Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session (Tuesday)
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Achieving clinical remission while reducing toxicity are primary objectives in the treatment of lupus nephritis (LN). Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) has demonstrated efficacy benefits with good tolerance as the induction therapy in LN patients of Hispanic or mixed race. However, a comprehensive view is lacking in its usage among Chinese patients with LN. We conducted this meta-analysis based on most updated studies to review the efficacy and safety of MMF induction therapy in Chinese patients with LN.
Methods: Relevant clinical trials were identified by searching PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Collaboration, Medline, National Guideline Clearinghouse, Best Evidence, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, Wangfang, SinoMed, China Science and Technology Journal Database, and WHO ICTRP (in February 2019). The search strategies consisted of (mycophenolate mofetil AND (cyclophosphamide OR azathioprine)) AND (lupus nephritis OR lupus glomerulonephritis OR proliferative glomerulonephritis OR membranous glomerulonephritis OR systemic lupus erythematosus) in English and in Chinese. Retrieved studies were assessed independently by two reviewers. Meta-analysis was conducted using RevMan5.3 software. This review was registered on PROSPERO (CRD42018086209).
Results: Eighteen randomized controlled trials (5 English and 13 Chinese articles; totalling 927 patients) were included in the analysis (Table 1). Complete remission (CR) and total remission (TR, CR + partial remission) were reported in 14 RCTs. MMF showed an efficacy advantage in terms of CR (44.7% vs 32.9%; relative risk [RR] 1.34; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.13, 1.58; p=0.0007) and TR (84.3% vs 70.9%; RR 1.16; 95% CI: 1.02, 1.33; p=0.03) compared to CYC (Figure 1). MMF was associated with lower risks of infection (RR 0.52; 95% CI: 0.38, 0.71; p< 0.0001), amenorrhea (RR 0.21; 95% CI: 0.11, 0.39; p< 0.00001), leukopenia (RR 0.44; 95% CI: 0.23, 0.83; p=0.01), alopecia (RR 0.12; 95% CI: 0.04, 0.37; p=0.0002), and gastrointestinal symptoms (RR 0.48; 95% CI: 0.32, 0.71; p=0.0002) than CYC (Table 2). Relapse rate seemed to be comparable between MMF and AZA groups (RR 1.16; 95% CI: 0.59, 2.28; p=0.68).
Conclusion: This meta-analysis of Chinese LN patient revealed that MMF is more effective than CYC in achieving CR and TR, and it is associated with lower incidences of infections, amenorrhea, leukopenia, alopecia, and gastrointestinal symptoms.

Table 1. Basic clinical data for the 18 studies included
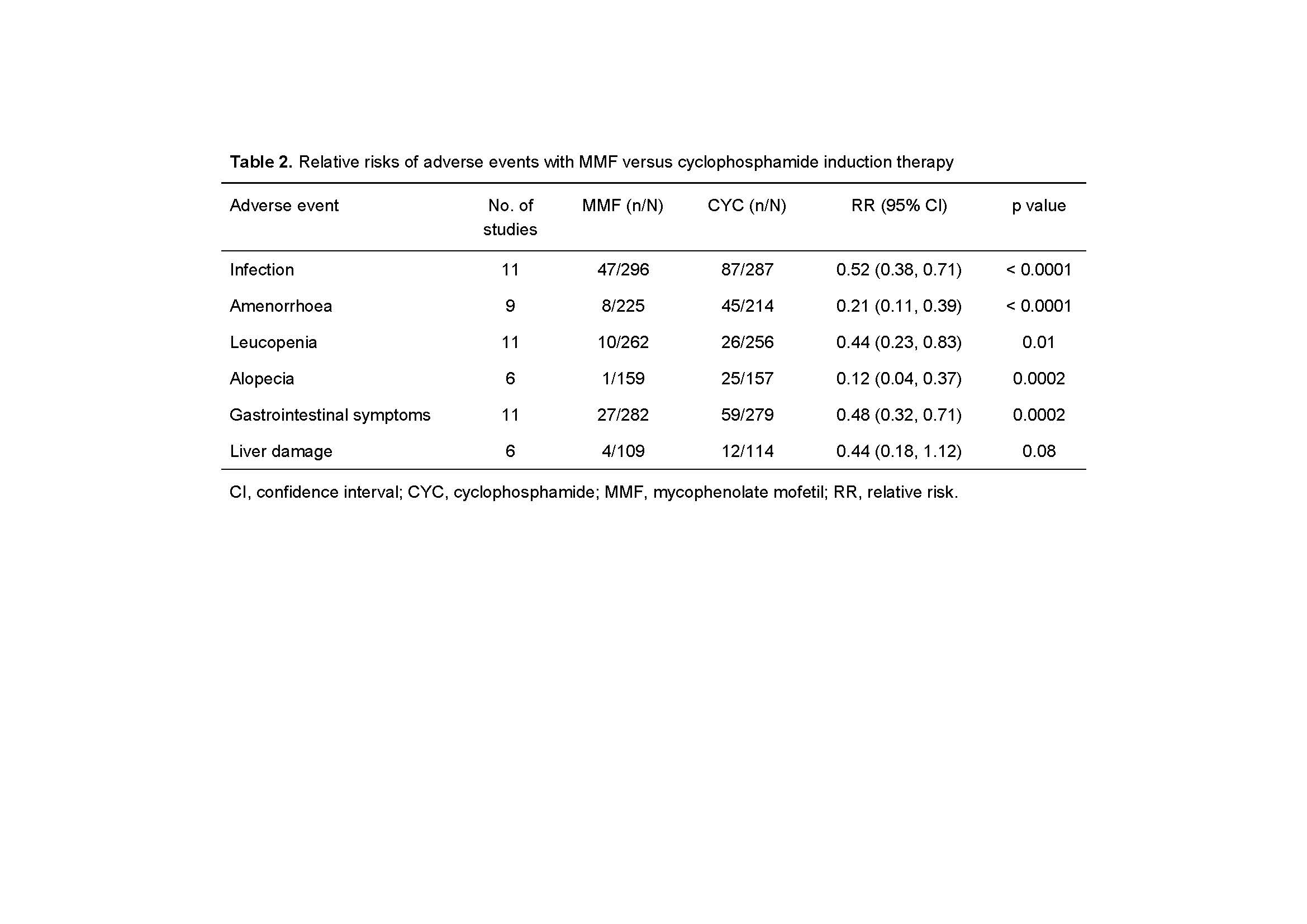
Table 2 Relative risks of adverse events with MMF versus cyclophosphamide induction therapy
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zhou M, yang Y, Han X, Yu X, zhang H. An Updated Meta-Analysis of the Efficacy and Safety of Mycophenolate Mofetil in the Induction Treatment of Chinese Patients with Lupus Nephritis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2019; 71 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-updated-meta-analysis-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-mycophenolate-mofetil-in-the-induction-treatment-of-chinese-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/. Accessed .« Back to 2019 ACR/ARP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-updated-meta-analysis-of-the-efficacy-and-safety-of-mycophenolate-mofetil-in-the-induction-treatment-of-chinese-patients-with-lupus-nephritis/
