Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In patients with ankylosing spondylitis, the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) is used to measure disease activity to initiate or maintain TNF inhibitor therapy. However, despite a low disease activity measured by BASDAI, some patients complain of pain or are found in high inflammatory status. In such cases, other disease activity measurement tools such as the Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score (ASDAS) may be recommended. The aim of this study was to identify patients with advanced AS who show high disease activity with ASDAS and require active treatment despite low BASDAI.
Methods: In a single center cohort, 1,240 patients with AS were followed up to 18 years. The BASDAI, ASDAS, and modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score (mSASSS) were obtained from electronic medical records. The mSASSS was measured almost every 2 years. We used the interpolation method to estimate the mSASSS at the time point when the BASDAI or ASDAS was measured. High disease activity was defined as BASDAI ≥ 4 or ASDAS ≥ 2.1 and low disease activity as BASDAI < 4 or ASDAS < 2.1 at each disease activity measurement. Changes in the distribution of high and low disease activities were investigated by assessing TNF inhibitor use and mSASSS.
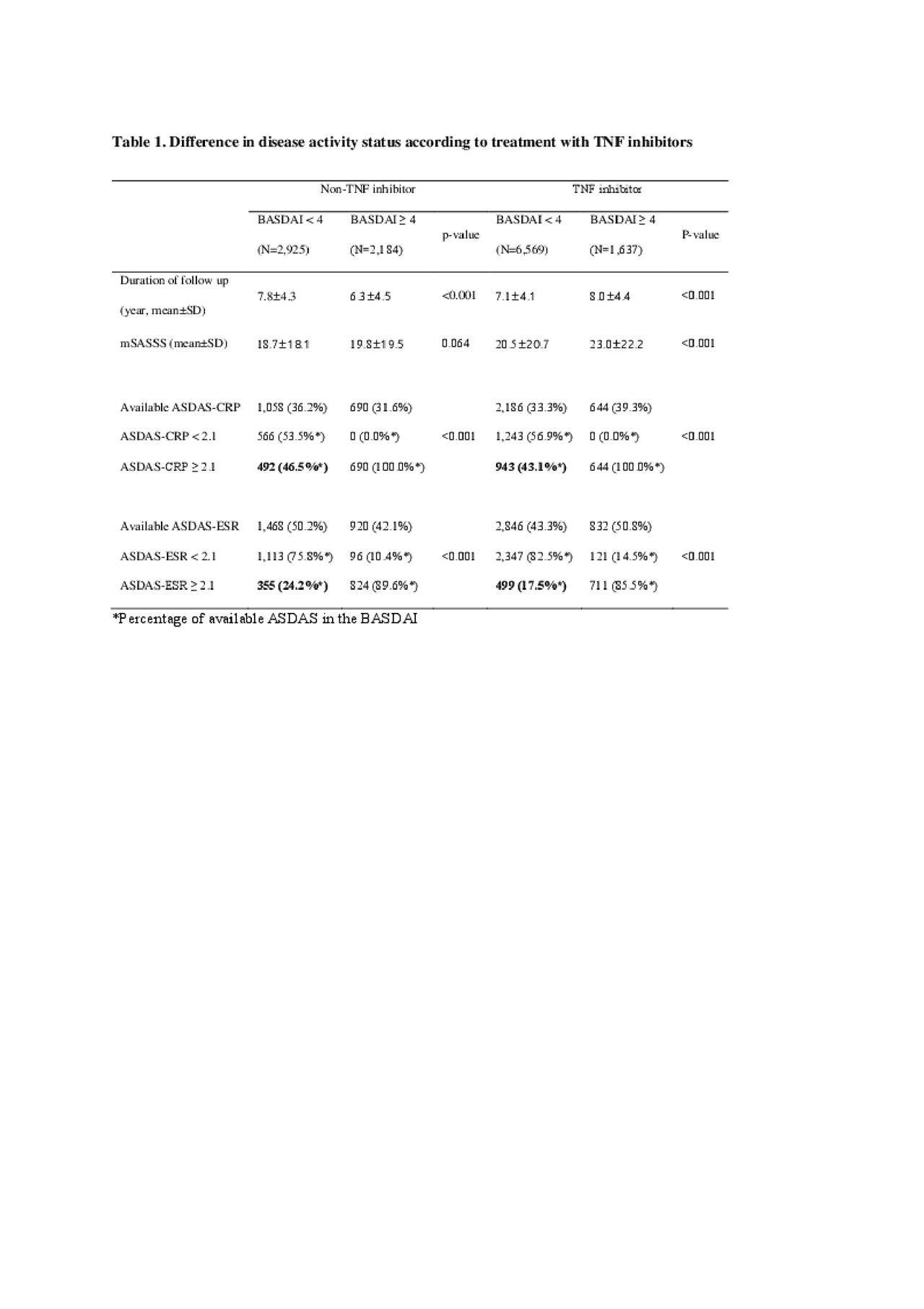
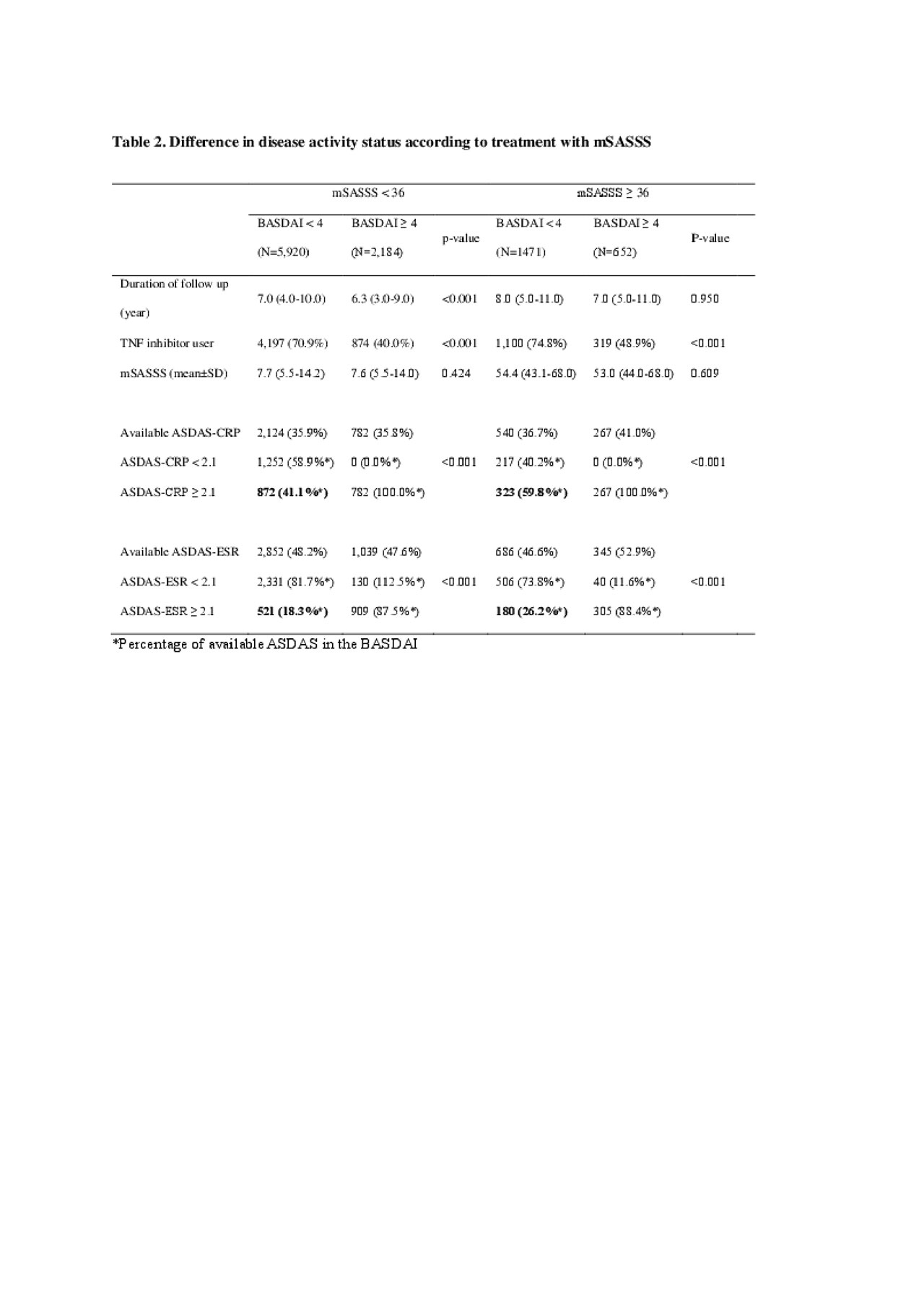
