Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The genetic background of rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) has been evaluated in Europeans, but little knowledge has been obtained in non-Europeans. In particular, The MUC5B promoter variant (rs35705950) has been noted as a common risk variant with large effect on both IPF and RA-ILD in Europeans. However, the frequency of the variant varies heterogeneously among ancestral populations. While its minor allele frequency (MAF) was common in Europeans (= 0.107 in 1000 Genomes Project Phase 3; 1KGP3), it was as low as 0.008 in east Asians. This observation implies that genetic underpinning of RA-ILD is heterogeneous among populations, and identification of additional risk variants other than MUC5B in east Asians should be warranted. Furthermore, previous studies assessed RA-ILD risk of the mutations in specific genes implicated with risk of pulmonary fibrosis through candidate gene approaches. There have been no studies that investigated genome-wide risk of RA-ILD. This study aimed to elucidate genome-wide risk of RA-ILD in non-Europeans.
Methods: This study enrolled 1,117 and 3,899 individuals affected with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) from Institute of Rheumatology Rheumatoid Arthritis (IORRA) and BioBank Japan (BBJ), respectively. IORRA is a RA cohort which was established in 2000 at Tokyo Women’s Medical University, Japan. In the IORRA cohort, we extracted the RA subjects who had normal CT scans and chest CT image of each subject was reviewed by an experienced physician, and findings were confirmed based on the concordance with those by the radiologist’s report. BBJ is a hospital-based cohort with multi-omics data from genotype to multitude phenotype. The status of RA or ILD in the BBJ cohort was examined through interviews and reviews of medical records. GWAS genotyping and imputation were conducted for all the subjects. After the quality control, we performed a GWAS meta-analysis of the IORRA cohort and the BBJ cohort, which included 358 RA-ILD cases and 4,550 RA subjects without ILD. We then conducted the stratified analysis of the effect of the GWAS risk allele in each computerized tomography (CT) image pattern.
Results: We identified one novel RA-ILD risk locus at 7p21 that satisfied the genome-wide significance threshold (rs12702634, odds ratio [OR] = 2.04, 95% confidence interval [95%CI] = 1.59-2.60, P = 1.5×10-8). Subsequent stratified analysis based on the CT image patterns demonstrated that the effect size of the RA-ILD risk allele (rs12702634-C) was large with the UIP pattern (OR = 1.86, 95%CI = 0.97-3.58, P = 0.062) and the probable UIP pattern (OR = 2.26, 95%CI = 1.36-3.73, P = 0.0015). The RA-ILD risk variant of rs12702634 was located in the intron region of RPA3 and UMAD1 and within the enhancer histone marks in several immune cells. The GTEx data showed that the rs12702634-C risk allele increased RPA3 expression levels in various tissues including lung.
Conclusion: We revealed one novel genetic association with RA-ILD in Japanese. The RA-ILD risk of the identified variant at RPA3–UMAD1 was relatively high in the CT image patterns related to fibrosis. Our study should contribute to the elucidation of the complicated etiology of RA-ILD.
