Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 10, 2019
Title: 3S112: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders I: Miscellaneous Disorders (945–950)
Session Type: ACR Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
Background/Purpose: Behcet’s disease(BD) is a uniqe systemic vasculitis mainly involving venous vessels in contrast to other systemic vasculitides. Diagnosing BD is a challenge, especially in countries with a low prevalence. International Study Group Criteria, accepted to as diagnostic, has low sensitivity, especially in early cases when major organ involvement such as uveitis or deep vein thrombosis(DVT) presents alone. Pathergy (skin prick) test, the only specific diagnostic tool, has quite a low positivity. We recently published a controlled study of assessing venous wall thickness(VWT) as a surrogate marker of venous disease in BD with doppler ultrasound (US) and observed a very sensitive and specific VWT in male BD patients. The common femoral vein(CFV) thickness measurement, as the primary site of US with the cut‐off values > 0.48‐0.49 mm, had a high area under the receiver operating characteristic curve( >0.8) with sensitivity and specificity of around 80% (1). In this study, we aimed to investigate the diagnostic performance of CVF thickness measurement in BD including females comparing with multiple control disease groups.
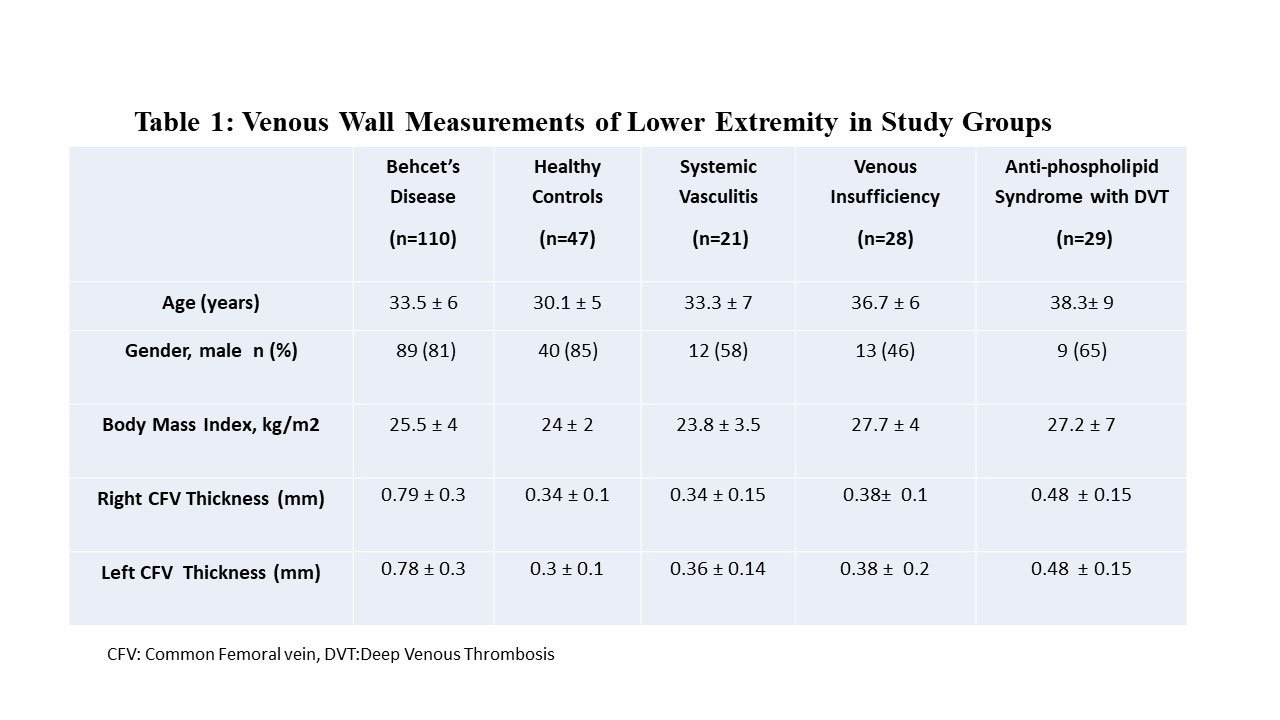
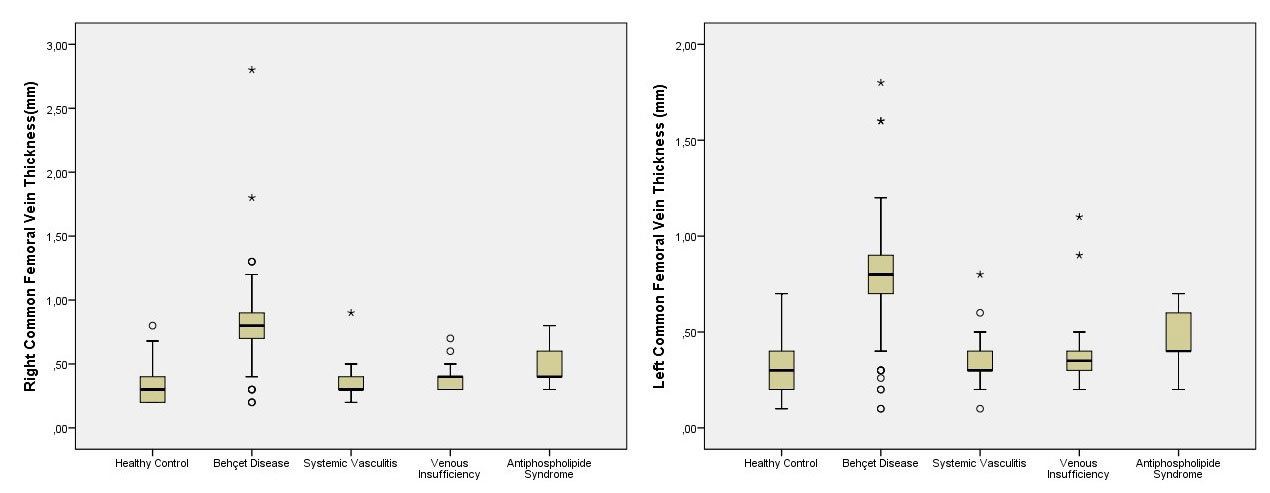
Methods: One hundred-ten patients with BD, 47 healthy controls (HC), 21 patients with systemic vasculitides, 28 patients with venous insufficiency, 29 patients with antiphospholipid syndrome(APS) having DVT history, were included the study. Behcet’s Syndrome Activity Score(BSAS) was used to assess disease activity. Bilateral CFV thickness was measured with US by an experienced radiologist blinded to cases(Figure 1).
