Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 9:00AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: In patients with rheumatic diseases herpes zoster (HZ) has been identified as one of the most common infections associated with immunosuppression. Shingrix is a recombinant inactive vaccine available for prevention of HZ infection. Due to paucity of data regarding its efficacy in patients with autoimmune disease on immunosuppressive medications, there is a need to investigate whether this patient population mounts an adequate response to Shingrix as compared to patients with no autoimmune disease and not on immunosuppressive medications.
Methods: Our study is an IRB approved single center prospective non randomized trial. Criteria for study group enrollment consisted of patients over age 50 with autoimmune conditions including rheumatoid arthritis(RA), psoriatic arthritis(PsA) and systemic lupus erythematosus(SLE) on bDMARDs, cDMARDs or tsDMARDs +/- steroids. Criteria for control group consisted of patients over age 50 without autoimmune diseases and not on immunosuppressive medications. At time of enrollment patients underwent bloodwork to establish a pre-vaccination serum antibody quantification. Patients then underwent two series of IM Shingrix vaccine (0.5mL each) administered 2 to 6 months apart. Repeat bloodwork was performed 6-12 weeks following 2nd dose of vaccine to assess post- vaccination antibody response. Pre and post vaccination response was then compared using Anti Varicella Zoster Virus IgG ELISA kit (Alpha diagnostic international). A level of 150 U/ml post vaccination was considered protective by the manufacturer of the kit.
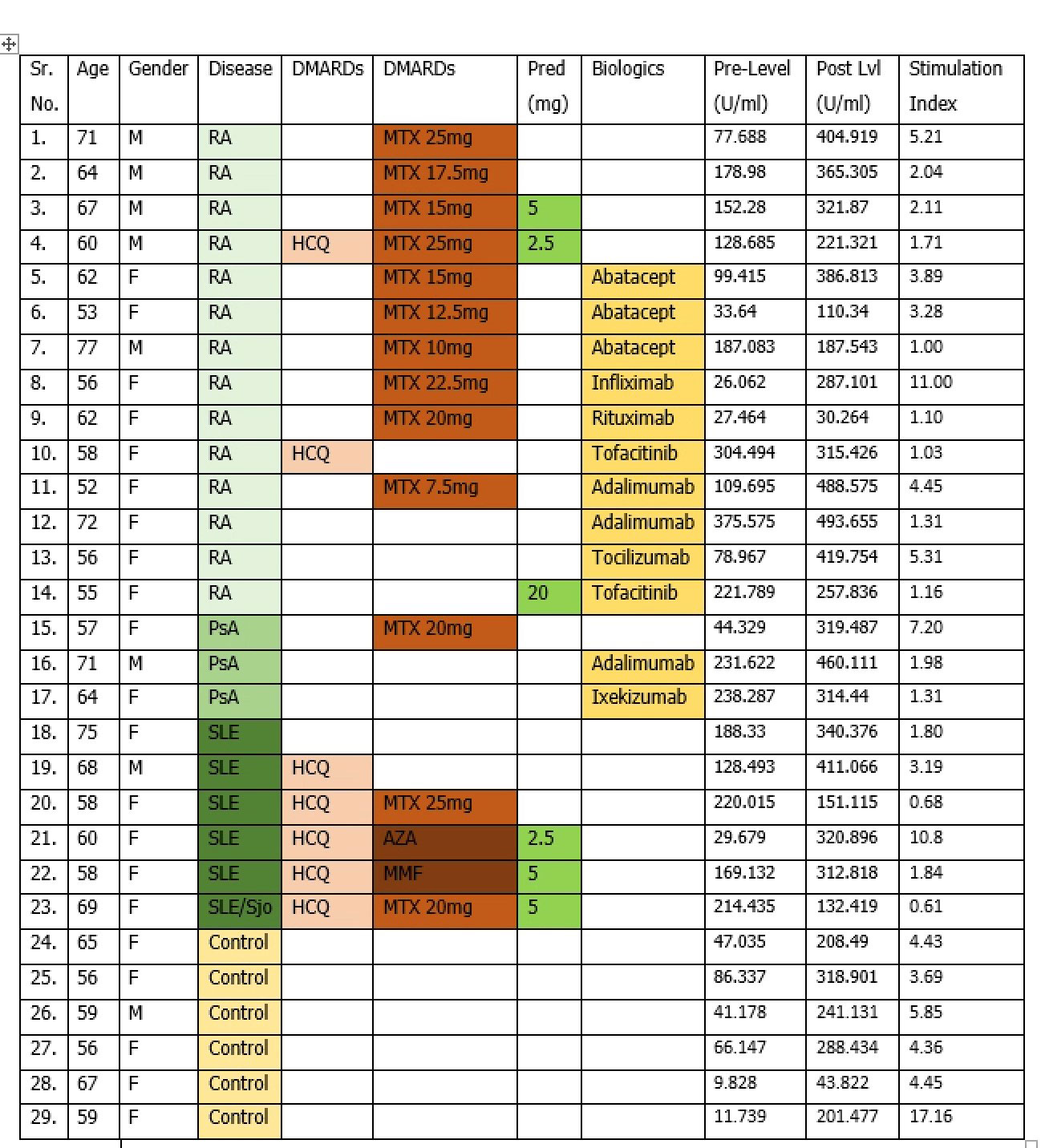
Results: We enrolled a total of 29 patients out of which 23 were a part of study group and 6 were a part of the control group. Pre vaccine varicella IgG titers (U/ml) were obtained (pre-level; figure 1) followed by 2 doses of vaccination after which post vaccination varicella IgG titers (U/ml) were measured (post lvl; figure 1). Stimulation index (S.I=post lvl/pre-level) was calculated for individual patients to assess response. Stimulation index mean was calculated for each group for comparison.
