Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Costs associated with rheumatic diseases significantly affect a considerable portion of patients’ income. The monthly income of northeastern Mexican families has been reported to be $708.71 USD. Various socioeconomic risk factors have been identified as contributing to poor adherence, with elevated medication costs being a significant factor. The affordability of medication depends on whether it is covered by each specific healthcare system. Our objective is to provide insights into medication utilization and associated costs, contributing to a better understanding of the economic aspects of rheumatic disease management.
Methods: We conducted an observational retrospective analysis, focusing on the review of prescriptions provided to patients hospitalized for rheumatic diseases at the time of their discharge from our institution. The study covered the period from March to December 2023. Medications prescribed at discharge were systematically categorized, as outlined in Table 1. Additionally, the average monthly expenses for DMARDs, immunosuppressants, biologics, and bisphosphonates were calculated using pricing data obtained from our institution’s internal pharmacy. The total cost was reported in US dollars (USD), considering an equivalence of USD 1 = 16.89 Mexican pesos (MXN).
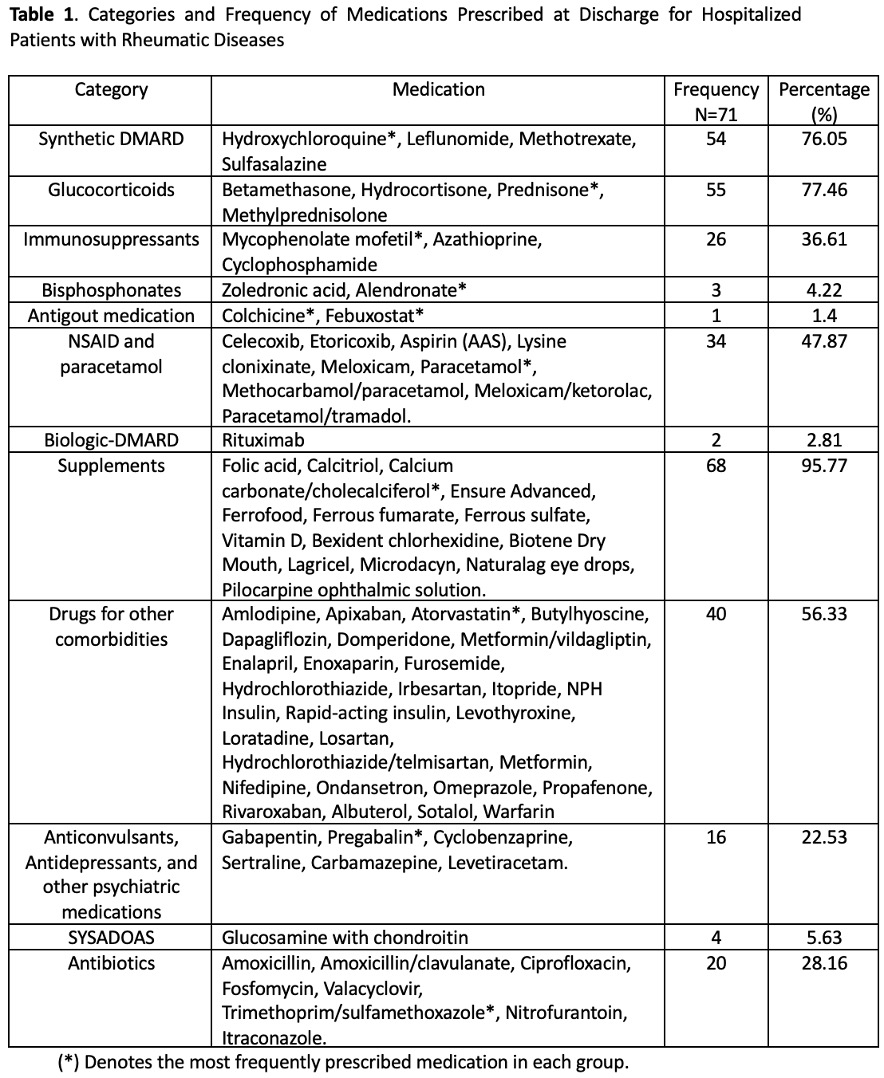
Results: During the period from March to December 2023, there were 143 hospitalized patients. Prescriptions were obtained from 71 patients, with an average of 7 medications per prescription. On average, patients took 6 tablets daily. The most frequently prescribed category of medications was supplements in 68 prescriptions (95.77%), specifically calcium carbonate/cholecalciferol. The second most frequently prescribed category was steroids in 55 prescriptions (77.46%), predominantly prednisone in its 5 mg presentation. The third most frequently prescribed category was conventional synthetic DMARDs in 54 prescriptions (76.05%), primarily hydroxychloroquine followed by methotrexate, leflunomide, sulfasalazine, and chloroquine. Nine prescriptions included >2 synthetic DMARDs. The average expenditure for this category was USD 110.69 monthly. The average expenditure for immunosuppressants was USD 395.29 and the average expenditure for bisphosphonates was USD 118.36.
Conclusion: The high average number of medications per prescription indicates the complexity of the treatment regimens. The economic aspects highlight potential challenges faced by patients in accessing and affording necessary medications, pointing towards areas where healthcare support or interventions may be beneficial.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Salcedo-Soto D, Bardan-Inchaustegui A, Gamez-Siller P, Lara Mendez D, Flores-Alvarado D, Esquivel-Valerio J, Cardenas-de la Garza J, Galarza-Delgado D. Analysis of Medication Usage and Monthly Costs in Hospitalized Patients with Rheumatic Diseases: A Retrospective Observational Study [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-medication-usage-and-monthly-costs-in-hospitalized-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-a-retrospective-observational-study/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-medication-usage-and-monthly-costs-in-hospitalized-patients-with-rheumatic-diseases-a-retrospective-observational-study/