Results: A total of 13,315 BASDAI, 4,578 ASDAS-CRP, and 6,066 ASDAS-ESR measurements were obtained from 1,240 patients. The mean duration from diagnosis of AS to the date of measuring the disease activity was 10.2 ± 3.9 years. Of these measurements, 1,435 (44.2%) had ASDAS-CRP ≥ 2.1 and 3,244 measurements had BASDAI < 4. In the TNF inhibitor group, the percentage of measurements with ASDAS-CRP ≥ 2.1 and BASDAI < 4 was similar to that in the non-TNF inhibitor group (492/1,058, 46.5% vs. 943/2,186, 43.1%) (Table 1). The percentage of measurements with ASDAS-CRP ≥ 2.1 and BASDAI < 4 was elevated in patients with mSASSS ≥ 36 compared to that in patients with mSASSS < 36 (323/540, 59.8% vs. 872/2,124, 41.1%) (Table 2).
Conclusion: Despite treatment with TNF inhibitors, some patients remain with high disease activity measurable by tools other than BASDAI. Moreover, the proportion of patients with high disease activity was high in the advanced radiographic progression group. These patients may need active treatment with therapies other than TNF inhibitors.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jun J, Koo B, Lee S, Kim J, Kang J, Kim T. ASDAS Is More Important Than BASDAI in Advanced Ankylosing Spondylitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/asdas-is-more-important-than-basdai-in-advanced-ankylosing-spondylitis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/asdas-is-more-important-than-basdai-in-advanced-ankylosing-spondylitis/