Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Submissions (ACR)
Ankylosing spondylitis and non-radiographic axial spondyloarthritis: part of a common spectrum or distinct diseases? Analysis of a longitudinal prospective cohort.
Background/Purpose:
Historically ankylosing spondylitis (AS) has been defined by the modified New York classification criteria which require the presence of radiographic sacroiliitis. More recently the use of MRI has led to the identification of patients with features of axial spondyloarthritis (SpA) who do not fulfill the modified New York criteria (non-radiographic axial SpA, nr-axSpA). The natural history of axial SpA is not completely understood and current knowledge is drawn largely from European data. We aimed to compare the features of AS and nr-axSpA in a North American cohort.
Methods:
Data were analyzed for all patients enrolled in a longitudinal spondyloarthritis cohort between January 2003 and December 2012 meeting modified New York criteria for AS or the ASAS classification criteria for nr-axSpA. Categorical variables were compared using Fisher’s exact test with two-tailed p values. For continuous variables, a mean patient value was calculated based on all visits for that patient. Variables were compared using t-tests.
Results:
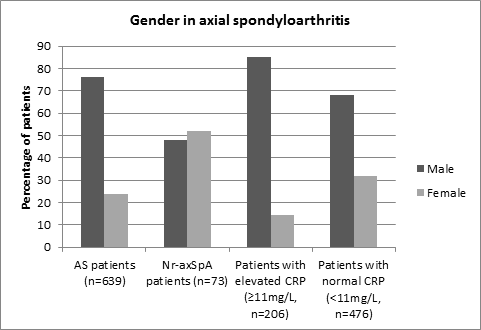
639 patients with AS and 73 patients with nr-axSpA were included. Of the nr-axSpA patients, 40 demonstrated inflammation on MRI, and 33 were classified according to ASAS clinical criteria for axial SpA (of whom 15 had MRI showing no inflammation and 18 did not have MRI). The proportion of male patients was higher in AS than in nr-axSpA (76.2% vs. 47.9%, p<0.0001). CRP and ESR levels were higher in AS than nr-axSpA (CRP 11.4 vs. 5.2, p<0.0001; ESR 13.7 vs. 9.9, p=0.018). Disease duration at last clinic visit was shorter in nr-axSpA than AS (12.1y versus 17.7y, p=0.0002), providing some indirect support to the notion that nr-axSpA may represent a subset of axial SpA seen earlier in the course of the disease than AS. The proportions of patients receiving biologic therapy, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, disease modifying anti-rheumatic drugs and glucocorticoids were similar in AS and nr-axSpA. Further investigation of gender, inflammation and radiographic severity in the combined axial SpA cohort revealed that 31.9% of patients with a normal CRP were female, compared to only 14.6% of patients with an elevated CRP (p<0.0001). 96.6% patients with an elevated CRP had radiographic AS, compared to 86.8% of those with a normal CRP (p<0.0001). When data were analyzed for only the female patients, the difference in acute phase response between AS and nr-axSpA lost significance (CRP 9.4 versus 5.2, p=0.09; ESR 16.3 versus 11.5, p=0.07).
Conclusion:
Analysis of this North American SpA cohort has identified some key differences between subsets of axial SpA, and highlights the influence of gender on inflammation and radiographic severity, thereby influencing the clinical classification of axial SpA patients.
Disclosure:
D. Wallis,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
2;
N. Haroon,
Janssen Pharmaceutica Product, L.P.,
5,
Pfizer Inc,
5,
Amgen,
5,
Abbott Laboratories,
5;
R. Ayearst,
None;
A. Carty,
None;
R. D. Inman,
Abbvie, Janssen, Pfizer, UCB,
5.
« Back to 2013 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/ankylosing-spondylitis-and-non-radiographic-axial-spondyloarthritis-part-of-a-common-spectrum-or-distinct-diseases-analysis-of-a-longitudinal-prospective-cohort/