Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 15, 2016
Title: Spondylarthropathies Psoriatic Arthritis – Pathogenesis, Etiology - Poster II
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: There was a biased repertoire of the immunoglobulin (Ig) heavy chain variable (VH) segment gene in B cells in patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS). Activation-induced cytidine deaminase (AID) plays an important role in Ig class switch recombination (CSR) and somatic hypermutation (SHM) to generate Ab diversity and B cell tolerance. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) express five different AID splicing variants [full-length (FL) and splicing variants (sv) 1–4]. In addition, translesion synthesis (TLS) DNA polymerases are involved in the repair of AID-mediated DNA lesions. We have previously reported that Ig SHM and CSR are upregulated in lupus autoimmune mice as a result of enhanced AID expression. In this study, we investigated the expression patterns of AID variants and TLS polymerase in PBMCs of AS patients so as to verify the relationship of the CSR and SHM bias with susceptibility to AS.
Methods: PBMCs were collected from 33 healthy controls (HC) and 62 patients with AS who fulfilled the modified New York classification criteria. We measured the mRNA expression of AID variants and TLS polymerases by quantitative RT-PCR.
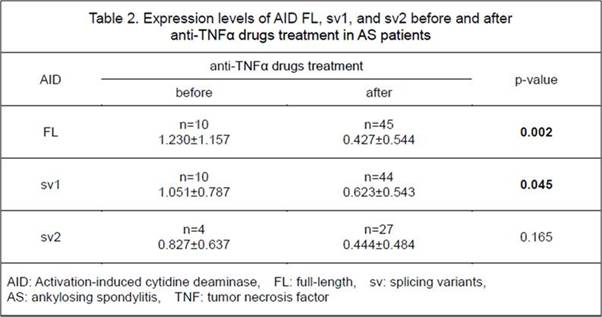
Results: The number of subjects expressing sv2 was significantly greater in AS patients compared to HC (p = 0.031, odds ratio = 2.77) (Table 1). Next, we investigated whether the treatment with TNF inhibitors (TNFi) affected the gene expression of AID variants. A significantly higher proportion of TNFi-treated group expressed sv2 compared to TNF-naïve group (p = 0.014). And we compared the level of AID variants expression between TNFi-treated and TNF-naïve group. The expression levels of FL and sv1 were significantly lower in the TNFi-treated group than TNF-naïve group (FL: p = 0.002, sv1: p = 0.045) (Table 2). In addition, we investigated mRNA expression levels of TLS polymerases in PBMCs from patients with AS and HC. The expression level of TLS pol was significantly lower in AS patients than in HC (p = 0.007) (Table 3).
Conclusion: Our results showed that patients with AS expressed significantly higher levels of sv2 than HC. TNFi treatment restored the gene expression of the AID variants (FL, sv1 and sv2) in patients with AS. Therefore pre-existing TNFa-induced AID expression in B cells may play an important role in the pathogenesis of AS. 
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Shim SC, Yoo IS, Park CK, Kim JY, Kim YM, Sheen DH, Park SR. Association of Polymorphisms of Activation-Induced Cytidine Deaminase with Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-polymorphisms-of-activation-induced-cytidine-deaminase-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-polymorphisms-of-activation-induced-cytidine-deaminase-with-ankylosing-spondylitis/