Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 1:00PM-2:30PM
Background/Purpose: Apremilast is an oral phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitor with a unique immunomodulatory mechanism of action and is approved for the treatment of psoriatic arthritis (PsA). Although peripheral arthritis is the most frequent clinical feature in patients with PsA, axial involvement may occur in up to 50% of patients, causing inflammatory back pain, stiffness, and changes on imaging. Here, we used whole-body magnetic resonance imaging (WB-MRI) to evaluate the efficacy of apremilast 30 mg twice daily on axial inflammation in patients with PsA.
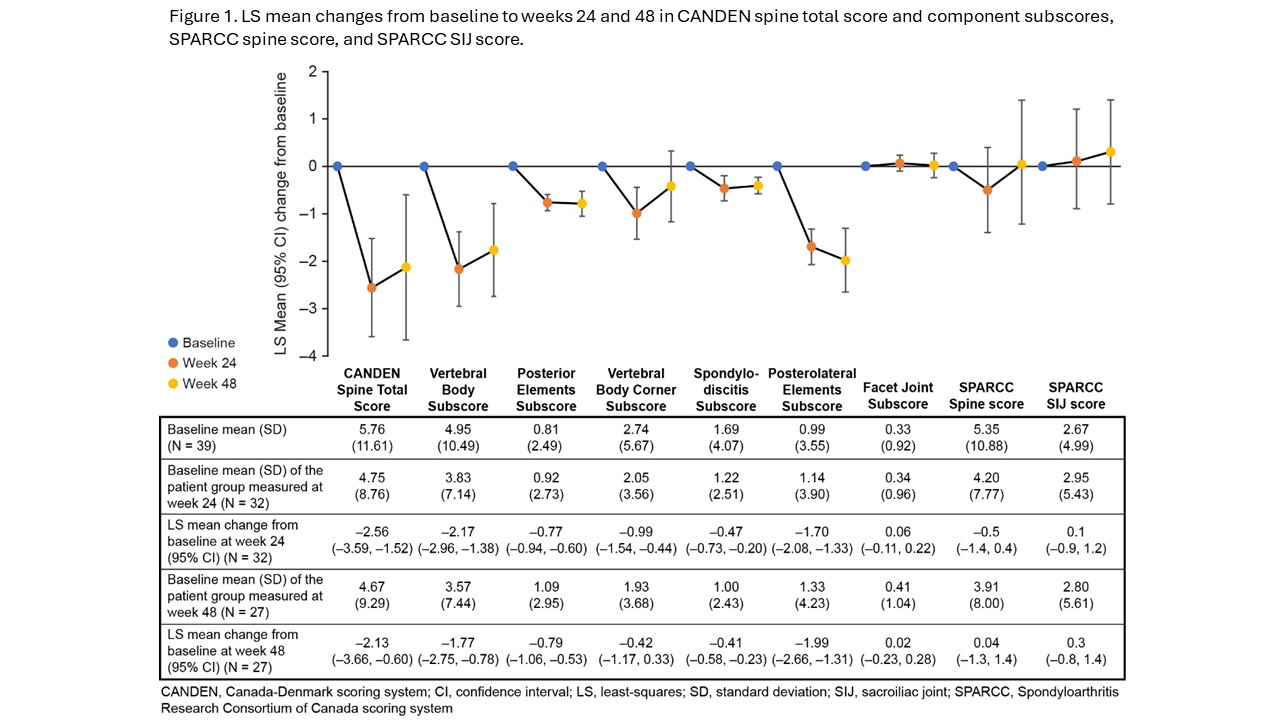
Methods: MOSAIC (NCT03783026) was a phase 4, single-arm, open-label trial that evaluated apremilast treatment (with or without stable methotrexate) in patients with active PsA (per Classification Criteria for Psoriatic Arthritis [CASPAR]) for up to 48 weeks. Contrast-enhanced WB-MRI was performed at baseline, week 24, and week 48, and images were evaluated and adjudicated by two experienced readers blinded to time point and response to apremilast. In patients deemed to have PsA spondylitis by the investigator and a baseline Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI) Item 2 (back pain) ≥4, MRI axial inflammation was assessed by calculating the least squares mean change from baseline to weeks 24 and 48 in the Canada-Denmark (CANDEN) total spine inflammation score and subscores (assessing individual anatomical locations including posterolateral elements), the Spondyloarthritis Research Consortium of Canada (SPARCC) spine score, and the SPARCC sacroiliac joint (SIJ) inflammation score.
Results: Overall, 122 patients were treated with apremilast. At baseline, the mean age was 47 years, 55% were women, mean PsA duration was 1.9 years, mean CANDEN spine score was 5.8, mean SPARCC spine score was 5.4, and mean SPARCC SIJ inflammation score was 2.7. Of 40 patients deemed to have PsA spondylitis by the investigator and a BASDAI Item 2 ≥4, 39 patients were analyzed for axial inflammation. At weeks 24 and 48, CANDEN total spine inflammation score, vertebral body, posterior elements, corner, non-corner, and posterolateral elements inflammation subscores were significantly reduced with apremilast relative to baseline. No significant change in facet joint inflammation subscore, SPARCC spine, or SPARCC SIJ scores were observed (Figure 1).
Conclusion: In patients with early PsA, apremilast reduced axial inflammation as assessed by the CANDEN MRI scoring system, which provides a comprehensive and detailed anatomy-based quantification of inflammatory changes in the spine. Apremilast significantly reduced inflammation in both vertebral bodies and posterolateral elements of the spine after 24 and 48 weeks of treatment.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ostergaard M, Maksymowych W, Lambert R, Boesen M, Valenzuela G, Bubb M, Kubassova O, Baraliakos X, Selmi C, Colgan S, Klyachkin Y, Deignan C, Zhou Z, Mease P. Apremilast Reduces Axial Inflammation in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis as Assessed by CANDEN MRI Scoring: Results from a Phase 4 Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-reduces-axial-inflammation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-as-assessed-by-canden-mri-scoring-results-from-a-phase-4-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-reduces-axial-inflammation-in-patients-with-psoriatic-arthritis-as-assessed-by-canden-mri-scoring-results-from-a-phase-4-study/