Session Information
Date: Monday, November 13, 2023
Title: (1052–1081) Immunological Complications of Medical Therapy Poster
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Describe patients(pts) hospitalized with COVID-19C(C19) who were on disease modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) before admission(BA); assess if clinical outcomes differed from pts without BA DMARD exposure
Methods: Retrospective review. Inclusion: admitted with C19, 18-85 years, 01/01/2020-12/31/2021, use of BA DMARDs (G1); without BA DMARD exposure age- & sex-matched to G1 (G2)
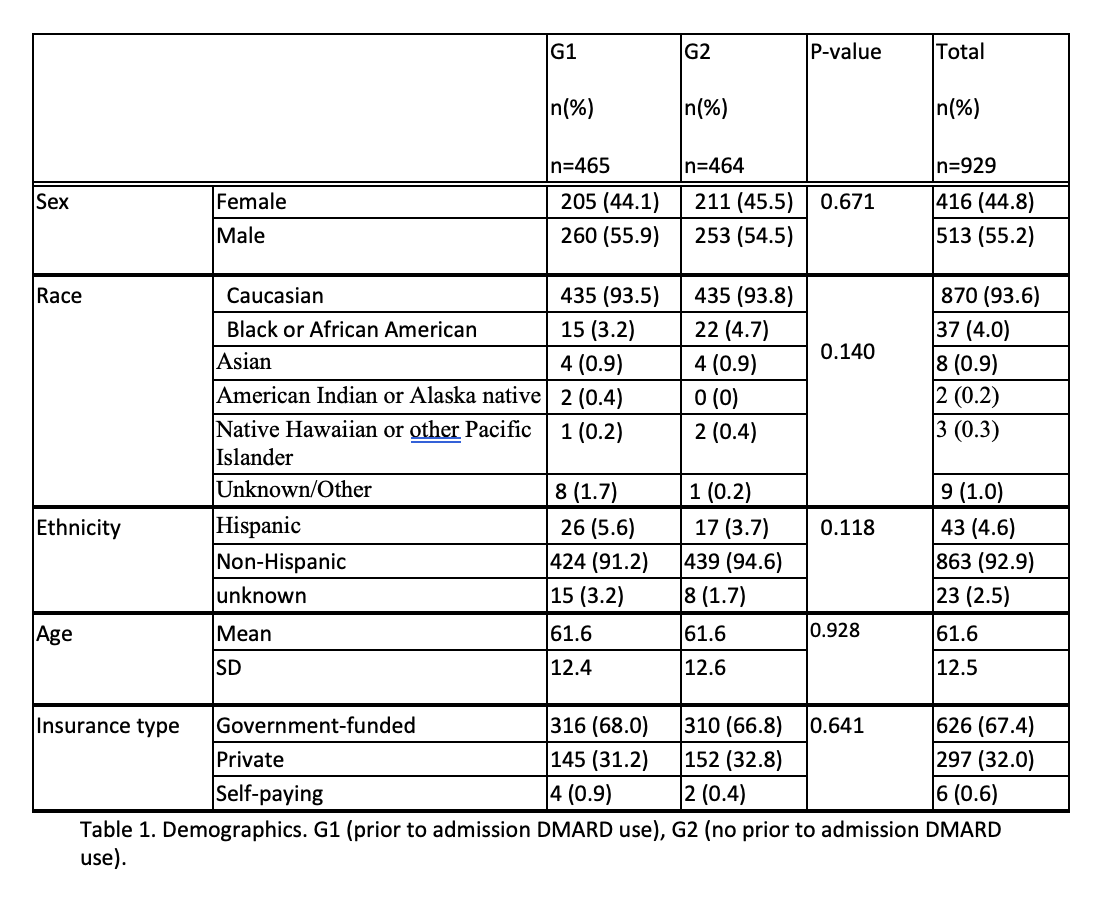
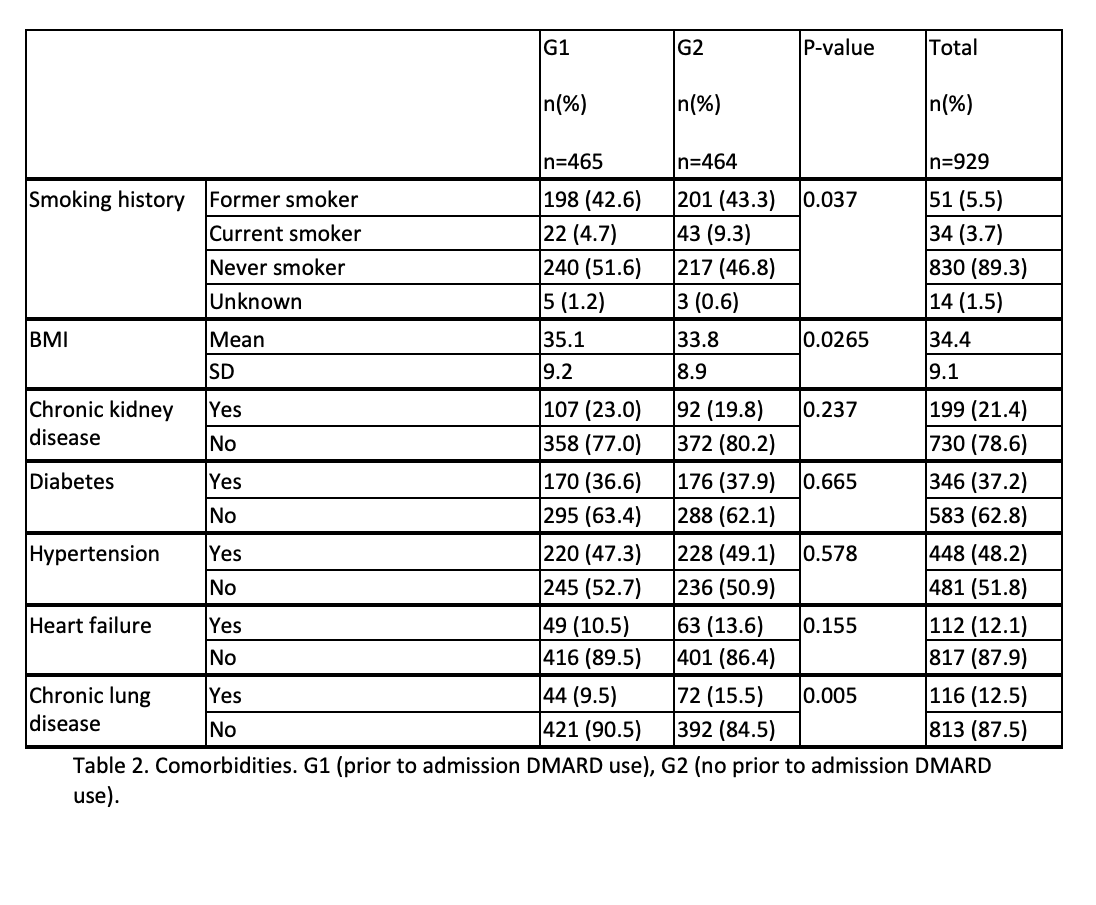
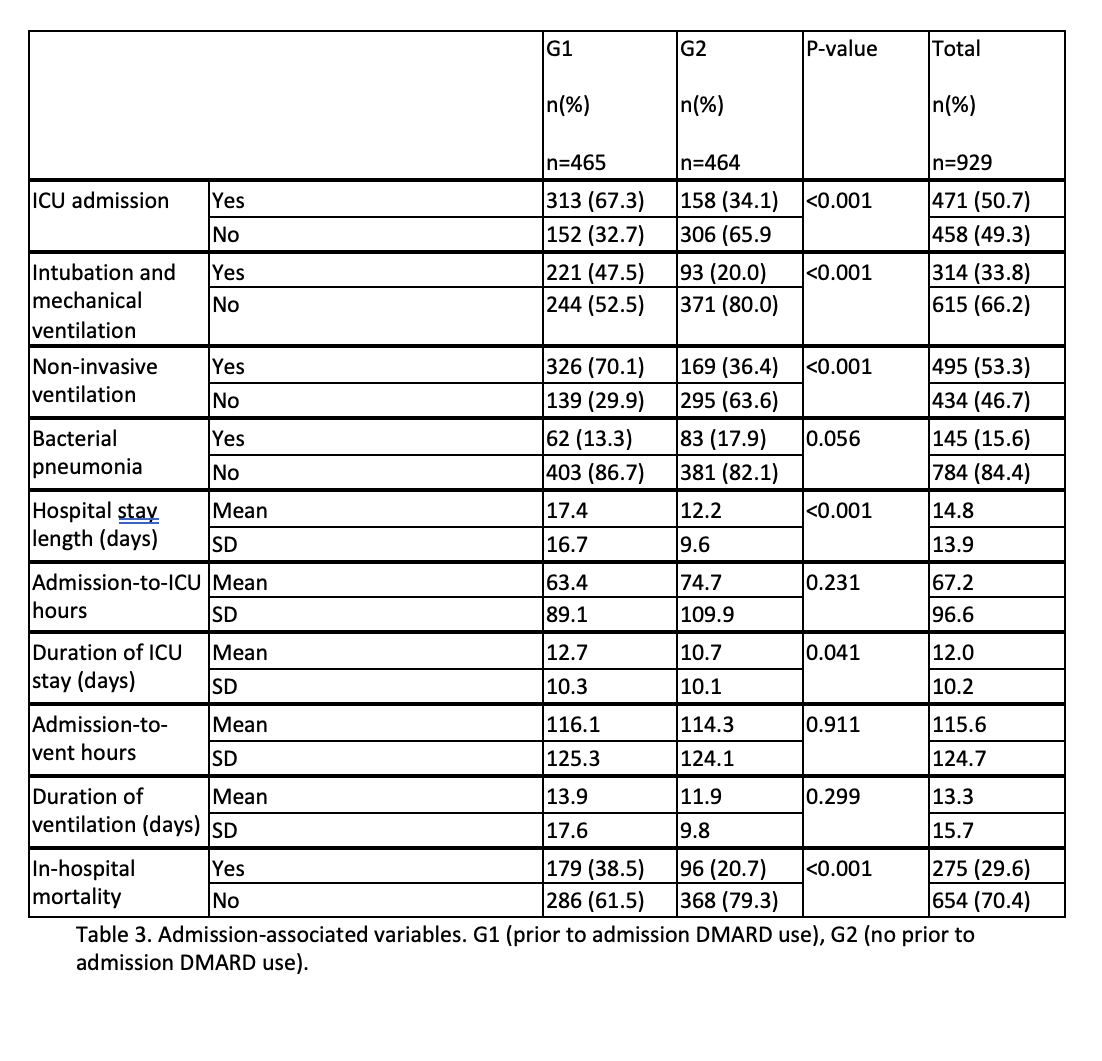
Results: In total, 929 pts were included; 44.8% were female, and 55.2%, male. Most were Caucasian(93.6%); 4.0% were Black, 0.9% Asian. Most were non-Hispanic (91.2%). Mean age was 61.6(standard deviation(s) 12.5). G1 composed 50.1% and G2 49.9%. No differences existed between groups(grps) when age (p 0.928), sex (p 0.671), race (p 0.140) or ethnicity (p 0.118) were compared. Mean BMI was 34.4 (s 9.1); greater in G1(35.1(s 9.2)) than G2(33.8 (s 8.9)) (p 0.025). Smoking history was seen in 49.9%; of these, 86.0% were former smokers and 14.0% were current smokers. Never-smokers composed 49.2% and 0.9% had unknown smoking status. G1 had more