Session Information
Date: Monday, November 14, 2022
Title: RA – Treatment Poster IV
Session Type: Poster Session D
Session Time: 1:00PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Patients with inflammatory rheumatic diseases (IRD) on immunomodulatory therapies have a higher likelihood of an impaired vaccine-induced immune response following an mRNA anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Determination of anti-S1 levels may serve as a surrogate for protection and may guide when to schedule a subsequent vaccine dose but data regarding the optimal timepoint for assessment are still limited.
Methods: Immune responses in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients treated with csDMARDs, bDMARDs (with the exception of rituximab) and JAK inhibitors were compared to healthy controls (HC) over 24 weeks following two doses of an anti-SARS-CoV-2 mRNA based vaccines in an observational prospective trial. Neutralization activity was determined using a Wuhan-Hu-1 pseudovirus (HIV-based) assay and the multiplex immune assay ABCORA.1
Clinical assessment and blood sampling was performed at baseline, 3 weeks after the 1st and 2 weeks after the 2nd vaccine dose and at 12 and 24 weeks. Antibody response to the receptor binding domain (RBD) within the SARS-CoV-2 S1 protein was measured with the Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV-2-S (Roche Diagnostics GmbH) test. The seroprofiling assay ABCORA was used to quantitatively determine IgG, IgA and IgM responses to RBD, S1, S2 and N which allows calculation of a sum of S1 SOC values that correlate to neutralization,.
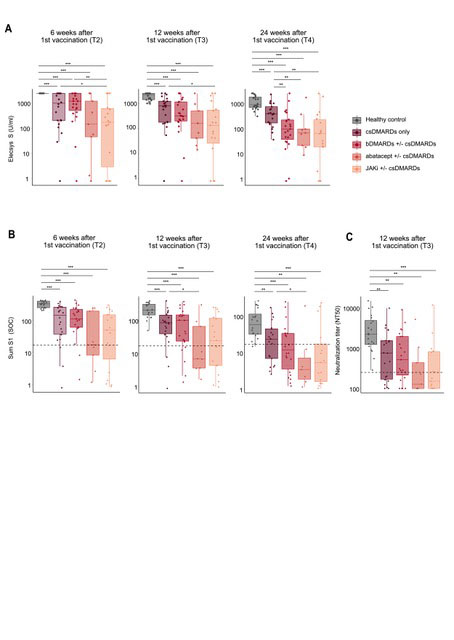
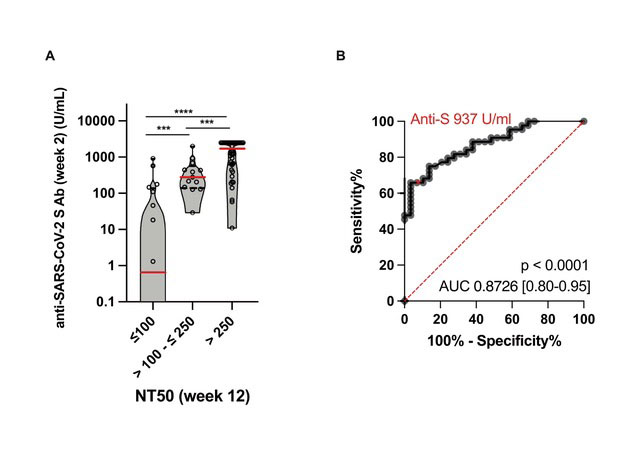
Results: We enrolled 77 RA patients on DMARD therapy and 21 HC. The immunogenicity analyses were based on 73 RA patients after exclusion of 4 patients with previously unnoticed SARS-CoV-2 infection. In contrast to HC, anti-S1 titers were lower at all timepoints with significantly reduced titers observed in patients on abatacept, JAK inhibitors and TNF inhibitors in combination with csDMARDs (Fig 1). Potent neutralizing activity (NT50 ≥ 250) was detected in all HC at week 12, in contrast to only 61.6% RA patients. NT50 correlated to the results based on the ABCORA assay. Peak anti-S1 titers as determined 2 weeks after the 2nd vaccine dose were predictive of potent neutralizing activity at week 12 (p < 0.0001) (Fig 2).
Conclusion: RA patients, in comparison to HC, revealed a slower kinetic, a lower magnitude and a more rapid decline of humoral immune responses depending on the treatment regimen. Whereas all HC developed a potent neutralizing activity after 12 weeks, 38.4% of RA patients did not show a relevant neutralizing activity at that timepoint. Peak anti-S responses two weeks after the second vaccine were able to predict the development of potent neutralizing activity thereafter and may contribute to individually tailor vaccination strategies.
References
1. Abela I et al. Nature Commun 2021. doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-27040-x
(A) Boxplots showing anti-S antibodies as determined by Elecsys Anti-SARS-CoV_2 (S) assay at 6, 12 and 24 weeks following the first vaccine dose in healthy controls and
RA patients stratified by different DMARD regimen. Results from Wilcoxon test to compare each group to the other are shown.
(B) Boxplots showing sum S1 reactivity (SOC) in healthy controls compared to RA patients stratified by different DMARD regimen at 6, 12 and 24 weeks after first vaccination. Dashed lines correspond to a sum S1 of 17. Results from Wilcoxon test to compare each group to the other are shown
(C) Boxplots showing NT50 values of healthy controls compared to RA patients stratified by DMARD regimen at 12 weeks after first vaccination. The dashed line corresponds to NT50 250. Results from Wilcoxon test to compare each group to the other are shown.
*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001.
(A) The violins illustrate the kernel probability density. Red lines indicate the medians, black lines indicate 1st and 3rd IQR. Dots represent individual patients.
***p<0·001, ****p<0·0001
(B) ROC curve peak anti-S at week 2 /NT50 at week 12. Performance of peak anti-S titers in discriminating RA patients with NT50 < 250 from patients with potent neutralizing activity (NT50 > 250) at week 12. ROC curve = receiver operating characteristic curves. Anti-S 937 U/ml represents the decisive anti-S threshold value. Sensitivity 66%, specificity 97%.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Schmiedeberg K, Abela I, Vuilleumier N, von Kempis J, Rubbert-Roth A. Anti-S1 Antibody Levels Two Weeks After the Second Dose of an mRNA anti-SARS-CoV2 Vaccine Predict Maintenance of a Potent Neutralizing Activity over 24 Weeks in RA Patients [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2022; 74 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-s1-antibody-levels-two-weeks-after-the-second-dose-of-an-mrna-anti-sars-cov2-vaccine-predict-maintenance-of-a-potent-neutralizing-activity-over-24-weeks-in-ra-patients/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2022
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-s1-antibody-levels-two-weeks-after-the-second-dose-of-an-mrna-anti-sars-cov2-vaccine-predict-maintenance-of-a-potent-neutralizing-activity-over-24-weeks-in-ra-patients/