Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Title: Abstracts: RA – Diagnosis, Manifestations, & Outcomes I: Bugs & Drugs (0980–0983)
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 2:45PM-3:00PM
Background/Purpose: Long-term vaccine-induced immunity to SARS-CoV-2 is critical to combat the pandemic. Vaccination against anti SARS-CoV-2 is recommended in patients with rheumatic diseases, but limited data are available in patients on immunosuppressive therapy. The objective of this study is to analyse magnitude and kinetics of mRNA vaccine induced anti-S1 titers in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) on DMARD therapy and healthy controls (HC).
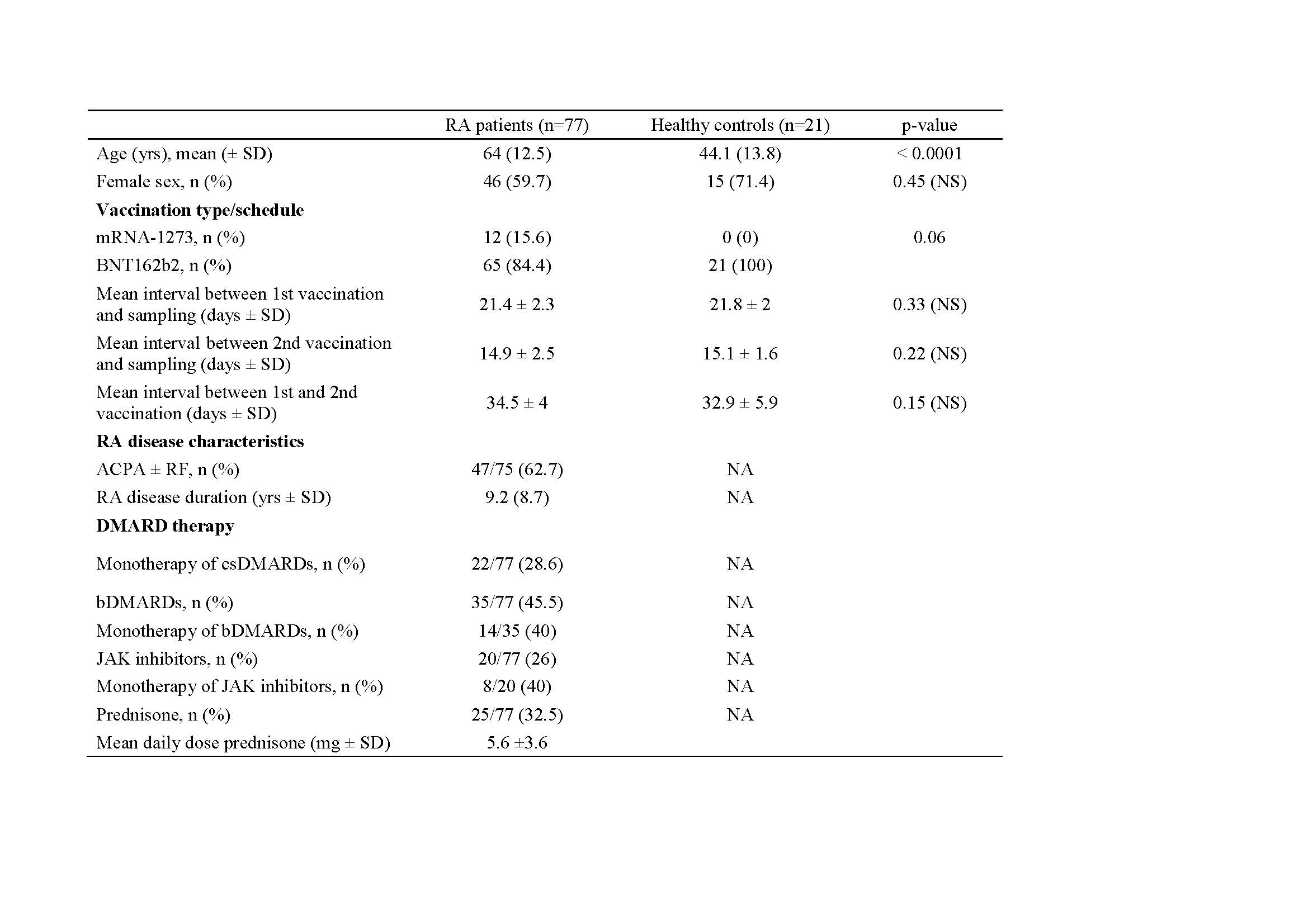
Methods: 77 consecutive RA patients and 21 HC were eligible for vaccination according to federal guidelines and were enrolled in the prospective RECOVER trial (Rheumatoid>Covid-19 Vaccine Immune>Response) between 10th January and March 15th 2021. Vaccination itself was not part of the study. The anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccines mRNA-1273 and BNT162b2 were applied according to the manufacturers` recommendations. All patients continued their DMARD therapy, patients on rituximab were excluded. Serum samples were obtained before the first vaccine, 3 weeks after the first, 2 weeks after the second vaccine and after 12 weeks. Quantitative antibody testing was performed using the Roche