Session Information
Date: Monday, November 8, 2021
Title: Abstracts: RA – Treatments II: New Findings in Established Therapies (1442–1445)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:45PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) are at a potentially increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, and immunosuppressive or biologic drugs used to treat RA might also be associated with a higher risk of infection or worse COVID-19 outcomes. Limited data to date suggest rituximab is associated with worse COVID-19 outcomes. The objective of our study was to evaluate the association between baseline use of rituximab and COVID-19 outcomes among patients with RA using a nationally representative sample of patients.
Methods: Our study sample included patients in the National COVID Cohort Collaborative (N3C), a centralized, harmonized, high-granularity electronic health record repository that is the largest, most representative U.S. cohort of COVID-19 cases and controls to date. N3C includes patient encounters from January 1, 2018 to provide information about pre-existing health conditions. We identified patients with RA who had two or more International Classification of Diseases (ICD)-10 codes for RA (M05.X or M06.X), and in sensitivity analyses we defined RA as having one or more than one RA-specific ICD-10 code (a more sensitive, less specific definition). We identified baseline use of DMARDs using the medication tables. Our primary outcomes were: SARS-CoV-2 infection, defined as COVID-19–positive polymerase chain reaction or antigen test, or an ICD-10-CM diagnostic code; and for those with COVID-19 diagnosis, hospitalization, invasive ventilation, and 30-day mortality. Multivariable logistic regression models assessed the association of rituximab use with the odds of COVID-19 and associated outcomes compared with the use of conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs) as the referent category. Analyses were adjusted for demographics, medical comorbidities, smoking status, US region, and body mass index (BMI).
