Session Information
Date: Monday, November 18, 2024
Title: Osteoporosis & Metabolic Bone Disease – Basic & Clinical Science Poster
Session Type: Poster Session C
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Excluding clinical trials, there is limited evidence on the effect of 12 months of romosozumab treatment on increasing bone mineral density (BMD) in real-world clinical practice due to its recent approval. In Spain, romosozumab (ROMO) was authorized in September 2022. Furthermore, real-life data are needed for subpopulations such as patients with osteoporosis due to glucocorticoids (GC), or those with rheumatoid arthritis. The objective of this study was to describe the clinical-analytical, bone density, and safety characteristics at 12 months in patients with a very high risk of fracture treated with ROMO.
Methods: This was a multicenter observational descriptive study developed in rheumatology clinics across Spain, including women with OP who initiated ROMO treatment from September 2022. The baseline characteristics of 97 patients with a very high risk of fracture were analyzed. Collected characteristics included age, sex, risk factors for OP (early menopause, previous fractures or parental hip), cardiovascular risk factors -CVRF- (smoking, high blood pressure -HBP-, dyslipidemia -DLP-, diabetes mellitus -DM-), gloremular filtration rate, disease requiring GC, major FRAX and hip score, BMD before and after ROMO treatment previous therapies, and safety data at 6 and 12 months (MACE). Statistical analysis was performed using R software, and the study was conducted with the approval of the local ethics committee.
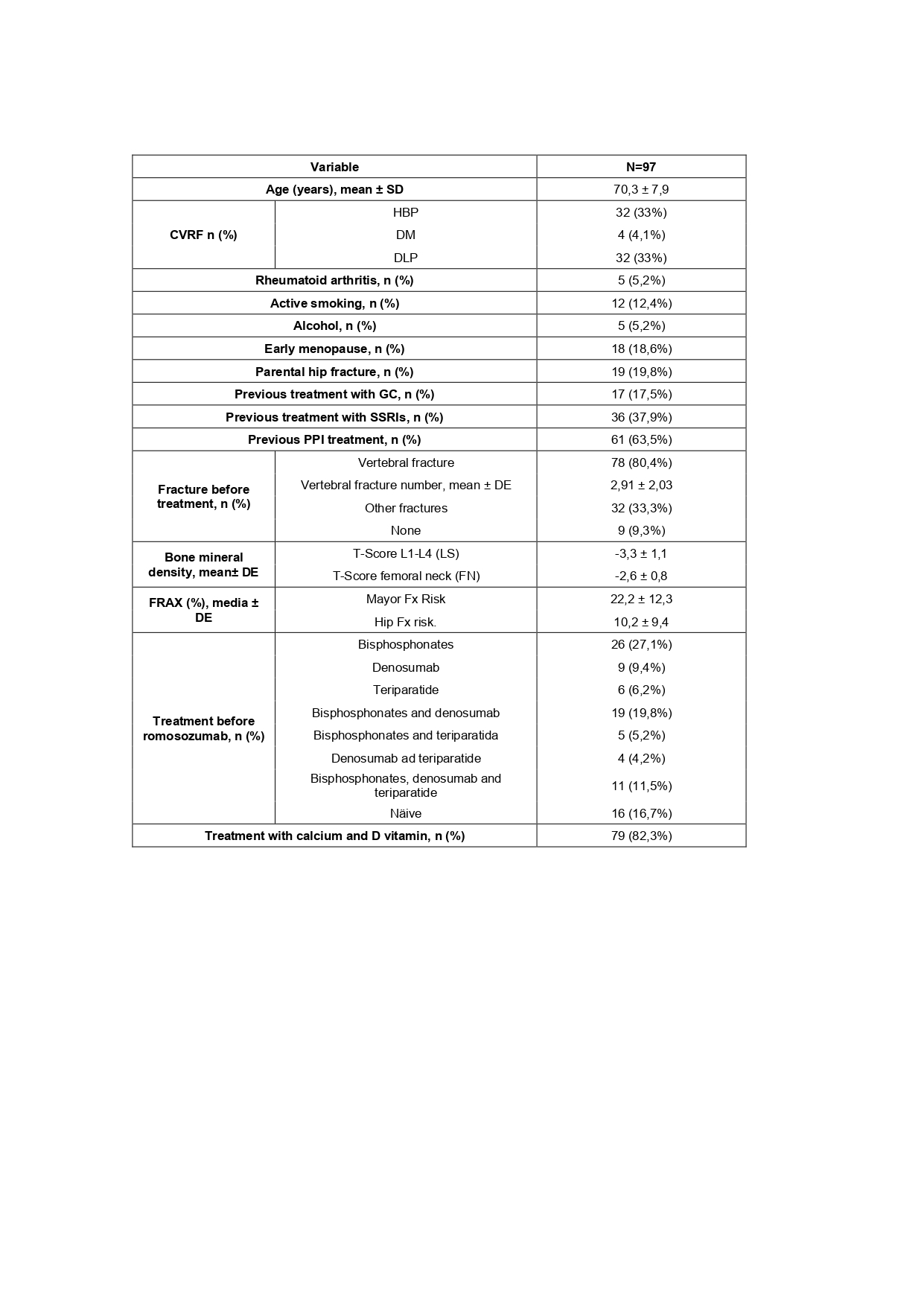
Results: The average age was 70.3 years. 78 cases (80,4%) had previous vertebral fractures and 32 cases (33.3%) had other fracture; 9 patients (9.3%) had no fractures prior to ROMO treatment. All 97 patients (100% women) were analyzed; 16.7% had not received prior treatment. More than 60% of patients were treated with previous therapies. The most used prior medications were bisphosphonates -BP- (n = 26), followed by denosumab -DMAb- (n = 9) and teriparatide -TPTD- (n = 6). Up to 11.5% of patients (n = 11) had previously received up to three drugs.
