Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Title: Spondyloarthritis Including Psoriatic Arthritis – Basic Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The etiopathogenesis of axial spondyloarthritis (AxSpA) is multifactorial. The possible role of alteration in gut microbiome (dysbiosis) has been recently suggested. However, the association of dysbiosis with structural damage is still unknown and further studies are needed to assess its association with disease activity. Objectives: To determine the alterations in the gut microbiota in AxSpA patients. To evaluate whether changes in the gut microbiota in AxSpA patients are associated with radiographic and enthesis involvement or disease activity.
Methods: Cross-sectional study of 33 patients with AxSpA (according to ASAS criteria) and 7 sex-age matched healthy donors (HDs) was studied. Disease activity variables such as C-reactive protein and ESR were measured. The enthesis affectation was evaluated using ultrasound to obtain the Madrid Sonographic Enthesitis Index (MASEI). Gut microbiota was evaluated using the Ion Torrent S5 platform and the sequences were processed using the QIIME2 analysis platform. Chi-square and Mann-Whitney tests were used for qualitative and quantitative variables, respectively, correlations between quantitative variables were determined using the Spearman Rho test and univariate analysis with a simple linear regression. Significant differences were considered p < 0.05.
Results: α and β diversity data showed non-significant differences between AxSpA patients and HDs. The analysis demonstrated a significant incresase in Coprococcus comes in AxSpA patients compared to HDs. Also, we observed that patients tend to differ from HDs in the families Bacteroidaceae and Bifidobacteriaceae and the genera Bacteroides, Bifidobacterium and Dialister.
AxSpA patients were divided in two groups: patients with active and patients with inactive disease. We observed that α-diversity indicator such as Shannon index was significantly decrease in patients with active disease (ASDAS >2.1). Family Brucellaceae was significantly decreased and family Peptostreptococcaceae was significantly increased in active group compared to inactive group. Moreover, species such as Alistipes finegoldii, Alistiper putredins and Paraprevotella clara were significantly decreased in active group.
Moreover, families Peptostreptococcaceae and Streptococcaceae were significantly increased in patients with pathological enthesis ultrasonography (MASEI >17) compared with patients with normal enthesis.
Finally, AxSpA patients were divided in other two groups: patients with a radiographic AxSpA and non-radiographic AxSpA. We observed that patients with radiographic AxSpA had an increase in family Erysipelotrichaceae, genus Ruminococcus and species Ruminococcus gnavus versus non-radiographic AxSpA. Further, positive correlation was observed between genus Roseburia and species Roseburia faecis with disease duration.
Conclusion: 1) AxSpA patients had a significant alteration of the gut microbiota. 2) These alterations are associated with disease activity and duration, and enthesis and radiographic involvement.
Funded by JA PI-0151-2018 and FIS PI19/00701
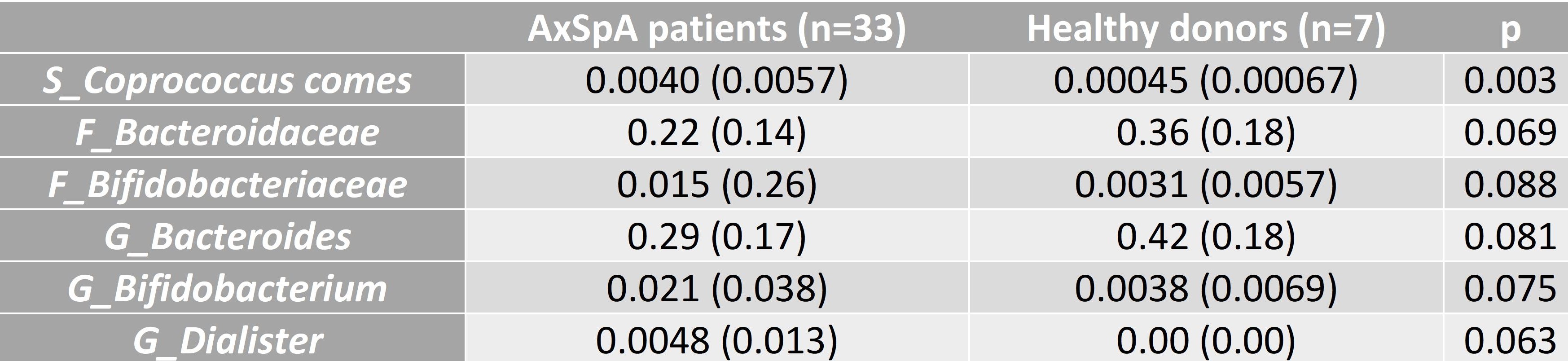 Table 1. Microbial composition between AxSpA and HD. Values are expressed as relative abundance (sqrt/arcsin).
Table 1. Microbial composition between AxSpA and HD. Values are expressed as relative abundance (sqrt/arcsin).
 Table 2. Microbial composition according to disease activity, radiographic and enthesis affectation. Values are expressed as relative abundance (sqrt/arcsin).
Table 2. Microbial composition according to disease activity, radiographic and enthesis affectation. Values are expressed as relative abundance (sqrt/arcsin).
 Table 3. Correlation studies and univariate analysis between gut microbiota an disease duration.
Table 3. Correlation studies and univariate analysis between gut microbiota an disease duration.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gómez-García I, Moreno-Indias I, Abalos-Aguilera M, Lopez-Medina C, Ladehesa-Pineda L, Aranda-Valera C, Gutierrez-Repiso C, Jimenez-Gomez Y, Barbarroja N, Lopez-Pedrera C, Tinahones F, Collantes-Estévez E, Escudero-Contreras A, Ruiz-Limon P. Association of Gut Dysbiosis with Radiographic and Enthesis Involvement, Disease Activity and Duration in Axial Spondyloarthritis. Data from CASTRO Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-gut-dysbiosis-with-radiographic-and-enthesis-involvement-disease-activity-and-duration-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-data-from-castro-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-of-gut-dysbiosis-with-radiographic-and-enthesis-involvement-disease-activity-and-duration-in-axial-spondyloarthritis-data-from-castro-registry/