Elecsys® Anti-SARS-CoV-2 S1 assay that measures antibodies to the S1 protein (range 0.4-2500 U/l) and nucleoprotein to exclude subclinical SARS-CoV-2 infection. A threshold level of anti-S1 that correlates to neutralization has been proposed at 133 U/l.1 . More recently, even lower cut-off levels ( >15 U/l) have been suggested.2
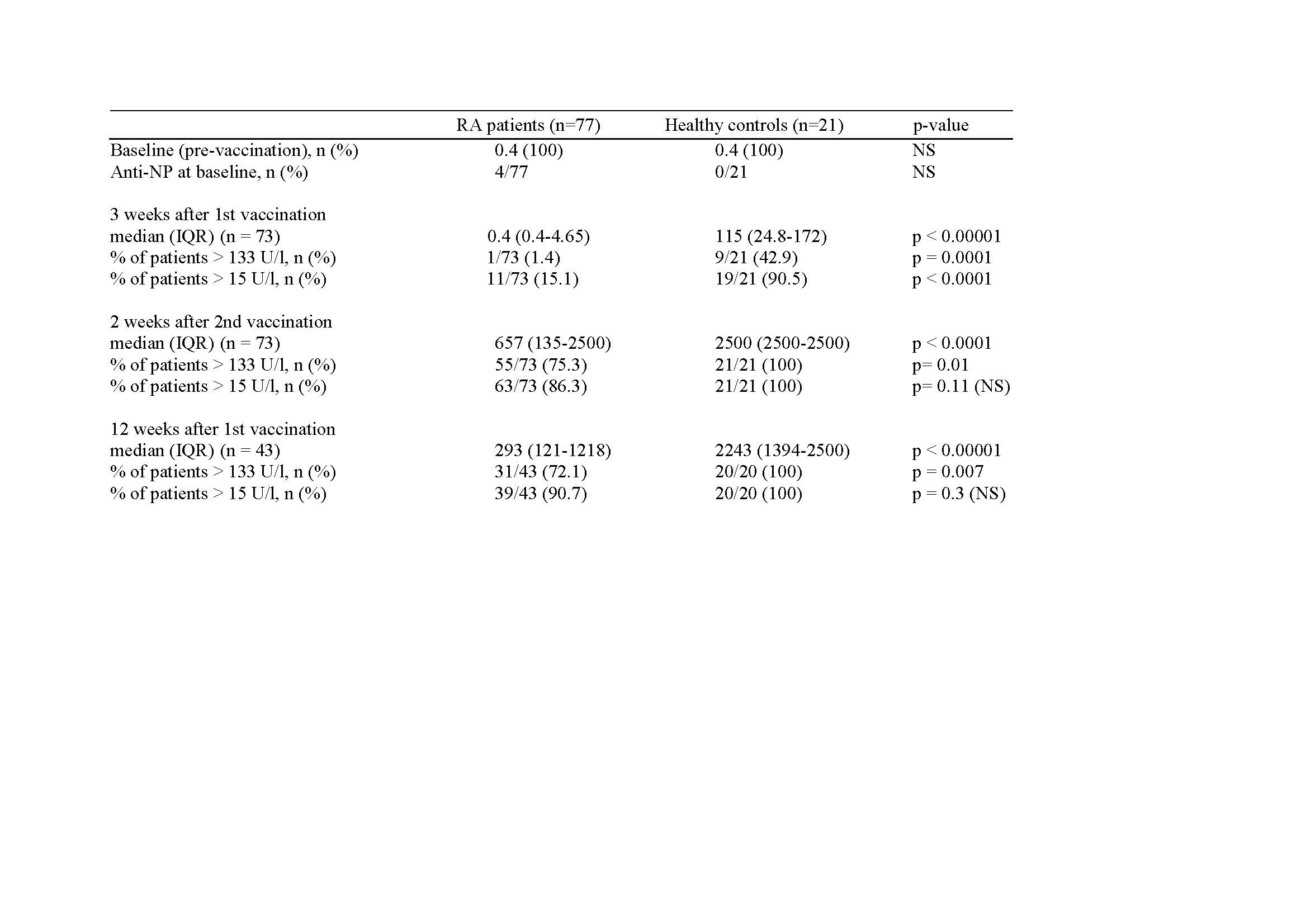
Results: Baseline characteristics are summarized in Tab. 1. Levels of anti-S1 antibodies after vaccination are presented in Table 2. 4/77 patients with antibodies to nucleoprotein at baseline were excluded from the analysis. At present, 43/73 patients reached the 12 week timepoint after the first vaccine dose. Median titers of anti-S1 antibodies were significantly lower in RA patients at all time points. 3 weeks after the first vaccine dose, 9/21 HC but only 1/73 RA patients developed anti-S1 titers exceeding 133 U/l (p = 0.0001) or 15 U/l (19/21 HC versus 11/73 RA patients). Two weeks after the second vaccine, the proportion of RA patients with anti-S1 titers exceeding 133 u/l was still significantly lower than in HC (75.3% versus 100%, p = 0.01). Of note, significantly fewer RA patients on abatacept (n=9) or JAK inhibitors (n = 19) achieved both threshold levels compared to patients on csDMARDs and/or anti-cytokine directed biologics.