never-smokers (51.6%) than G2 (46.8%); G1 had fewer current smokers (4.7%) than G2(9.3%) (p 0.037). Prevalence of chronic kidney disease (21.4%, p 0.237), diabetes (37.2% , p 0.665), hypertension (48.2%, p 0.578), and heart failure (12.1%, p 0.155) were similar between grps. Chronic lung disease(CLD) in 12.5%; more G2 pts had CLD(15.5%) than G1(9.5%) (p 0.005). Mean Charlson Comorbidity Index (CCI) was 3.9(s 3.2) and was similar between grps (p 0.357). Mean hospital stay length(HSL): 14.8 days(s 13.9); HSL was longer in G1(17.4(s 16.7)) than G2(12.2 (s 9.6)) p< 0.001. ICU admission occurred in 50.7%; mean duration of ICU stay: 12.0 days(s 10.2); mean admission-to-ICU(ATI) interval: 67.2 hours(s 96.5). G1 had more ICU admissions (67.3% vs 34.1%, p< 0.001), and longer ICU stays (12.7 days, s 10.3) than G2 (10.7, s 10.0), p 0.0413; the ATI was similar between grps(p 0.231). Intubation and mechanical ventilation (IMV) occurred in 33.8%; more G1 pts had IMV(47.5%) than G2(20.0%), p< 0.001. Mean admission-to-ventilation interval(IAV) was 115.6 hours(s 124.5) and was similar between grps(p 0.911). Mean vent duration was 13.3 days (s 15.7) and was similar between grps(p 0.299). Non-invasive ventilation(NIV) occurred in 53.3%; more G1 pts (70.1%) received NIV than G2(36.4%), p< 0.001. Mean admission-to-NIV duration was 70.7 hours(s 118.9) and was similar between grps(p 0.322). Mean admission respiratory rate(RR) was 23.3(s 6.6), and similar between grps (p 0.385). Mean RR during admission was 21.8(s 3.3); G1 was greater (22.6, s 3.4) than G2(21.0, s 3.0), p< 0.001. Mean maximum RR was 38.5(s 14.6); G1 was greater (40.5, s 13.2). than G2(36.5, s 15.6), p< 0.001. In-hospital mortality occurred in 29.6%. G1 was greater (38.5%) than G2 (20.7%); p< 0.001
Conclusion: Comorbidity burden was similar between grps. Although more G2 pts had CLD, G1 pts had worse respiratory outcomes including greater RR, longer HSL, greater IMV and NIV, and overall greater mortality. Our study suggests that BA DMARD exposure may predispose to worse respiratory outcomes and survival outcomes in pts hospitalized with C19 and this subset of pts may require closer monitoring when hospitalized.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Akpoviroro O, Sausers N, Akpoviroro O, Uwandu Q, Castagne M, Rodrigues E, Khoalone L, Humayun s, Woodard J. Association Between COVID-19 and Disease-Modifying Antirheumatic Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2023; 75 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-covid-19-and-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2023
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-covid-19-and-disease-modifying-antirheumatic-drugs/