Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: In view of the continuous pressure of biologicals on healthcare budgets, it is essential to assess the value of biologicals for patients from different perspectives. A Willingness To Pay (WTP) represents the patients’ preference for health as a consequence of treatment in monetary terms. The aim of this study was to investigate WTP for treatment with infliximab by patients with ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and explore factors associated with WTP.
Methods: Data were used from patients participating in the European AS Infliximab Cohort (EASIC) open-label extension of the AS Study for the Evaluation of Recombinant Infliximab Therapy (ASSERT). Demographics, clinical data (including BASDAI, BASFI, BASMI, BAS-G and Assessment of SpondyloArthritis International Society 20 (ASAS20) response) and data on WTP were collected at baseline of EASIC. WTP comprised a hypothetical scenario exploring whether the patient would be willing to pay for beneficial effects of infliximab and, if so, what amount they would be willing to pay per administration. To investigate factors associated with WTP, a series of models were explored using a zero inflated negative binomial regression (ZINB) technique.
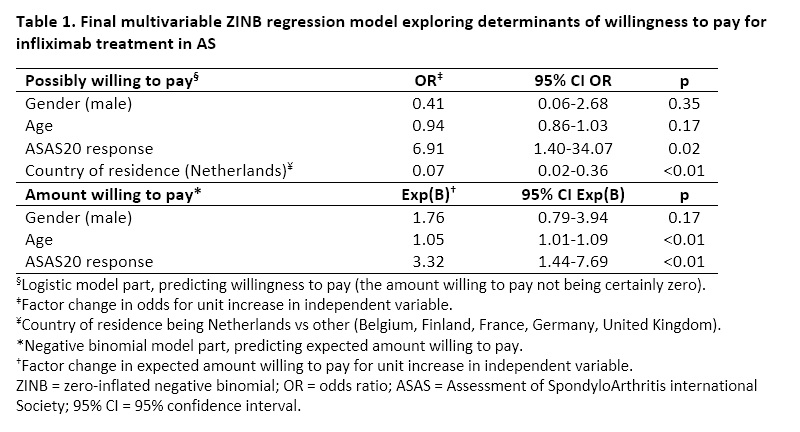
Results: Eighty-five patients completed the WTP. Average age was 43.4 years, 67 patients (78.8%) were male and 62 patients (72.9%) had achieved an ASAS20 response. Sixty-three patients (74.1%) were willing to pay, and among these patients the mean (median) [Interquartile Range] amount willing to pay was €275 (100) [50-200] per administration. Multivariable ZINB analysis showed that ASAS20 response was associated with a 7-fold increase in the likelihood to be willing to pay (OR=6.91, 95%-confidence interval [95%CI] 1.40-34.07) and a 3-fold increase in the amount willing to pay (exp(B)=3.32, 95%CI 1.44-7.69). In addition, country of residence was associated with willingness to pay (residence in the Netherlands vs. other participating countries: OR=0.07, 95% CI 0.02-0.36), while increased age was associated with the amount willing to pay (exp(B)=1.05, 95%CI 1.01-1.09).
Conclusion: In a hypothetical scenario, three quarter of patients with AS stated to be willing to pay an out-of-pocket contribution for treatment with infliximab. Treatment response contributed to the willingness as well as to the amount patients were willing to pay. Despite its limitations, the WTP method seems a valuable addition to the common approaches used for investigating treatment benefits in AS.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Webers C, Essers I, van Tubergen A, Braun J, Heldmann F, Baraliakos X, Boonen A. Are Patients with Ankylosing Spondylitis Willing to Pay for Treatment with Infliximab? [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-willing-to-pay-for-treatment-with-infliximab/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/are-patients-with-ankylosing-spondylitis-willing-to-pay-for-treatment-with-infliximab/