Session Information
Date: Saturday, November 16, 2024
Title: RA – Treatment Poster I
Session Type: Poster Session A
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The oral Janus kinase 1-preferential inhibitor filgotinib (FIL) is approved at doses of 100 mg (FIL100) and 200 mg (FIL200) for the treatment of moderate to severe active RA. Previous integrated safety analyses from clinical trials have shown that safety and tolerability is broadly similar between the FIL doses, with a lower incidence of herpes zoster with FIL100 vs FIL 200.1 This analysis provides an update on selected treatment-emergent adverse events for FIL up to a median (maximum) exposure of 4.3 (8.3) years.
Methods: FIL rheumatoid arthritis data were integrated from 7 clinical trials: the Phase 2 DARWIN studies (NCT01888874, NCT01894516), the Phase 3 FINCH studies (NCT02889796, NCT02873936, NCT02886728) and the long-term extension studies DARWIN 3 (NCT02065700) and FINCH 4 (NCT03025308). Exposure-adjusted incidence rates (EAIRs)/100 patient-years of exposure (PYE), censored at time of first event, were determined for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), venous thromboembolism (VTE), arterial systemic thromboembolism (ASTE), nonmelanoma skin cancer (NMSC), malignancies (excluding NMSC), herpes zoster, serious infections and deaths. Data were from completed studies and up until May 8, 2023, for FINCH 4. MACE and VTE only include positively adjudicated events with a data cutoff of May 8, 2023.
Results: In total, 3,691 patients received FIL, with a total exposure of 14,127 PYE. Median (maximum) exposure was 4.3 (8.3) years in the pooled FIL group, 3.6 (8.1) years for FIL100 and 4.4 (8.3) years for FIL200. Baseline demographics and disease characteristics were balanced between the dose groups.2
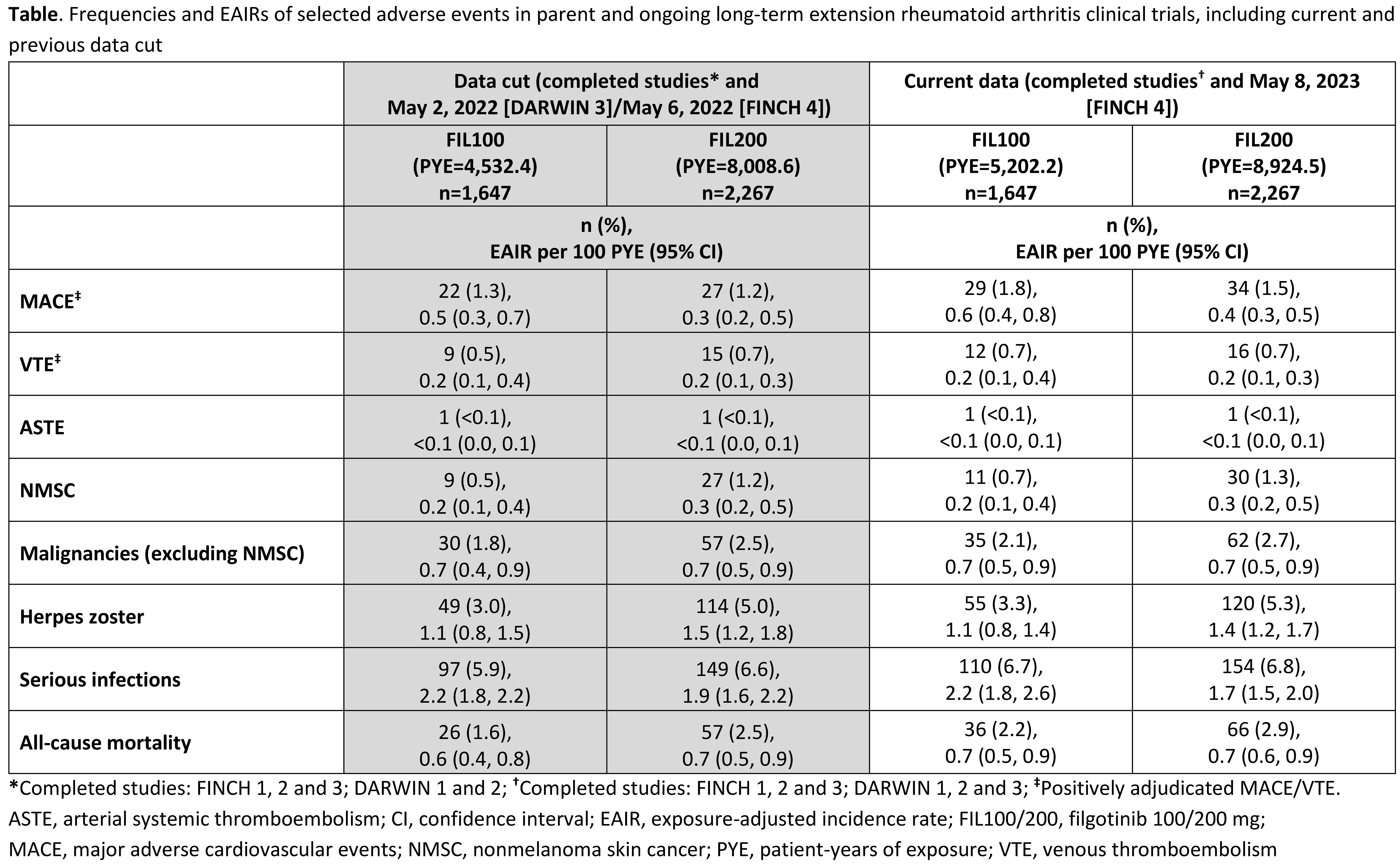
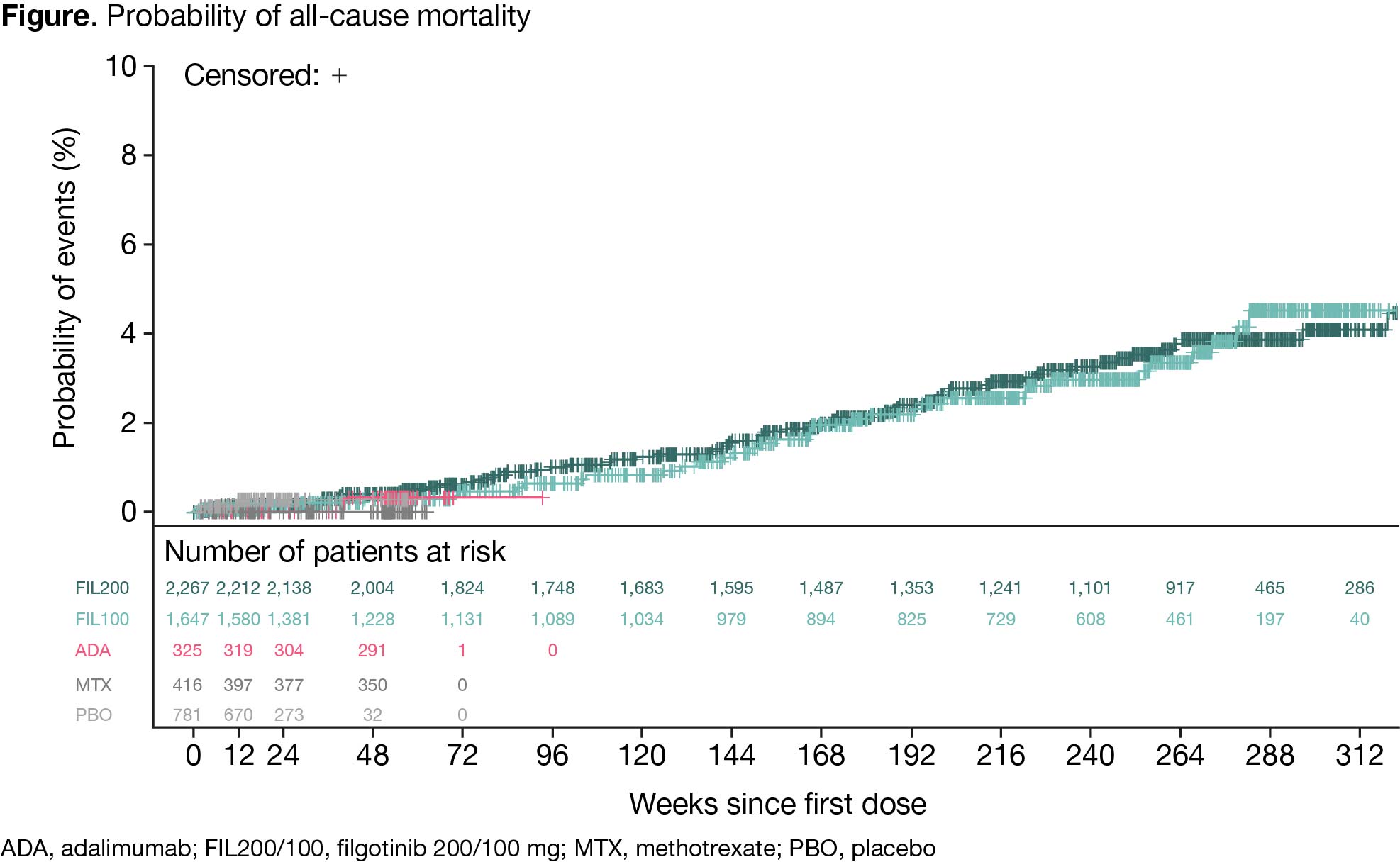