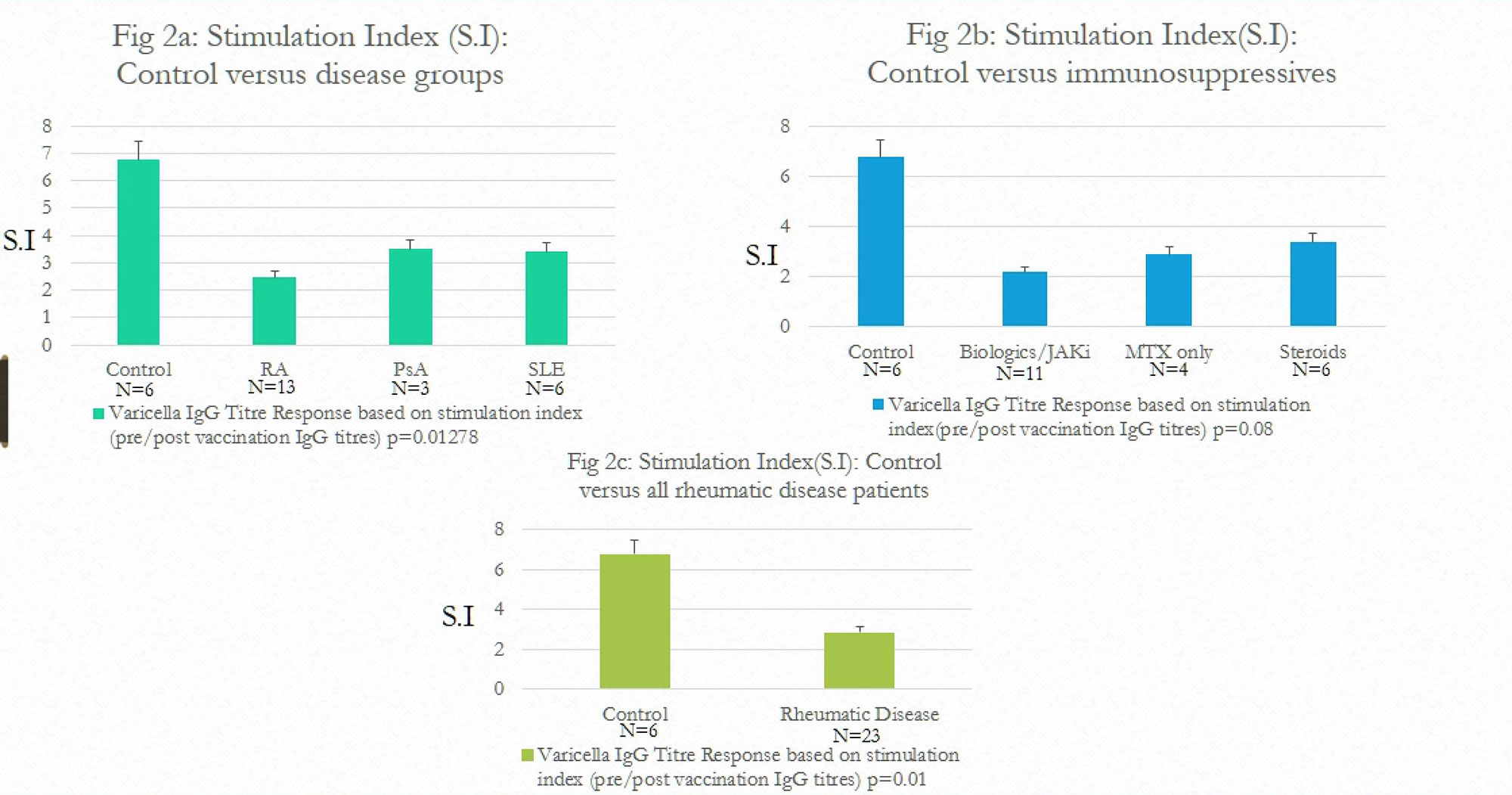
Control group had 6.7 fold increase (S.I=6.7) in antibody titers in comparison to 2.4 fold increase in RA, 3.4 fold increase in PsA and 3.3 fold increase in SLE groups. (Fig 2a)
Control group had 6.7 fold increase in antibody titers compared to 2.1 fold increase in patients on biologics, 2.8 fold in patients on MTX and 3.4 fold in patients on steroids. (Fig 2b)
Overall, antibody titre response of control group patients was at least 3 times higher compared to patients with rheumatic diseases. (6.7 vs. 2.8). (Fig 2c)
Conclusion: Our study shows that patients with rheumatic diseases on treatment do mount a response to Shingrix vaccine but the increase in antibody titers is lower than controls.
Using a protective level of antibody titers at 150 U/ml, most rheumatic disease patients (91%) did reach a protective level of immunity supporting the need to offer Shingrix vaccination to our patients. The vaccine was well tolerated with no major adverse events.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kifayat A, Wasserman a, Sperber K, Nes D, Arnaboldi P, Ash J. Antibody Response to Shingrix Vaccination in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis, Seronegative Spondyloarthropathy and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus on Immunosuppressive Medications [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antibody-response-to-shingrix-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-seronegative-spondyloarthropathy-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-on-immunosuppressive-medications/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/antibody-response-to-shingrix-vaccination-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-seronegative-spondyloarthropathy-and-systemic-lupus-erythematosus-on-immunosuppressive-medications/