Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 12, 2019
Title: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes Poster III: Comorbidities
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is the most common lung disease among rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients. Although the overall mortality rates for RA have decreased in general, ILD is associated with increased morbidity and mortality of RA patients, especially in older age groups. We have launched a multicenter prospective cohort of RA-ILD named as KOrean Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung disease (KORAIL) cohort, to explore clinical prognosis using biomarkers and imaging modalities. This is the first disclosure of results originated from KORAIL cohort.
To describe general clinical characteristics of KORAIL cohort. To elucidate the role of serum concentration of Krebs von den Lungen-6 (KL-6), a potential biomarker of ILD, in evaluation of current status and prediction of functional change during first 1 year after enrollment. The association between KL-6 concentration and inflammatory cytokines were also investigated.
Methods: Entering clinical information to e-case report form, chest CT, pulmonary function test, and blood samples were conducted at baseline and followed every year. Serum KL-6 concentration (U/mL) was measured through the Nanopia KL-6 assay latex-enhanced immunoturbidimetric assay method. Multiplex ELISA was used to measure serum concentration of TNF-alpha, IL-6, GM-CSF, and IL-17.
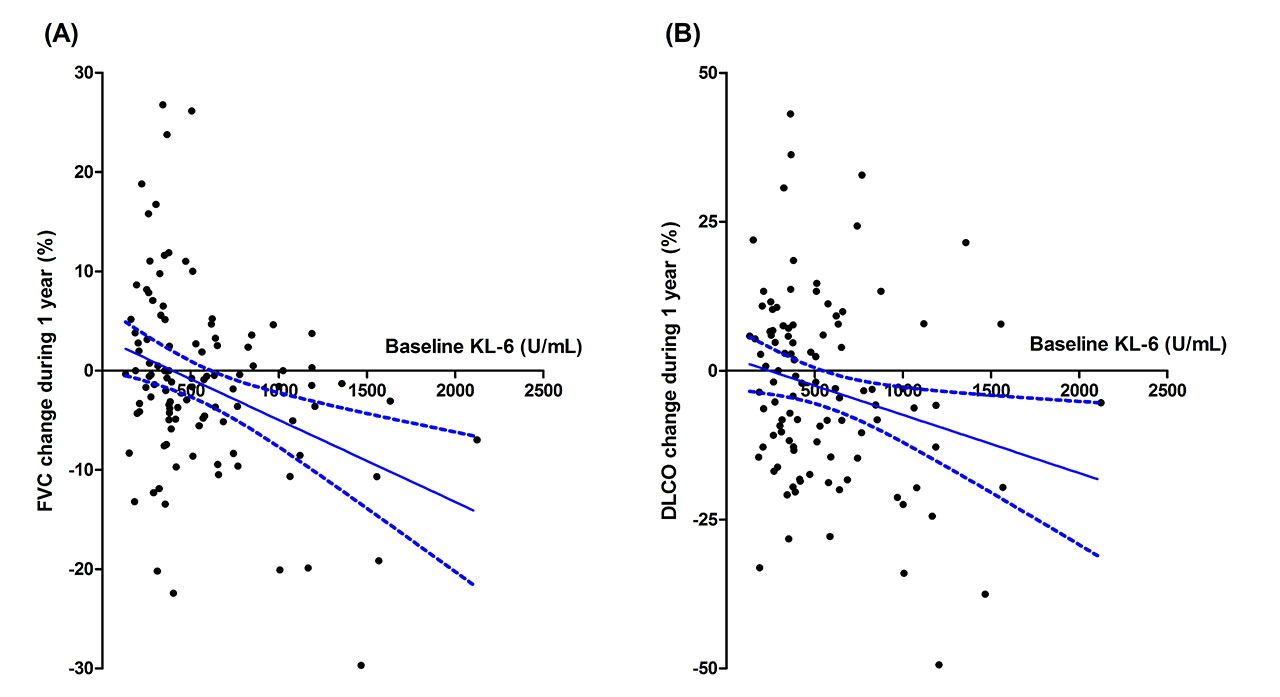
Results: One hundred and sixty eight patients with RA-ILD have been enrolled from six university hospitals in Korea. Till January 2019, 129 patients (76.8%) were followed for 1 year, 71 patients (42.3%) for 2 years, and 21 patients (12.5%) for 3 years. RA was diagnosed at 58.7±11.3 (mean±SD, years old), ILD at 63.7±8.6, and enrolled at 66.4±8.0. Baseline KL-6 was significantly associated with baseline DLCO (r=-0.196, p=0.029), 1 year change(%) of FVC (r=-0.319, p=0.001) (figure A) and DLCO (r=-0.191, p=0.048)(figure B). TNF-alpha, IL-6, GM-CSF, and IL-17 had no association with functional deterioration or KL-6.
Conclusion: KL-6 could predict functional deterioration of RA-ILD in next 1 year.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Yoon Y, Lee E, Choe J, Lee H, Park Y, Kang E, Ha Y, Lee Y, Jang S. Association of Serum KL-6 Level and Change of Pulmonary Function in Interstitial Lung Disease of Rheumatoid Arthritis – Data from Prospective KOrean Rheumatoid Arthritis Interstitial Lung Disease (KORAIL) Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-serum-kl-6-level-and-change-of-pulmonary-function-in-interstitial-lung-disease-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-data-from-prospective-korean-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-kor/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-serum-kl-6-level-and-change-of-pulmonary-function-in-interstitial-lung-disease-of-rheumatoid-arthritis-data-from-prospective-korean-rheumatoid-arthritis-interstitial-lung-disease-kor/