Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Sunday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: The mechanism underlying the association between ankylosing spondylitis (AS) and HLA-B27 is still unknown. One of the hypotheses involves the interaction of HLA-B27 homodimers with KIR3DL2 receptors on CD4+ T cells. KIR3DL2 is a member of the killer immunoglobin-like receptor (KIR) family of MHC class I ligands that transmit activating or inhibitory signals to KIR expressing lymphocytes. KIR3DL2 binds to HLA-B27 homodimers whereas KIR3DL1 interacts with native HLA-B27 complexes. Previous work has shown an expansion of KIR3DL2 positive IL-17A producing CD4+ T cells in HLA-B27 positive patients with AS. Multiple other IL-17A producing lymphocyte subsets including γδ T cells have been implicated in AS pathogenesis. The purpose of this study was to further characterize the expression of KIR3DL2 and KIR3DL1 on these lymphocyte subsets.
Methods: Human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were prepared by Ficoll density gradient centrifugation from the blood of healthy individuals. To measure cytokine production, PBMC were stimulated with PMA/ionomycin for 4 hours in the presence of brefeldin A/monensin followed by intracellular staining. In other experiments, PBMC were stimulated with phytohemagglutinin (PHA) for up to 3 days in medium supplemented with IL-2 and IL-7. Cells were analyzed using a 19-parameter flow cytometry panel that distinguishes natural killer (NK) cells, mucosal-associated invariant T (MAIT) cells, CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells, CD4-CD8- DN αβ T cells and γδ T cells further subdivided into Vδ1+, Vδ2+ and other γδ T cells. MAIT cells were identified using MR1 tetramers. Lineage markers were combined with antibodies specific for relevant KIRs and cytokines. Flow cytometric analysis was performed using a 5-laser BD LSRFortessa cytometer and FlowJo software.
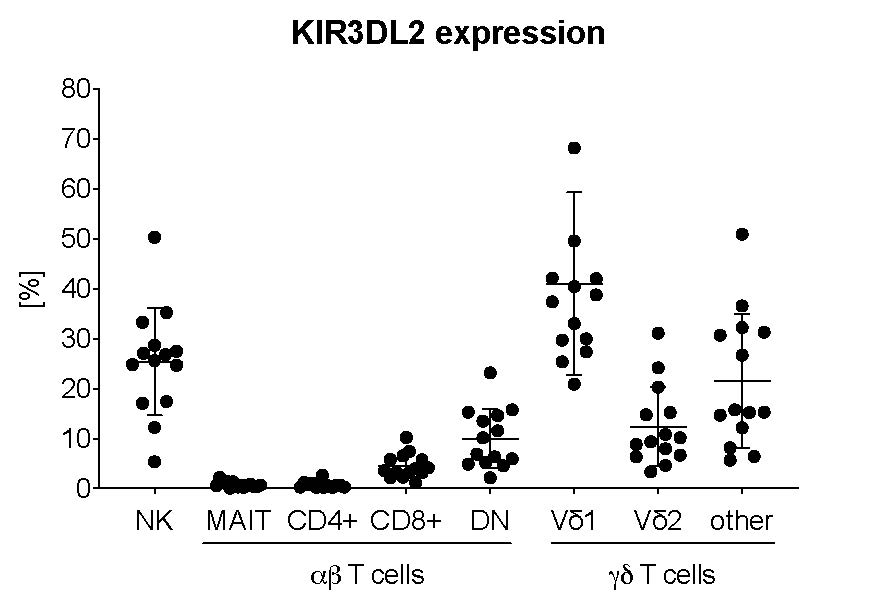
Results: KIR3DL2 and KIR3DL1 were variably expressed by all lymphocyte subsets analyzed. The highest frequencies of KIR expressing cells were observed for NK and γδ T cells, in particular Vδ1 cells. Only a small fraction of CD4+ T cells stained positive for KIR3DL2 in our cohort of healthy individuals. The highest frequency of IL-17A secreting cells was observed amongst MAIT and CD4+ T cells. When stratified based on KIR3DL2 expression, IL-17A expression was enriched in KIR3DL2+ cells in most subsets, regardless of whether the blood was from HLA-B27+ or HLA-B27- subjects. γδ and other T cells but not NK cells upregulated KIR3DL2 and KIR3DL1 upon stimulation with PHA in vitro.
Conclusion: AS-associated KIRs (KIR3DL2, KIR3DL1) are strongly expressed on γδ T cells in healthy individuals and further upregulated upon stimulation. Our data suggest that studies testing the KIR hypothesis for the HLA-B27 association of AS should consider a wider spectrum of KIR expressing lymphocytes including γδ T cells.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lefton M, Sharma N, Ermann J. Ankylosing Spondylitis-associated Killer Immunoglobin-like Receptors Are Strongly Expressed on γδ T Cells [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ankylosing-spondylitis-associated-killer-immunoglobin-like-receptors-are-strongly-expressed-on-%ce%b3%ce%b4-t-cells/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ankylosing-spondylitis-associated-killer-immunoglobin-like-receptors-are-strongly-expressed-on-%ce%b3%ce%b4-t-cells/