Results: Bilateral CFV thickness was significantly higher in BD compared to all comparative groups (p< 0.001 for all)(Table 1 and Figure 2). No correlations were present between CFV thickness and both BSAS and CRP levels (p >0.05 for all). In only 2 (8%) patients with venous insufficiency and 2 (10%) patients with systemic vasculitis, bilateral CVF thickness was higher than the cut- off values. Interestingly, APS was the only control group with positivity, in 12 (41%) patients with APS, bilateral CFV thickness was higher than the cut-offs. There was no difference between male vs female BD patients regarding CVF thickness (right CFV:0.78±0.3 mm vs 0.79±0.1 mm,p=0.96, left CFV:0.78±0.3 vs 0.81±0.1, p=0.80). Although a higher CVF thickness tendency was observed in VBD, no statistically significant difference was present between BD patients with (n=40) and without (n=58) vascular involvement (right CFV:0.82±0.3 mm vs 0.75±0.3 mm, p=0.122, left CFV:0.84 ± 0.3 vs 0.76±0.3, p=0.165).
Conclusion: Increased CFV thickness is present in BD patients, independent of vascular involvement. We also found that CFV thickness is a distinctive feature of BD, rarely present in other inflammatory/vascular diseases such as ankylosing spondylitis (previously shown), systemic vasculitides and venous insufficiency (except APS with DVT). CFV thicknesses are easily and reliably measured by Doppler US. We, therefore, suggest that assessment of CFV can be a diagnostic tool for Behcet’s disease with a good sensitivity and specificity to differentiate BD from similar disorders.
(1): Alibaz-Oner et al. Clinical Rheumatology (2019) 38:1447–51.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Alibaz-Oner F, ERGELEN R, YILDIZ Y, Yazici A, MUTIS A, ERTURK Z, ALDAG M, Cefle A, Artim-Esen B, MUMCU G, ERGUN T, Direskeneli H. Assessment of Femoral Vein Wall Thickness with Doppler Ultrasound Can Be a Diagnostic Tool for Behcet’s Disease [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-femoral-vein-wall-thickness-with-doppler-ultrasound-can-be-a-diagnostic-tool-for-behcets-disease/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/assessment-of-femoral-vein-wall-thickness-with-doppler-ultrasound-can-be-a-diagnostic-tool-for-behcets-disease/