Conclusion: The development of anti-S1 titers after vaccination with mRNA vaccines against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with RA is overall slower and results in lower antibody titers in comparison to healthy controls. Our data suggest that patients on abatacept or on JAK inhibitors have an increased risk of an impaired anti-S1 response compared to RA patients on csDMARDs or anti-cytokine directed biologics. Strategies need to be developed to optimize vaccine induced humoral immunity in patients with RA.
Ref.: 1Resman Rus K et al J Clin Virol 2021, 2Rubio-Acero R et al medRxiv 2021
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rubbert-Roth A, Vuilleumier N, Ludewig B, Schmiedeberg K, Rottlaender Y, Pirker I, VonKempis J. Anti-S1 Antibodies After Vaccination with Anti SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccines in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis Differ in Magnitude and Kinetics from Healthy Controls: Results from a Prospective, Observational Controlled Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-s1-antibodies-after-vaccination-with-anti-sars-cov-2-mrna-vaccines-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-differ-in-magnitude-and-kinetics-from-healthy-controls-results-from-a-prospective-observ/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/anti-s1-antibodies-after-vaccination-with-anti-sars-cov-2-mrna-vaccines-in-patients-with-rheumatoid-arthritis-differ-in-magnitude-and-kinetics-from-healthy-controls-results-from-a-prospective-observ/