2 central readers and an adjudicator; agreement by 2 readers confirms positive (+)/negative (–) MRI result. Pt clinical characteristics and medical history at screening were compared between MRI+ and MRI– cohorts to determine those associated with MRI-detected inflammation of SIJ and/or Spine (Figure).
Results: Of 487 pts screened to date, those with non-missing MRI results included 459 for SIJ (34% MRI+), 461 for Spine (30% MRI+), and 433 for both SIJ and Spine (15% SIJ+/Spine+, 26% SIJ+/Spine– or SIJ–/Spine+, 59% SIJ–/Spine–). Male gender and serum CRP levels were significantly higher in both SIJ+ vs SIJ– and Spine+ vs Spine– cohorts. SIJ+ cohort pts were younger (mean age: 44.7 vs 47.4 yrs) with higher spinal pain score (mean: 7.7 vs 7.3) and fewer tender joints (mean: 12.6 vs 15.5) vs SIJ– cohort pts (all nominal p< 0.05). Consistent numerical differences (not statistically significant) were seen in spinal back pain score and tender joint counts between the Spine+ and Spine– cohorts (Table). The SIJ+ cohort had numerically higher proportions of pts with a history of inflammatory back pain, nail psoriasis, and scalp psoriasis vs the SIJ– cohort. Pts with palmoplantar psoriasis history were less likely to exhibit MRI-detected inflammation in the SIJ or Spine (Figure). Differences between the SIJ+/Spine+ (N=65) and SIJ–/Spine– (N=257) cohorts were generally aligned with those of the site-specific cohorts (data not shown).
Conclusion: Preliminary findings from an established STAR PsA cohort: 1) are consistent with the recognized positive association between serum CRP levels and axial involvement in PsA and 2) provide initial evidence that several clinical characteristics may associate with presence/absence of MRI-detected axial inflammation. STAR is actively enrolling.
1. Gladman. Trials. doi.org/10.1186/s13063-022-06589-y
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Baraliakos X, Bird P, Deodhar A, Gladman D, Helliwell P, Poddubnyy D, Kavanaugh A, Ostergaard M, Soriano E, Tam L, Chakravarty S, Leibowitz E, Gong C, Xu S, Fuerst T, Saeed N, Landewé R, Mease P. Associations Between Clinical Characteristics and Screening MRI Findings: Exploratory Analysis of the Ongoing Phase 4, Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled STAR Study of Biologic-Naïve Patients with PsA with MRI-Confirmed Axial Involvement [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-clinical-characteristics-and-screening-mri-findings-exploratory-analysis-of-the-ongoing-phase-4-multicenter-randomized-controlled-star-study-of-biologic-naive-patients-with-ps/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/associations-between-clinical-characteristics-and-screening-mri-findings-exploratory-analysis-of-the-ongoing-phase-4-multicenter-randomized-controlled-star-study-of-biologic-naive-patients-with-ps/