Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Monday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Oral and/or genital aphthous ulcers are the most common symptoms of Behçet´s disease (BD), and are often refractory to conventional treatment. The inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-4 apremilast (APR) has demonstrated efficacy in the treatment of this manifestations. Our aim was to compare the efficacy and safety of APR in monotherapy or combined with disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs (DMARDs) in BD patients with oral and/or genital ulcers refractory to conventional treatment.
Methods: National multicenter open-label study on 51 BD patients treated with APR at maintained standard dose of 30 mg twice daily. The main outcome was achievement of oral and/or genital ulcers remission.
Results: We included 51 patients (35 women/16 men), mean age of 47.7±13.2 years. Before APR, all patients had received several systemic conventional drugs. The main clinical symptoms for starting APR were oral (n=19) and genital (n=2) aphthous ulcers or both (n=30). Other manifestations present at APR onset were: arthralgia/arthritis (n=16), folliculitis/pseudofolliculitis (n=14), asthenia (n=7), erythema nodosum (n=3), furunculosis (n=2), paradoxical psoriasis by TNFi (n=2), ileitis (n=2), deep venous thrombosis (n=2), erythematosus and scaly skin lesions (n=1), fever (n=1), eating disorder (n=1), fibromyalgia (n=1), unilateral anterior uveitis (n=1) and neurobehçet (n=1).
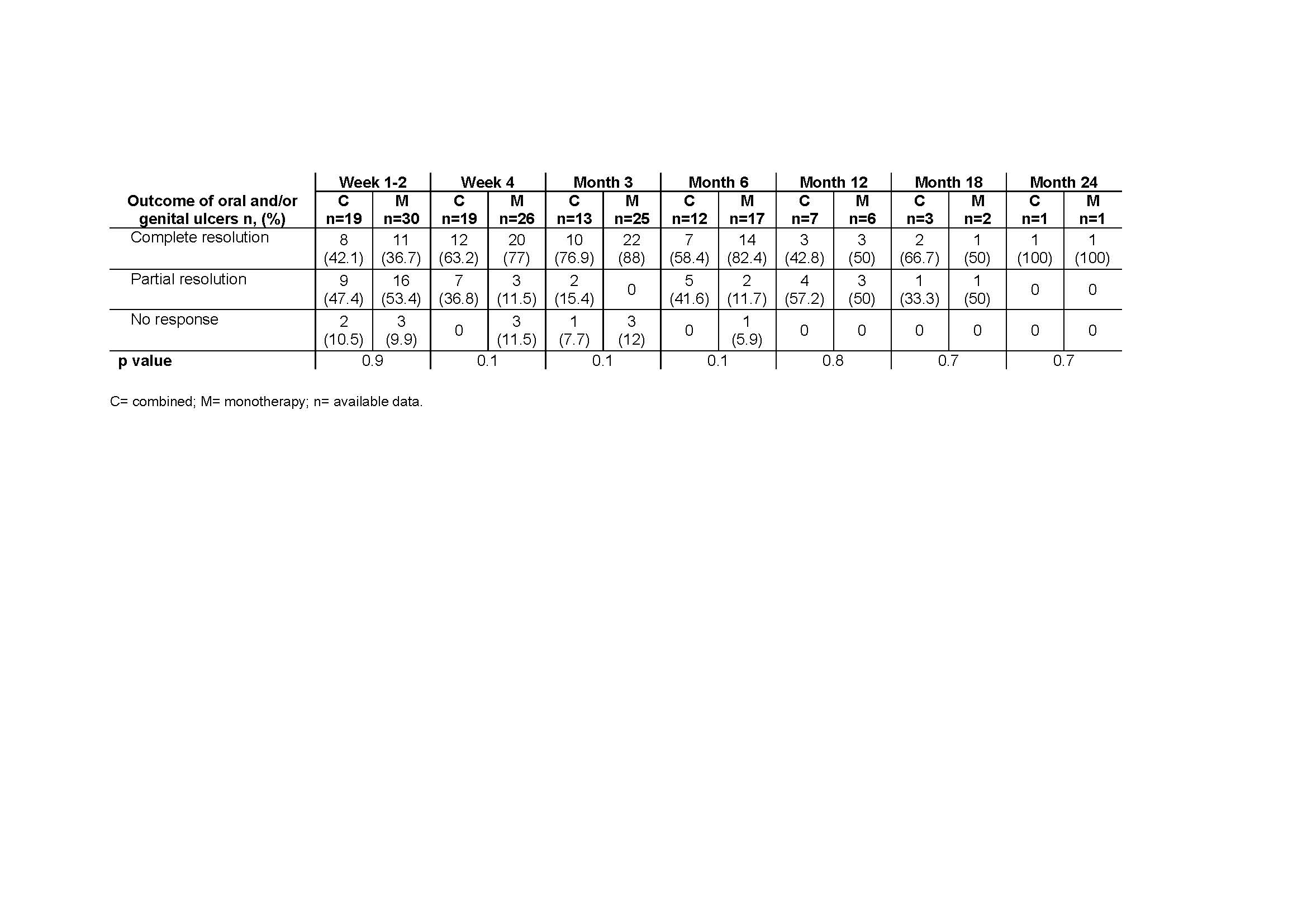
Excluding corticosteroids, colchicine or NSAIDs, APR was given in monotherapy in 31 cases or combined with conventional or biologic DMARDs in 20. There were not found statistically significant differences in baseline characteristics or sides effects, neither in previous treatment, except for tocilizumab that was more frequent in the combined group. The main demographic and clinical features are shown in TABLE 1.
After a mean follow-up of 8.45±6.9 months, most of the patients experienced clinical improvement in both groups, without statistically significant differences. TABLE shows the evolution of the mucocutaneus manifestations in each group, combined vs monotherapy. In this period of time, 33 patients developed any side-effect (TABLE 1), 11 (55%) patients in the combined group and 22 (70%) patients in the monotherapy group), most of them mild and during the first 3 months of treatment.
Apremilast was discontinued in 11 patients due to: not obtaining the expected improvement (5), intense gastrointestinal adverse effects (n=4), desire of pregnancy (n=1) and development of neurological involvement (n=1).
Conclusion: Apremilast leads to a rapid and maintained improvement in many patients with highly refractory mucocutaneous ulcers of BD. This therapy seems as effective and safe in monotherapy as in combination with DMARDs.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Atienza-Mateo B, Calderón-Goercke M, PRIETO- PENA D, Gonzalez-Mazon I, Sanchez-Bilbao L, Martín-Varillas J, Loricera J, Calvo Río V, Graña J, Espinosa G, Moriano C, Pérez-Sandoval T, Martín-Martínez M, Díez E, García-Armario M, Martínez E, Castellvi I, Moya Alvarado P, Sivera F, Calvo-Alen J, de la Morena I, Ortiz-Sanjuán F, Román-Ivorra J, Pérez-Gómez A, Heredia S, Olivé-Marqués A, Prior-Español �, Díez C, Alegre-Sancho J, Ybáñez A, Martínez-Ferrer �, Narváez J, Figeras I, Turrión A, Romero-Yuste S, Trénor P, Ojeda S, González-Gay M, Blanco R. Apremilast in Combination vs Monotherapy for Refractory Oral And/or Genital Ulcers in Behçet’s Disease: National Multicenter Study of 51 Cases [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-in-combination-vs-monotherapy-for-refractory-oral-and-or-genital-ulcers-in-behcets-disease-national-multicenter-study-of-51-cases/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apremilast-in-combination-vs-monotherapy-for-refractory-oral-and-or-genital-ulcers-in-behcets-disease-national-multicenter-study-of-51-cases/