Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The available data on the impact of JAK inhibitors (JAKi) on rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD) are currently limited. This study aimed to examine the benefit/risk balance of JAKi in RA-ILD in France.
Methods: A prospective national multicenter observational study was conducted, identifying patients with RA-ILD from the MAJIK-SFR registry, which includes adult patients initiating JAKi. Pulmonary assessment data were specifically collected from centers with at least one RA-ILD patient on JAKi, using a dedicated form. Data were gathered at JAKi initiation and follow-up visits (6, 12, and an average of 21 months post-inclusion), including chest high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT), pulmonary function tests (FVC and DLCO), acute exacerbations of ILD, respiratory infections, and lung cancers.
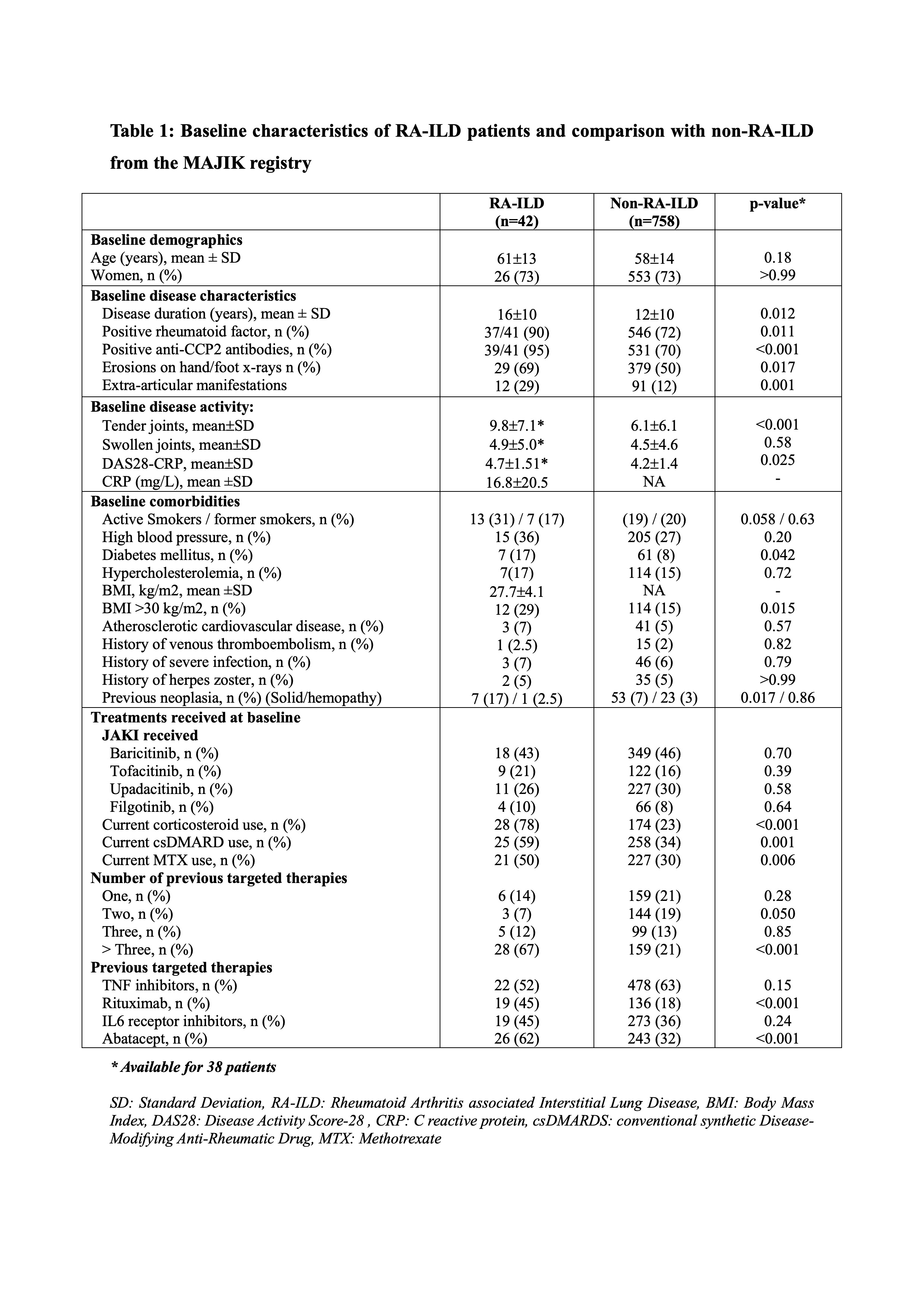
Results: We enrolled 42 patients (26 women, 62%) with RA-ILD initiating JAKi, with a mean age of 61±12 and a mean disease duration of 16±10 years (Table 1). Compared to the 778 RA patients without ILD from the MAJIK registry for whom data were consolidated, RA-ILD patients were older, more immunopositive, displayed more severe and active disease, had more prevalent comorbidities, were more frequently treated with corticosteroids and csDMARDs in combination with the JAKi, and have received more likely rituximab and abatacept as previous therapies (Table 1).
The mean duration of ILD was 4±2 years. At baseline, 17/36 patients (47%) presented with dyspnea, 10/37 patients (27%) with cough and 2 patients (5%) were on long-term oxygen therapy. Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP) and usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) accounted for 46% and 43% of the chest HRCT ILD patterns, respectively.
No significant changes in FVC and DLCO during follow-up were observed (FVC (L)/LDCO (%): 3.20 L/65% at inclusion; 3.12 L/63% at 12 months follow-up and 3.03 L/60% at end of follow-up). Chest HRCT lesions remained stable in 62% of patients. Regression of chest HRCT lesions was observed in 3 patients associated with an improvement >5% in the initial FVC value at the last assessment. Progressive ILD was identified during follow-up in 8 patients (19%), defined by a progressive worsening of FVC by >5% during follow-up and worsening of ILD lesions on chest HRCT or of their respiratory symptoms. Cox proportional hazards analyses identified higher age at diagnosis of ILD, active smoking extra-articular involvement and lower baseline DLCO as predictive factors for progression of RA-ILD. From articular perspective, a significant decrease in DAS28-CRP was observed at 6 months (-1.30 points, p< 0.001) and 12 months (-1.35 points, p< 0.001).
With regard to tolerance, 5 infectious pneumonia and one pulmonary tuberculosis were observed. Only one acute regressive exacerbation of ILD was noted. No lung cancer, MACE, VTE or death occurred during the 21-month follow-up period. JAKi were discontinued in 17 patients: 8 for joint inefficacy, 4 for intolerance, and none were related to ILD progression.
Conclusion: The analysis indicates a stability of RA-ILD upon JAKi together with notable joint efficacy. JAKi had an expected tolerance profile without new safety signal in a higher risk population.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Triboulet F, Juge P, Truchetet M, Pham T, Roux n, Flipo R, Leske C, roux c, Seror R, Basch A, BROCQ O, Chazerain P, Coury-Lucas F, Damade R, Dernis E, Gottenberg J, Ramon A, Ruyssen-Witrand A, Salmon J, Shipley E, Tournadre A, PRATI C, Dieudé P, Avouac J. Assessment of Interstitial Lung Disease in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Treated with JAK Inhibitors: A National Multicenter Observational Study from the MAJIK-SFR Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-jak-inhibitors-a-national-multicenter-observational-study-from-the-majik-sfr-registry/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-interstitial-lung-disease-in-rheumatoid-arthritis-patients-treated-with-jak-inhibitors-a-national-multicenter-observational-study-from-the-majik-sfr-registry/