Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Background/Purpose: Most of the currently available biological agents used in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) target a cellular or soluble factor involved in the physiopathology of the disease. Alternatively, cellular therapies are scarce in the therapeutic management of RA. Apoptotic cells display immunologic properties that have been used to resolve inflammation in various experimental models of autoimmune diseases (diabetes, demyelinating diseases) as well as in bone marrow transplantation to favour engraftment and prevent graft versus host disease. Apoptotic cell approach has been successfully assessed to prevent arthritis development in experimental rat model. Here we evaluated a cell-based therapeutic approach based on the immuno-modulatory properties of apoptotic cells to treat RA. In this study, we thus investigated the effects apoptotic cell injection to treat arthritis in a mouse model of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA).
Methods: CIA was induced in susceptible DBA/1 mice using type II bovine collagen immunization. Four to 8 days after arthritis development (d20 post-immunization) mice presenting arthritic symptoms were treated with apoptotic cells (5.10e6 cell/mouse). As control, methotrexate was used (MTX, 15 mg/kg, twice) alone or with apoptotic cells. Regulatory T cells (Treg) were assessed by FACS at time of sacrifice (day 40/45).
Results: Apoptotic cell injection demonstrated a significant decrease of arthritis score (p>0.01; 4 independent experiments), associated with an increased percentage of Treg in the spleen at time of sacrifice (Figure: Apoptotic cell injection in collagen induced arthritis attenuates arthritis score either after early or late injection. Data are obtained in DBA1 mice immunized with bovine type II collagen). In addition, MTX was sufficient to decrease arthritis as well and apoptotic cell injection did not influence MTX efficiency and vice-et-versa. Whereas MTX did not affect the percentage of Treg, MTX + apoptotic cell treatment induced a strong increase of Treg in the spleen and draining lymph nodes.
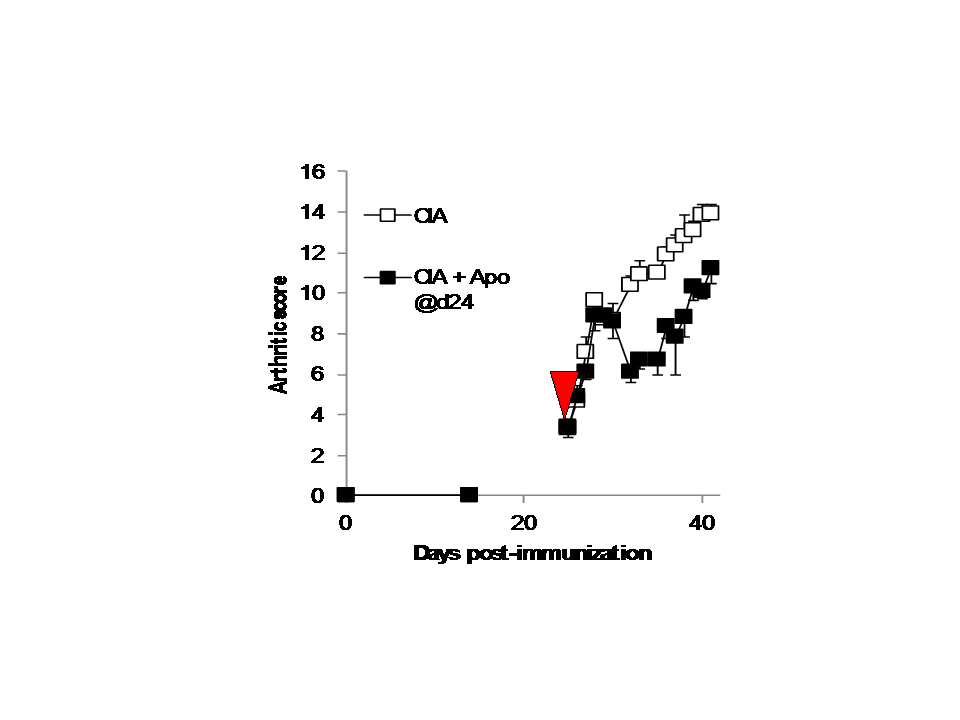 |
Conclusion: Apoptotic cell injection is an effective treatment to reduce arthritis severity and should be consider in clinic as an alternative method for the treatment of patients with RA. A phase I/II clinical trial using this therapeutic approach is currently planned by our group in patients with RA refractory to biological agents.
Disclosure:
S. Perruche,
None;
A. Clauzon,
None;
F. Bonnefoy,
None;
E. Toussirot,
None;
P. Saas,
None.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/apoptotic-cell-based-therapy-to-treat-collagen-induced-experimental-arthritis-rationale-for-the-use-of-apoptotic-cells-in-the-treatment-of-rheumatoid-arthritis/

