Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: As many other rheumatologic diseases, pathogenesis of Polymyalgia Rheumatica (PMR) is
not well understood. Genetic factors seem to play a role. Some studies have suggested a seasonal
variation, indicating a possible infectious trigger; others have shown and association with statins
initiation. Our objective was to compare PMR patients with matched controls in order to identify
possible triggers in the year previous to PMR development.
Methods: PMR patients (fulfilling ACR 2012 criteria) belonging to a Health Management Organization
(HMO) of a tertiary university hospital were matched 1:1 by gender and date of birth with controls
belonging to the same HMO. Date of PMR diagnosis was considered as the index date for patients and
their correspondent control. Electronic medical records were manually reviewed and data on infections,
hospitalizations, surgeries, vaccines and starting of statins in the year previous to the index date were
recorded for both PMR patients and controls and compared between them. For PMR patients, season
where disease symptoms started was also analyzed.
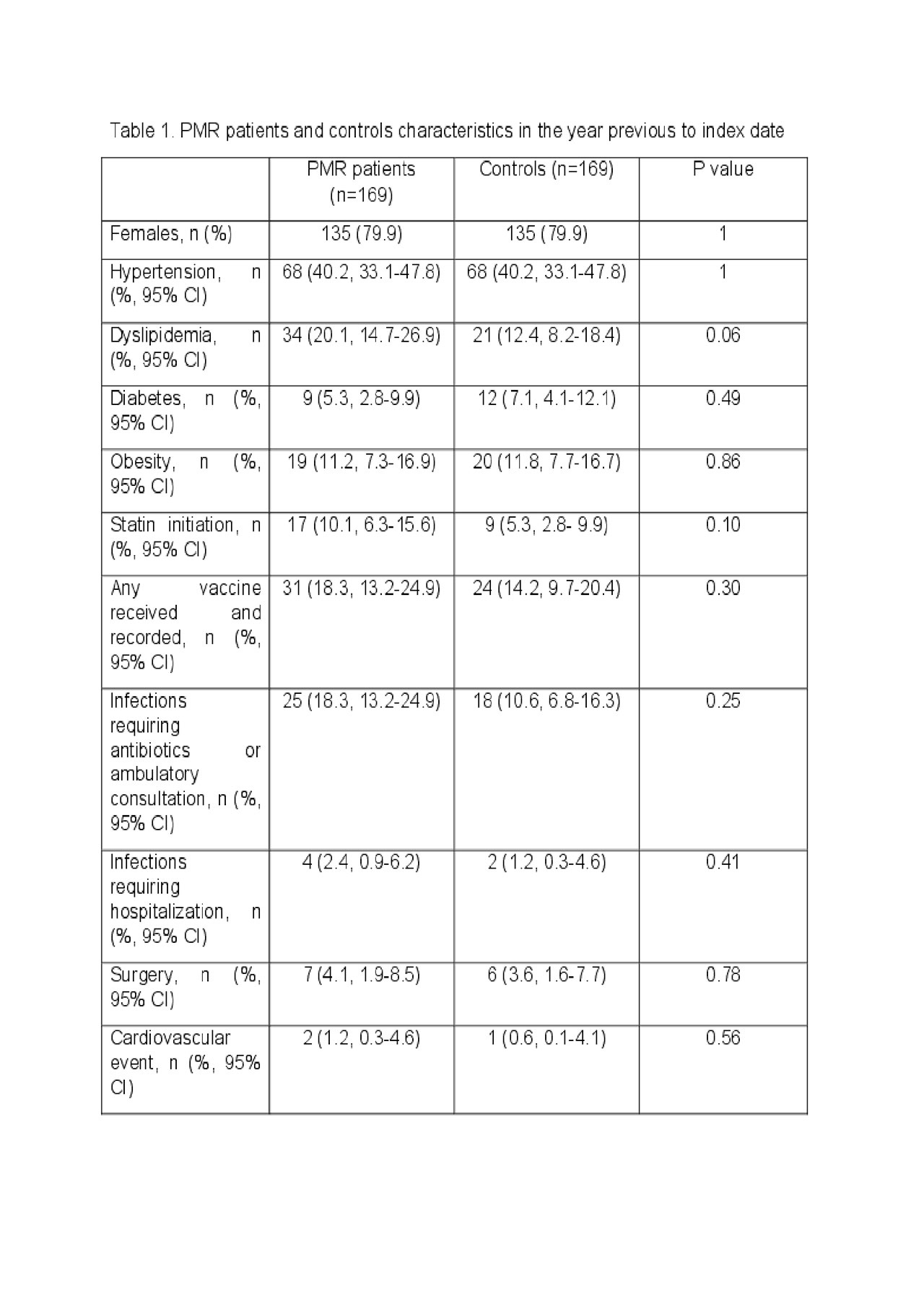
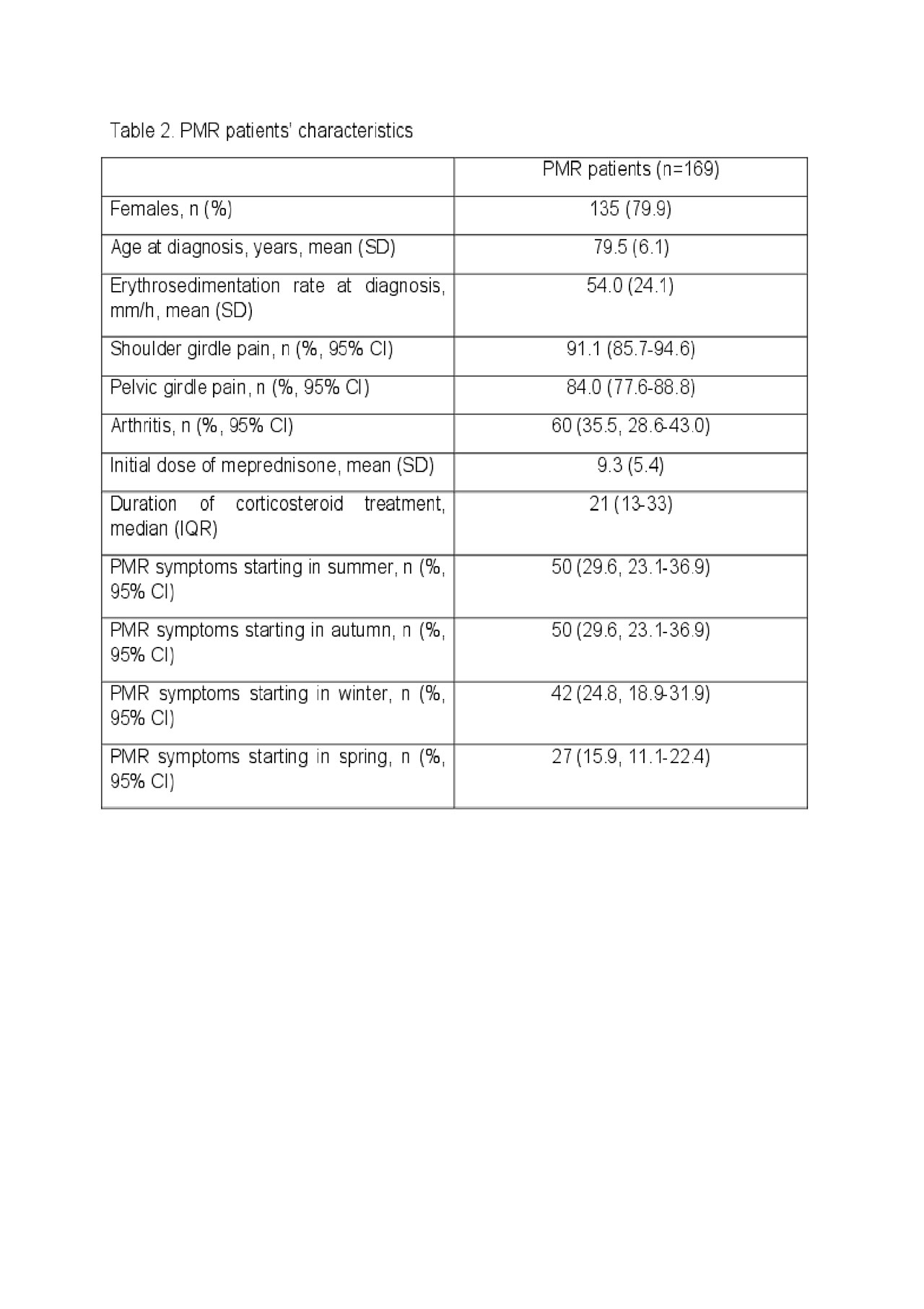
Results: 169 PMR patients and 169 controls were included. 79.9 % were females. Age at PMR diagnosis
was 79.5 years (SD 6.1). No differences were found between PMR patients and controls regarding
infections, hospitalizations, vaccines, surgeries or statin initiation in the year previous to PMR diagnosis
(table 1). PMR symptoms started in summer in 50 patients (29.6%, 95% CI: 23.1-36.9), in autumn in 50
(29.6%, 95% CI: 23.1-36.9), winter in 42 (24.8%, 95% CI: 18.9-31.9) and spring in 27 (15.9%, 95% CI: 11.1-
22.4) (Table 2).
Conclusion: We didn’t find an identifiable trigger for the development of PMR when analyzing the year
previous to diagnosis comparing to matched controls. No seasonal pattern was clearly seen.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Tobar Jaramillo M, Santos Andrade V, Scolnik M, Lo Giudice L, Jaramillo Gallego J, Scaglioni V, Soriano E. Are There Any Identifiable Triggers in Polymyalgia Rheumatica? A Matched-Control Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-there-any-identifiable-triggers-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica-a-matched-control-study/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-there-any-identifiable-triggers-in-polymyalgia-rheumatica-a-matched-control-study/