Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Vasculitis – Non-ANCA-Associated & Related Disorders Poster III
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Vascular inflammation in Behcet’s Disease (BD) is one of the most important causes of mortality due to pulmonary artery involvement (PAI) or Budd-Chiari syndrome. In this study, we aimed to evaluate the clinical features, course and factors affecting the recurrence risk of BD-associated PAI.
Methods: BD patients followed up between 1990-2022 were included. All data were acquired from the patient charts. Findings were classified according to the vascular structures in which thrombotic or aneurysmal formation was detected. Factors affecting the risk of relapses were determined using multivariate Cox regression analysis.
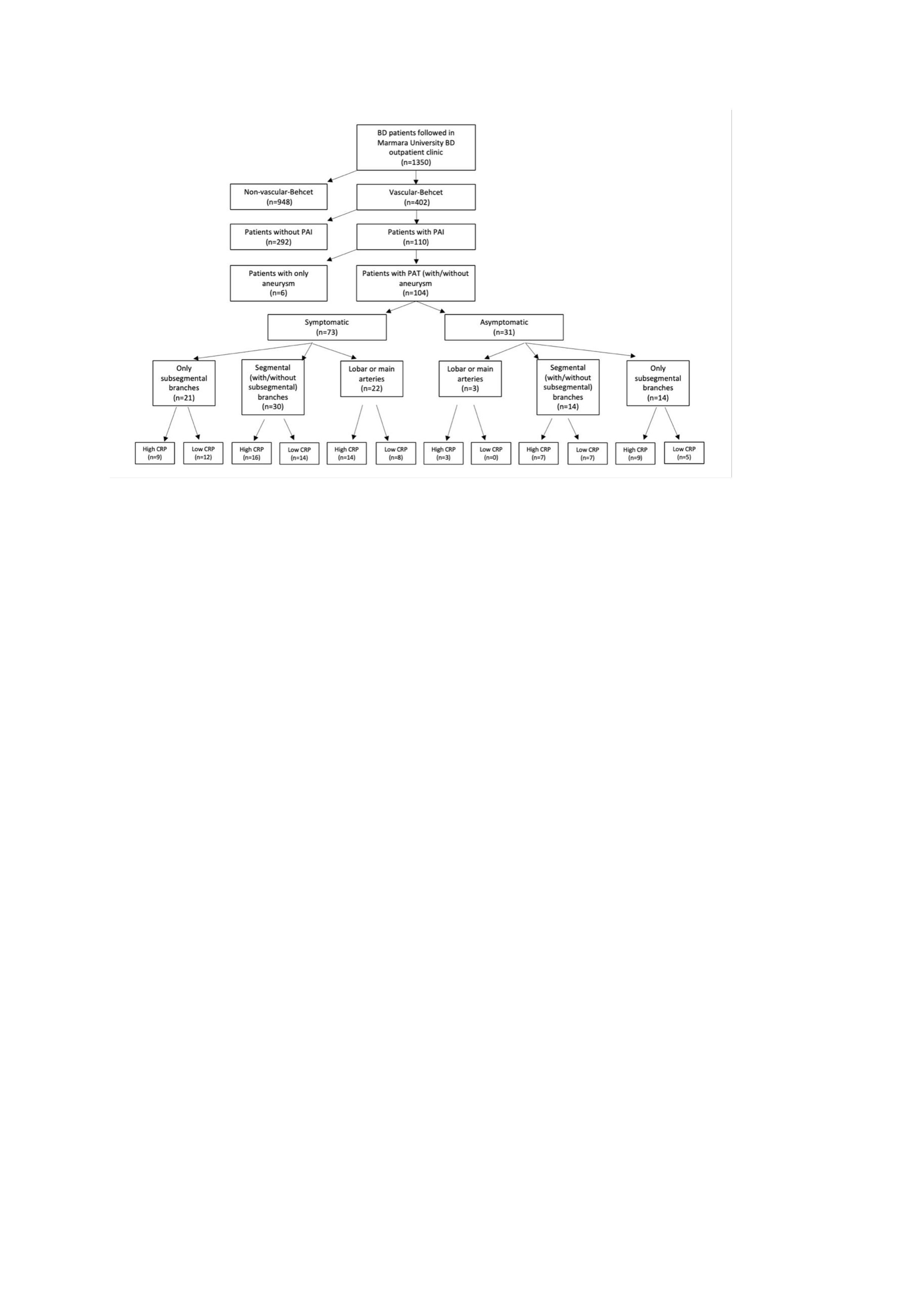
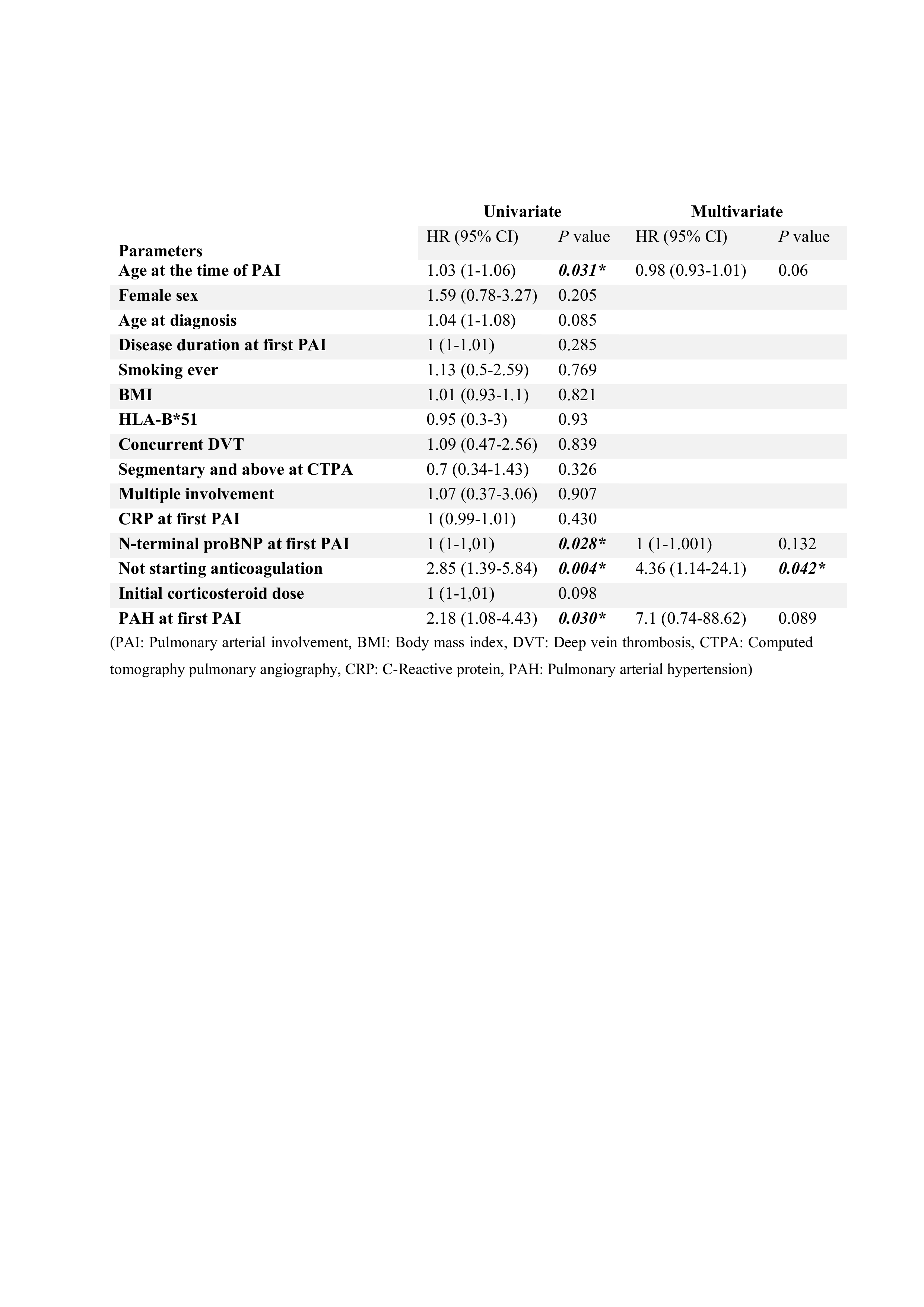
Results: Among 1350 BD patients, 110 (8.1%) had PAI. The mean age (SD) of patients with PAI was 42.4 (11.6) years, and the male/female ratio was 2.2 (76/34). Thirty-two (29.1%) of 110 patients were asymptomatic. (Figure 1) Symptomatic patients with PAI were significantly older (p=0.031), and female gender (p=0.001) and recurrence rates (p=0.019) were higher than asymptomatic patients with PAI. Pulmonary arterial thrombosis (PAT) was seen in 104 (94.5%) and aneurysms in 9 (6.6%) patients. PAI relapses were observed at least once in 31 (28.2%) patients. In multivariate analysis, the Cox regression model was significant (p=0.013) and not starting anticoagulants (HR 4.36, 95% CI 1.14-24.1), p=0.042), independently increased the PAI relapse risk. (Table 1)
Conclusion:
PAT is the main presentation type of PAI in BD while aneurysmatic formation is rare. In one-third of patients with PAI, relapses develop during follow-up despite immunosuppressive treatment. When added to immunosuppressive treatment, anticoagulant therapy significantly decreases the relapse rate in BD patients with PAI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Abacar K, Boncukcuoğlu A, Aksoy A, Kocakaya D, Cimşit Ç, Direskeneli H, Alibaz Öner F. Anticoagulant Treatment May Decrease the Relapse Rate in Pulmonary Arterial Involvement of Behçet’s Disease When Added After the First Event [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anticoagulant-treatment-may-decrease-the-relapse-rate-in-pulmonary-arterial-involvement-of-behcets-disease-when-added-after-the-first-event/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anticoagulant-treatment-may-decrease-the-relapse-rate-in-pulmonary-arterial-involvement-of-behcets-disease-when-added-after-the-first-event/