Session Information
Date: Monday, November 9, 2020
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Axial spondyloarthritis (ax-SpA) corresponds to a group of chronic inflammatory disease mainly affecting the axial skeleton. TNF and IL-17A have been identified as key inflammatory mediators driving the inflammatory process of ax-SpA. Epigenetics refers to different mechanisms that alter gene expression without involving changes in DNA sequence. The mechanisms of epigenetics include microRNA, histone modifications or DNA methylation. DNA methylation is associated with a repressed chromatin state and inhibition of gene expression. It is recognized that aberrant DNA methylation can result in immune cell autoreactivity. Epigenetics have been rarely evaluated in ax-SpA. We previoulsy reported that patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) had an imbalance between HAT and HDAC activities (Toussirot E et al, PlosOne 2013). In this study, we aimed to evaluate the global DNA methylation of patients with ax-SpA.
Methods: Case-control study (NCT03092583). Patients with radiographic (AS) or non radiographic (nr) ax-SpA (ASAS criteria) and healthy controls (HC) were evaluated. All the patients were biologic naïve and under NSAIDs. Disease activity was evaluated by BASDAI and ASDAS. CD4+T cells and CD14+ monocytes were isolated form peripheral blood and then DNA was extracted (E.Z.N.A. Blood DNA kit, Omega Bio-Tek). Global DNA methylation (5-mC) was determined using MethylAmp global DNA methylation quantification kit (Epigentek) using 150ng of total DNA.
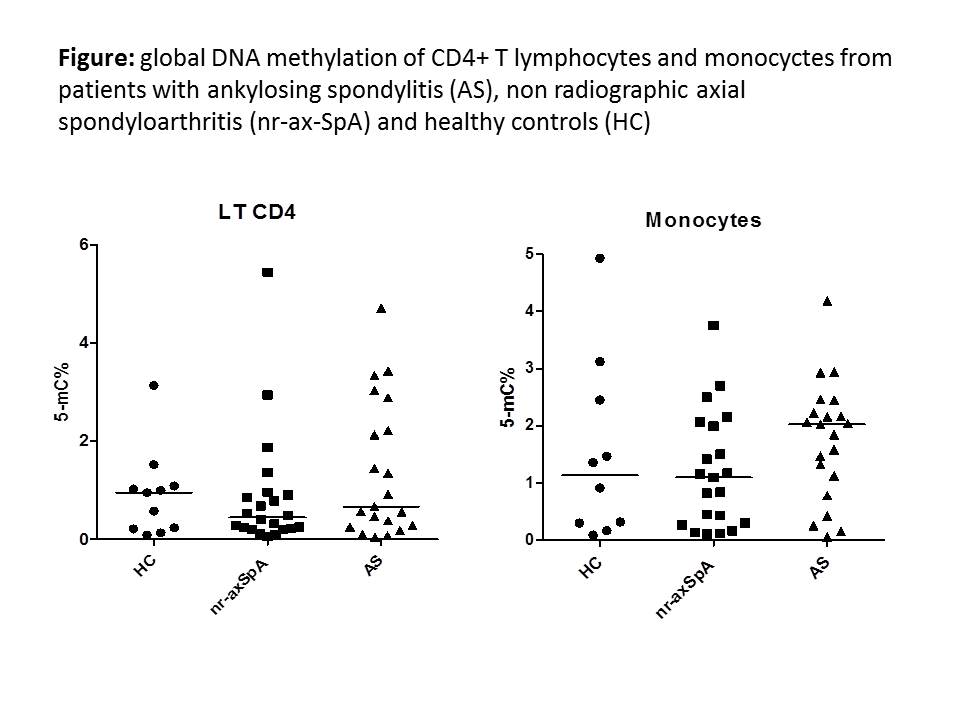
Results: 25 patients with AS (18 M; mean age ± SEM: 48.9 ± 3.5 y; mean disease duration: 14.9 ± 2.2 y; B27+: 84%), 21 with nr-axSpA (11 M; age: 42 ± 3.3 y; disease duration: 7.9 ± 2.3 y; B27+: 68%) and 11 HC (7 M; age: 48.4 ± 3.9 y) were evaluated. Patients had active disease (BASDAI and ASDAS in AS and nr-axSpA: 5.1 ± 0.4 and 5.4 ± 0.5; 4.7 ± 0.4 and 5 ± 0.4, respectively). In CD4+ T lymphocytes, global DNA methylation was lower in the whole group of patients (AS and nr-ax-SpA) compared to HC (0.91 ± 0.26 vs 1.08 ± 0.19 % of 5-mC) (NS). Conversely, DNA methylation was higher in monocytes from patients compared to HC (1.43 ± 0.16 vs 1.15 ± 0.5 % of 5-mC) (NS). When analysing the results between ax-SpA subgroups, an hypomethylation was more evident in the CD4+T lymphocytes from patients with nr-axSpA compared to AS and HC, a result that was not observed in the monocyte subpopulation (Figure).
Conclusion: A global DNA hypomethylation is observed in patients with ax-SpA, especially in the nr-axSpA subgroup. These results were more evident in T CD4+ lymphocytes. Additional analysis on a larger series of patients is required to confirm these preliminary results. In addition, we aim to examine the specific DNA methylation status of the TNF promoter gene.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Toussirot E, Pasquereau S, Vauchy C, Nehme Z, Wendling D, Balbalnc J, Laheurte C, Puyraveau M, Herbein G. Assessment of Global DNA Methylation in Peripheral Blood Cell Subpopulations of Patients with Axial Spondyloarthritis : Preliminary Results [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020; 72 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-global-dna-methylation-in-peripheral-blood-cell-subpopulations-of-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-preliminary-results/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2020
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-global-dna-methylation-in-peripheral-blood-cell-subpopulations-of-patients-with-axial-spondyloarthritis-preliminary-results/