Session Information
Session Type: ACR Poster Session A
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Mirogabalin (DS-5565) is a novel ligand of the alpha-2-delta subunit of voltage-gated calcium channels. Mirogabalin possesses unique binding characteristics to alpha-2-delta subunits, and potent and long-lasting analgesic effects in fibromyalgia models and neuropathic pain models. Phase III clinical trials of mirogabalin in patients with fibromyalgia, diabetic peripheral neuropathic pain and postherpetic neuralgia are ongoing. Fibromyalgia is often associated with anxiety and depressive symptoms. In the present study, we investigated the anxiolytic effects of mirogabalin in intramuscular acidic saline injection model (Sluka model) in rats, an experimental animal model for fibromyalgia.
Methods: Male SD rats received two repeated intramuscular injections of acidic saline (pH 4.0) into the gastrocnemius muscle. After development of hyperalgesia, the animals received the test compound orally and the anxiolytic effects were determined in open field test and elevated plus maze test at 2 h after administration. Dose levels of mirogabalin were set at 3 and 10 mg/kg, and the normal and model control groups received vehicle (distilled water).
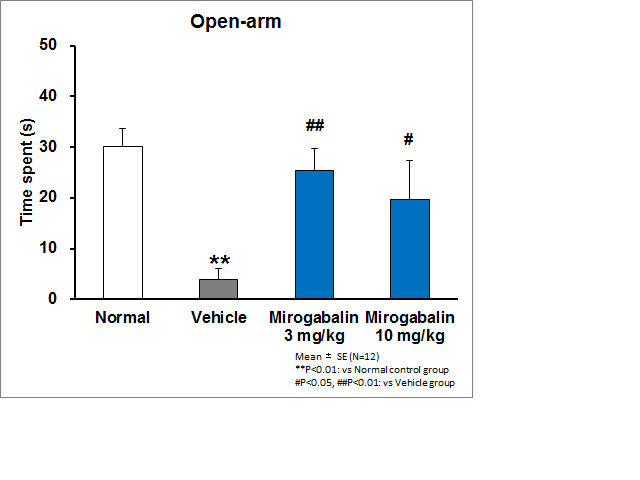
Results: Sluka model rats showed mechanical hyperalgesia demonstrated by decreased pain thresholds to von Frey filaments. In the open filed test, Sluka model rats significantly preferred the wall-area to the central-area compared with normal rats. In the elevated plus maze test, Sluka model rats exhibited significant decreases in the number of entries and time spent in the open-arm, and significant increases in time spent in the closed-arm. Taken together, Sluka model rats showed anxiety-related behaviors. A single oral administration of mirogabalin (3 and 10 mg/kg) significantly alleviated and normalized above anxiety-related behaviors in both tests.
Conclusion: Sluka model rats showed anxiety-related behaviors in open field test and elevated plus maze test. Mirogabalin alleviated the anxiety-related behaviors in Sluka model rats. Mirogabalin may provide effective anxiety relief for patients with fibromyalgia, as well as pain relief.
Figure 1 Effects of mirogabalin on anxiety-like behavior in open-field test in Sluka model rats. 
Figure 2 Effects of mirogabalin on anxiety-like behavior in elevated plus maze test in Sluka model rats. 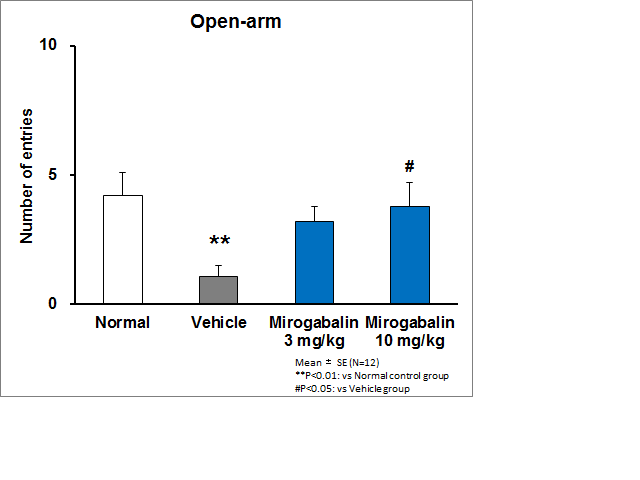
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Domon Y, Arakawa N, Murasawa H, Kobayashi H, Saeki K, Kitano Y. Anxiolytic Effects of the Novel α2δ Ligand Mirogabalin (DS-5565) in Sluka Model, an Experimental Animal Model of Fibromyalgia [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016; 68 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anxiolytic-effects-of-the-novel-%ce%b12%ce%b4-ligand-mirogabalin-ds-5565-in-sluka-model-an-experimental-animal-model-of-fibromyalgia/. Accessed .« Back to 2016 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anxiolytic-effects-of-the-novel-%ce%b12%ce%b4-ligand-mirogabalin-ds-5565-in-sluka-model-an-experimental-animal-model-of-fibromyalgia/