Cardiovascular risk factors included: 33% HBP; 33% DLP; 4.1% DM, and 12.4% active smoking. Seventeen patients (17.5%) had OP due to glucocorticoids (GC-induced OP). Reasons for GC treatment included 6 cases of asthma, 4 hematological diseases, and 6 rheumatic diseases (2 polymyalgia rheumatica, 2 rheumatoid arthritis, 1 systemic lupus erythematosus, and 1 Sjögren’s syndrome). See table 1.
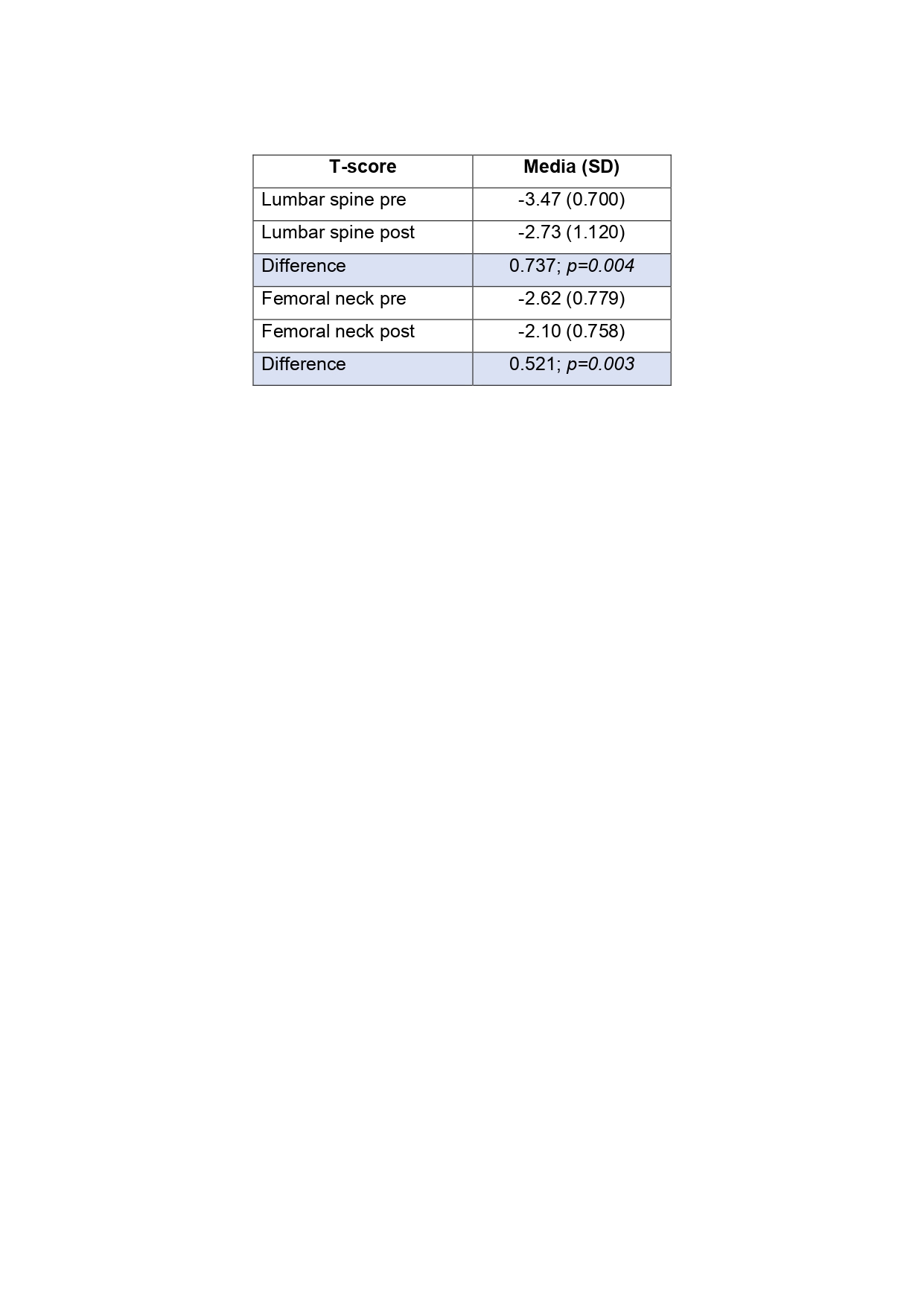
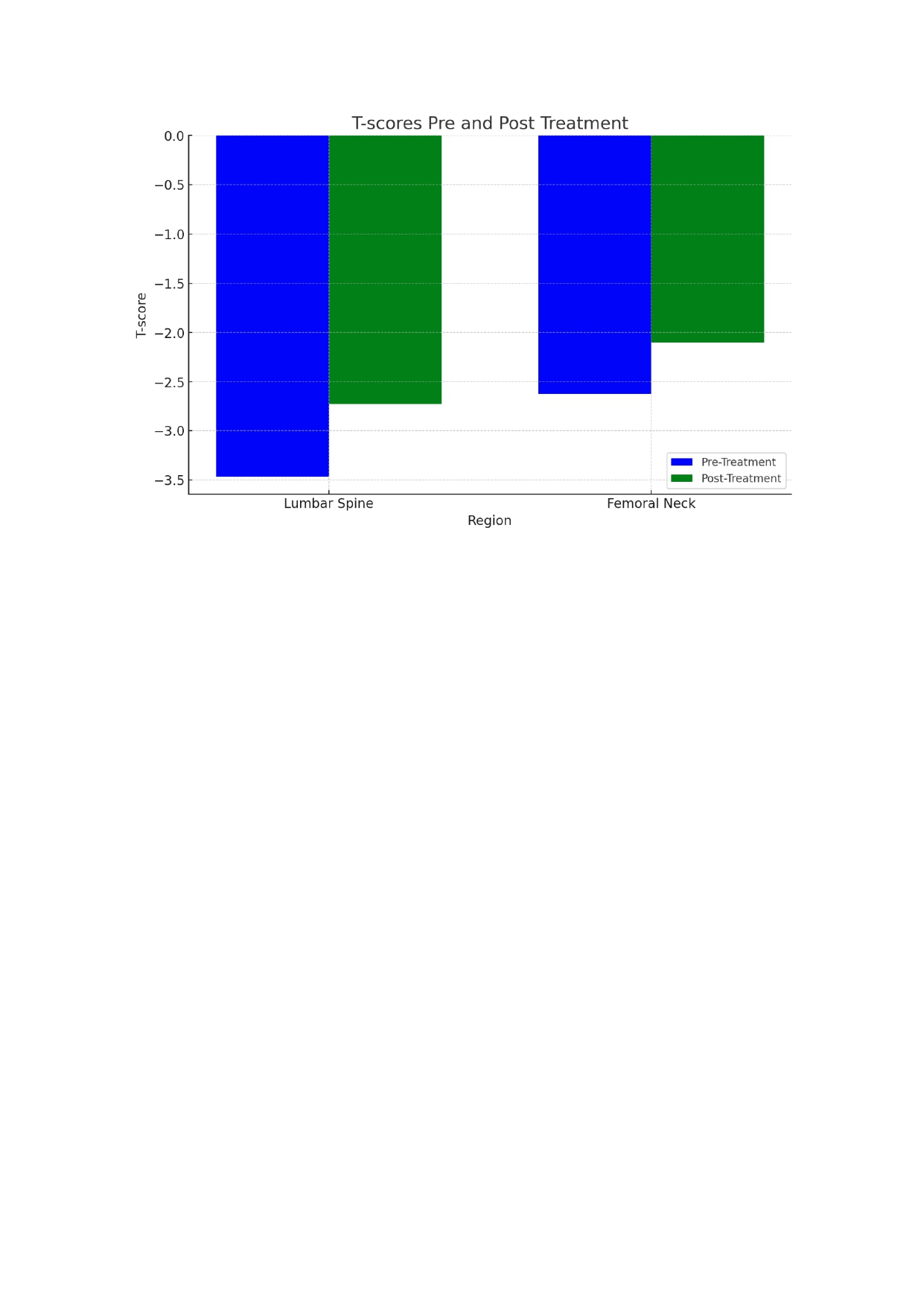
Of the 97 patients, 12-month safety data were available for 35 patients; none had suffered a major adverse cardiovascular event (MACE) during treatment. Twelve-month densitometric data (BMD) were available for 16 patients. The difference in pre-post lumbar spine T-score was +0.74 and in the femoral neck was +0.52. Both figures show a statistically significant improvement after one year with ROMO (See Table 2, and Figure 1).
Conclusion: This real-world dataset demonstrates rapid progress in a Spanish patient population. After one year of treatment, the T-scores of the lumbar spine and femoral neck increased significantly. Not a single case of MACE nor any other safety issues were detected. More studies are needed to assess the efficacy of ROMO in treating glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis and in patients with rheumatoid arthritis or other rheumatologic diseases.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Moreno Garcia M, González Mazario R, uson Rodriguez y, meriño Ibarra E, Giner E, Cobeta García J, Arce Benavente M, Fábregas canales m, Ullier Bellmunt J, Boselli G, martinez Valles p, Fragío Gil J, Vazquez Galeano c, Turrion Nieves A. Analysis of Effectiveness and Safety of Romosozumab in Patients with Very High Risk of Fracture in a Spanish Population [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-effectiveness-and-safety-of-romosozumab-in-patients-with-very-high-risk-of-fracture-in-a-spanish-population/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-effectiveness-and-safety-of-romosozumab-in-patients-with-very-high-risk-of-fracture-in-a-spanish-population/