Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: Previous studies have described alterations in fat and lean mass in patients with RA, but the effect of treatments on body composition remains unclear. The objectives of our study were to analyze the change in body composition in patients with RA after 6 months of a TNF inhibitor therapie and to identify the associated factors.
Methods: A controlled cross-sectional observational study of a prospective cohort over a 24-week period was performed. The study subjects were RA patients (ACR/EULAR 2010) with moderate-high mean inflammatory activity during the course of the disease who were selected to initiate first biologic therapy with a TNF inhibitor. All patients were assessed by a predefined questionnaire collecting clinical, analytical and body composition data by Dual-Energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) at the cut-off date, as well as after 24 weeks of biologic therapy. The main variables were Fat Mass Index (FMI, Kg/m2), Lean Mass Index (LMI, Kg/m2) and total lean mass difference during the 6 months of treatment, expressed as total lean mass delta (kg). The inflammatory activity according to DAS28 and CRP was evaluated. Inflammatory mediators, adipocytokines levels and Insulin-like Growth Factor I (IGF-I) were also analyzed. Other included variables were comorbidities, anthropometric and clinical-analytical measurements, therapies and physical activity measured by the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ) per Metabolic Equivalent of Task (METs). Statistical analysis included descriptive analysis, bivariate and one models of multivariate analysis.
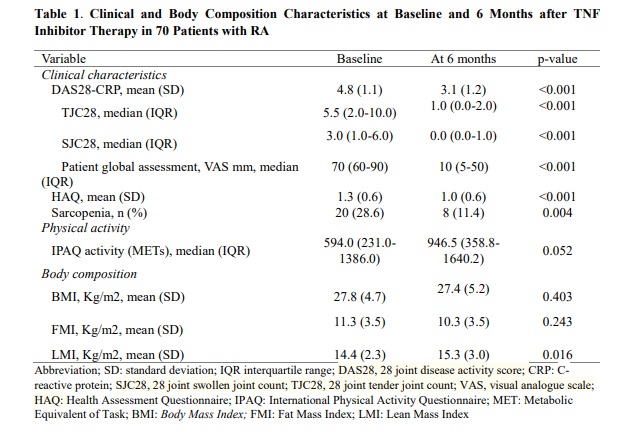
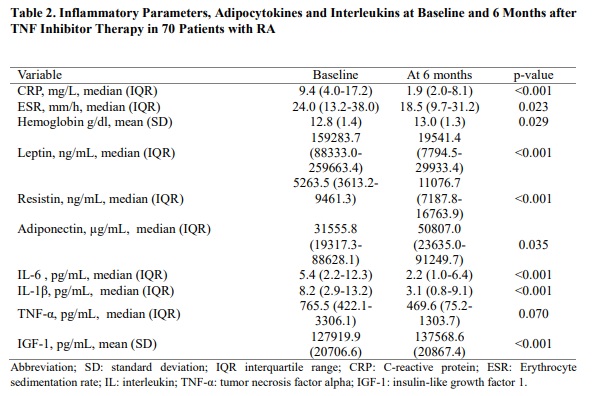
Results: A total of 70 RA patients were included, most of them were female (81.4%) with a mean (SD) age of 56.2 (12.3) years. Table 1 shows the clinical and body composition characteristics at baseline and after 24 weeks of treatment with a TNF inhibitor. Table 2 shows the differences in analytical data, adipocytokines and interleukins. Patients reported clinical and analytical improvement in disease activity, with a significant decrease in inflammatory cytokines and increased resistin and adiponectin values. With respect to body composition, patients experienced a significant increase in LMI (p=0.016). However, regarding FMI, although a decrease was observed during the treatment period, these differences did not reach statistical significance (p=0.243). Significant inverse correlations were observed between LMI and level of adiponectin (p=0.019), IL-6 (p=0.001), CRP (p=0.046), IGF-1 (p=0.009) and ESR (p=0.010). Furthermore, lean mass gain after 6 months of Anti-TNF treatment was significantly inversely correlated with disease duration (p=0.004), inflammatory activity by DAS28-CRP (p=0.023), CRP (p=0.012), as well as with physical function by HAQ (p=0.024). In the multivariate model, lean mass gain was negatively associated with inflammatory parameters, such as CRP (β = -0.440) and DAS28 (β = -0.333).
Conclusion: In RA patients, after 6 months of treatment with TNF inhibitors, a higher Lean Mass Index was observed. The lower inflammatory activity after starting the biological therapy is associated with a higher lean mass gain in these patients. Nonetheless, no alterations in Fat Mass Index have been observed.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
García-Studer A, Ortiz-Márquez F, Borregón-Garrido P, Mucientes-Ruiz A, Manrique-Arija S, Mena Vázquez N. Analysis of Body Composition in Patients with Moderate-Severe Rheumatoid Arthritis Treated with Anti-TNF Drugs [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-body-composition-in-patients-with-moderate-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-anti-tnf-drugs/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/analysis-of-body-composition-in-patients-with-moderate-severe-rheumatoid-arthritis-treated-with-anti-tnf-drugs/