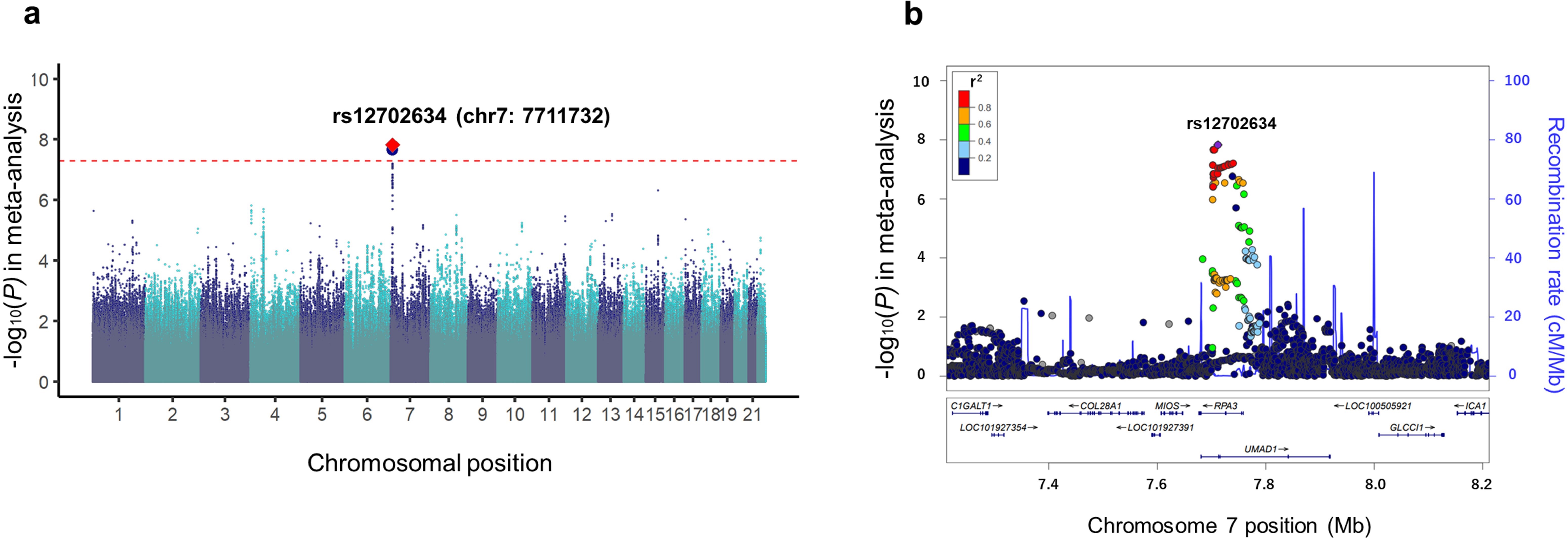 Association results of the GWAS meta-analysis for the three datasets.
Association results of the GWAS meta-analysis for the three datasets.
 The odds ratio and the 95% confidence interval of rs12702634-C in each dataset and CT image pattern.
The odds ratio and the 95% confidence interval of rs12702634-C in each dataset and CT image pattern.
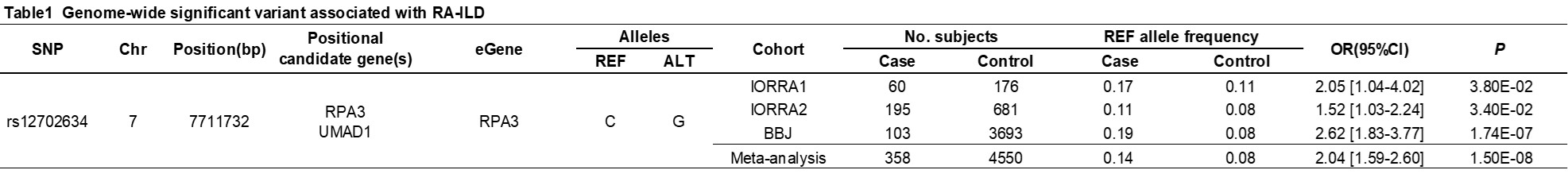 Genome-wide significant variant associated with RA-ILD.
Genome-wide significant variant associated with RA-ILD.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shirai Y, Honda S, Ikari K, Kanai M, Takeda Y, Kamatani Y, Morisaki T, Tanaka E, Kumanogoh A, Harigai M, Okada Y. Association of the RPA3-UMAD1 Locus with Interstitial Lung Diseases Complicated with Rheumatoid Arthritis in Japanese [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-the-rpa3-umad1-locus-with-interstitial-lung-diseases-complicated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-japanese/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-the-rpa3-umad1-locus-with-interstitial-lung-diseases-complicated-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-in-japanese/