Results: A total of 57,725 patients met our eligibility criteria of which 16,342 were SARS-CoV-2 positive during the study period. Mean (±SD) age of the cohort was 62 (±14.6) years, 75% females, 68% White and 76% were non-smokers (Table 1). 1477 (2.6%) patients were exposed to rituximab prior to their first positive COVID-19 test. Pulmonary disease was seen in 40% of the cohort. In multivariable-adjusted models, compared to the use of csDMARDs, baseline rituximab use was associated with increased odds of hospitalization among those who were diagnosed with COVID-19 (adjusted odds ratio, aOR 2.0, 95% CI 1.3-3), and invasive ventilation (aOR 2.6, 95% CI 1.13-5.7) (Table 2). No DMARD use was also associated with significantly higher odds of hospitalization among those who were diagnosed with COVID-19. Results were similar in sensitivity analyses where RA cohort was defined based on the presence of at least one ICD-10 code for RA (n=80,063).
Conclusion: We leveraged data from a large national repository to study the association between baseline use of DMARDs and various COVID-19 outcomes. Compared to csDMARD use, rituximab use in patients with RA was associated with higher odds of COVID-19 hospitalizations and invasive ventilation. These results stress the need of prioritizing COVID-19 vaccination for RA patients.
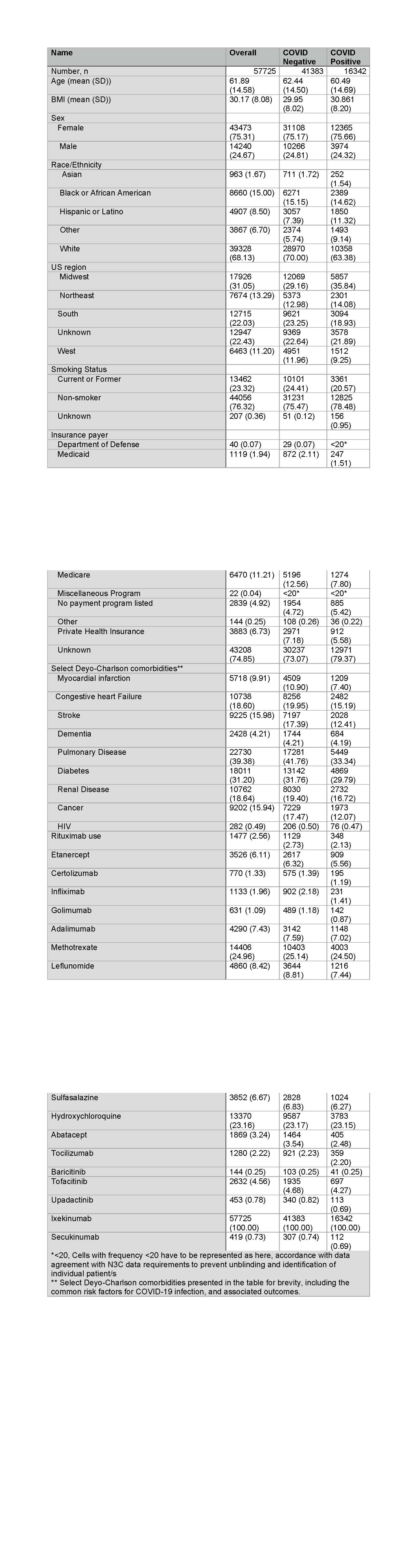 Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the cohort
Table 1. Baseline characteristics of the cohort
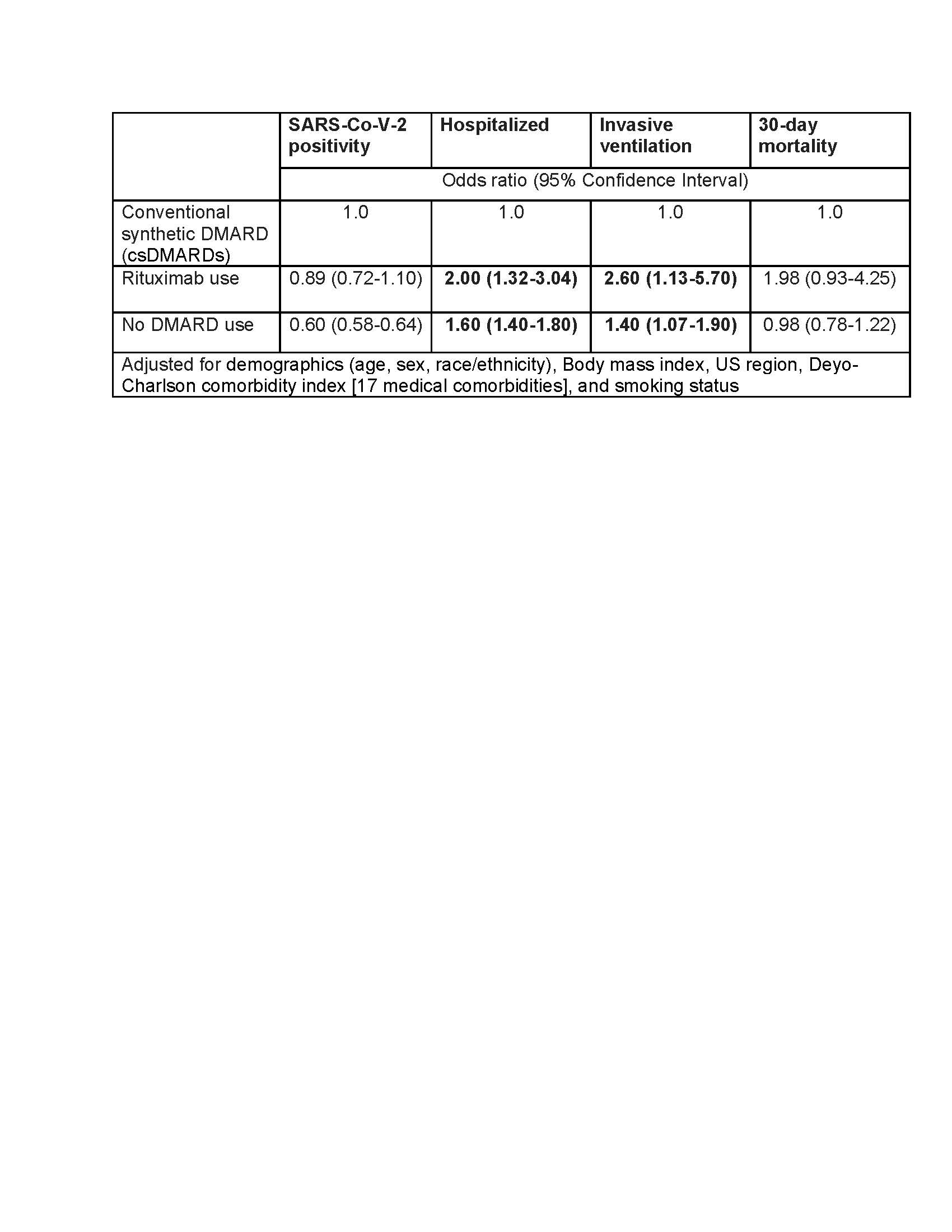 Table 2. Multivariable-adjusted association of Rituximab and no DMARD use with COVID_19 and COVID_19 outcomes
Table 2. Multivariable-adjusted association of Rituximab and no DMARD use with COVID_19 and COVID_19 outcomes
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Singh N, Hu C, Madhira V, Fitzgerald K, Bergquist T, Anderson K, Olex A, Patel R, Singh J. Association Between Baseline Use of Rituximab and COVID-19 Outcomes in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-baseline-use-of-rituximab-and-covid-19-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/association-between-baseline-use-of-rituximab-and-covid-19-outcomes-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-ra/