Incidences of adverse events of special interest (AESIs), including MACE, VTE, ASTE, NMSC, malignancies (excluding NMSC), serious infections, herpes zoster and all-cause mortality, were comparable between the data cut in 2022 and the current analysis (Table). The EAIR (95% confidence interval [CI])/100 PYE of serious infections was 2.2 (1.8, 2.6) and 1.7 (1.5, 2.0) in the FIL100 and FIL200 dose groups, respectively. The EAIR (95% CI)/100 PYE of herpes zoster was 1.1 (0.8, 1.4) for FIL100 and 1.4 (1.2, 1.7) for FIL200 (Table). Owing to the study designs, duration of exposure was shorter in the FIL100 (5,202.2 PYE) than in the FIL200 group (8,924.5 PYE); comparisons of EAIRs between treatment groups should therefore be made with caution. Over 312 weeks, the risk of all-cause mortality was similar for FIL100 and FIL200 (Figure).
Conclusion: In this updated integrated safety analysis, the safety profile of FIL remains stable over time and similar to that from the previous analysis. No new safety information concerning AESIs were identified in the overall rheumatoid arthritis population.
References:
1. Winthrop KL, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2023;82:721–22
2. Winthrop KL, et al. Ann Rheum Dis 2022;81:184–92
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Winthrop K, Aletaha D, Caporali R, Tanaka Y, Takeuchi T, Modgill V, Ekoka Omoruyi E, de Vries D, Van Beneden K, Gottenberg J, Burmester G. An Update on the Integrated Safety Analysis of Filgotinib in Patients with Moderate to Severe Active Rheumatoid Arthritis over a Median of 4.3 Years [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-update-on-the-integrated-safety-analysis-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-over-a-median-of-4-3-years/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-update-on-the-integrated-safety-analysis-of-filgotinib-in-patients-with-moderate-to-severe-active-rheumatoid-arthritis-over-a-median-of-4-3-years/