Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Osteoporosis is a common condition that often goes unnoticed until it results in fractures, significantly increasing morbidity and mortality rates. Recent advancements in deep learning have demonstrated the ability to detect low bone density using simple radiographs, including chest X-rays (CXR). This underscores the urgent need to explore the application of deep learning models for osteoporosis screening in real-world settings.
The initial model, OsPor-Screen(Jang et al. 2022), was validated exclusively using CXRs from the Health screening dataset, which mainly included images from relatively healthy individuals. This limitation restricted its applicability in actual clinical settings. To overcome this, we developed and implemented a robust model specifically for osteoporosis screening in diverse, real-world environments. The new model was validated across various healthcare facilities, representing different stages of the healthcare delivery system and distinct medical settings. Furthermore, we aimed to compare the performance of our model with that of osteoporosis screening using quantitative ultrasound (QUS).
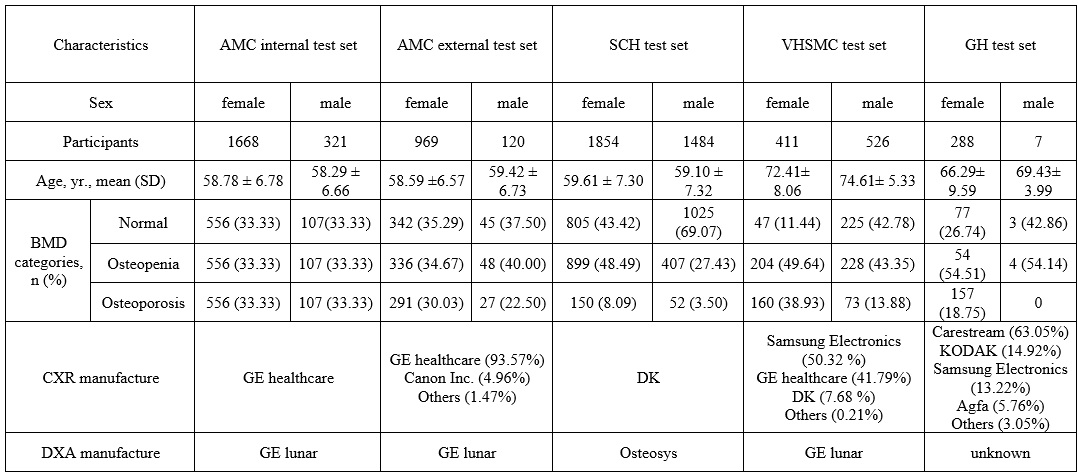
Methods: The CXR:OSTEO was tested with five test datasets. Asan Medical Center (AMC), which is a tertiary hospital, internal test dataset was a part of the training dataset and AMC external dataset was an external dataset from the same hospital. Seoul Chuk Hospital (SCH) specializes in spine and joint care. Veteran Health System Medical Center (VHSMC) provides comprehensive medical and specialized care to veterans and their families. Gradient Health (GH), a leading provider of global medical imaging datasets, offers access to an extensive and diverse collection of 5 million de-identified medical images.
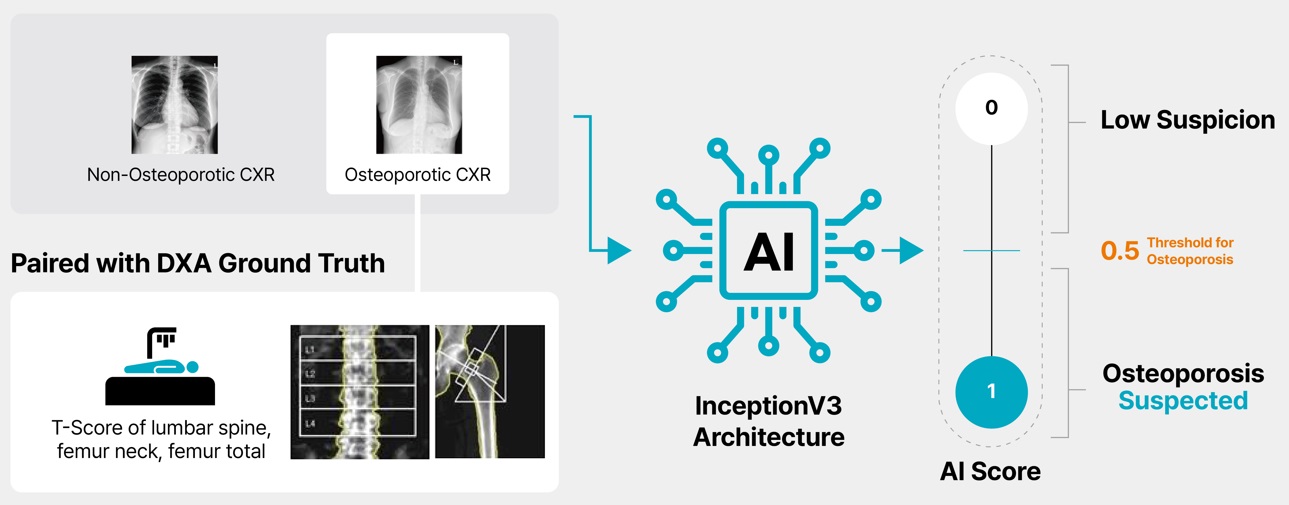
All 5 test datasets comprised paired posteroanterior chest radiographs and Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA) examinations conducted on individuals aged 50 years and older.The Advanced model, CXR:OSTEO goes further than the OsPor-Screen, which predicts osteoporosis in a single CXR image, to predict osteoporosis in multiple regions of a CXR image. To comprehensively evaluate the screening performance for the two validation datasets, the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and area under the ROC curve (AUC) were calculated.
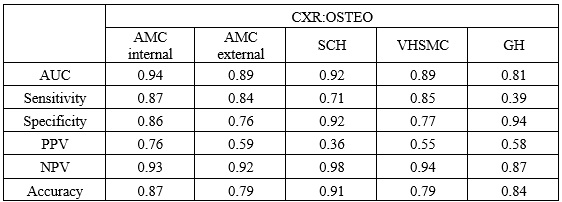
Results: Across more than seven different CXR machines and two different DXA manufacturers in various populations, CXR:OSTEO showed excellent performances in the internal and four external datasets. The AUCs were near and over 0.9 and the result was 0.81 in the global region. For osteoporosis screening guidelines in USPSTF, performance of QUS is 0.77 in women and 0.80 in men.(“Osteoporosis to Prevent Fractures: Screening” 2018) Another study(Adami et al. 2024) also reported that the maximum performance of QUS in a dataset of 200 patients was an AUC of 0.81.
Conclusion: We developed the CXR-OSTEO model to screen for osteoporosis using chest X-rays and validated it with four external test datasets. These results support that screening for osteoporosis using CXR:OTSEO is the most effective method in the real clinical setting.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
jang M, Kim M. Artificial Intelligence Classifier for Osteoporosis Detection from Chest Radiographs: Performance Evaluation and Literature Comparison with Quantitative Ultrasound [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/artificial-intelligence-classifier-for-osteoporosis-detection-from-chest-radiographs-performance-evaluation-and-literature-comparison-with-quantitative-ultrasound/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/artificial-intelligence-classifier-for-osteoporosis-detection-from-chest-radiographs-performance-evaluation-and-literature-comparison-with-quantitative-ultrasound/