Session Information
Date: Sunday, November 7, 2021
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 8:30AM-10:30AM
Background/Purpose: The optimal first-line treatment of patients (pts) with early rheumatoid arthritis (eRA) is yet to be established. The main objectives were to assess and compare clinical and radiographic outcomes after 48 weeks of active conventional therapy (ACT) with conventional synthetic (cs)DMARDs plus glucocorticoid versus each of three biological (b)DMARDs with different modes of action (certolizumab pegol, abatacept and tocilicumab), all combined with methotrexate (MTX).
Methods: The NORD-STAR trial (NCT01491815) was conducted in the Nordic countries and Netherlands (1). In this investigator-initiated, randomized, open-label, blinded-assessor study pts with treatment-naïve, eRA with DAS28 >3.2, and positive RF or ACPA, or CRP >10mg/L were randomized 1:1:1:1. Methotrexate (25 mg/week) was combined with: 1) ACT: oral prednisolone (tapered quickly; discontinued at wk 36); or: sulphasalazine, hydroxychloroquine and mandatory intra-articular (IA) glucocorticoid (GC) injections in swollen joints; 2) certolizumab 200 mg EOW SC (CZP); 3) abatacept 125 mg/wk SC (ABA); tocilizumab 162 mg/wk SC (TCZ). IA GC was allowed in all arms except wks 20-24 and 44-48. Co-primary outcomes were clinical disease activity index remission (CDAI≤2.8) at wk 48 and change in total van der Heijde-modified Sharp Score from baseline to wk 48 (∆vdHSSw0-w48).
As predefined in the statistical analysis plan, 6 primary null hypotheses were tested: no difference between ACT and each of the 3 bDMARDs for each of the two co-primary outcomes. Multiplicity was handled by Bonferroni correction of the co-primary outcomes (resulting in a 0.025 significance level per outcome), and then applying Dunnet’s multiple comparison procedure with ACT as reference within each outcome. Logistic regression with non-responder imputation (NRI) (dichotomous outcomes) and analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) (∆vdHSS) were applied with inter- or extrapolation for missing values and adjusted for baseline value (only ANCOVA), gender, ACPA status and country.
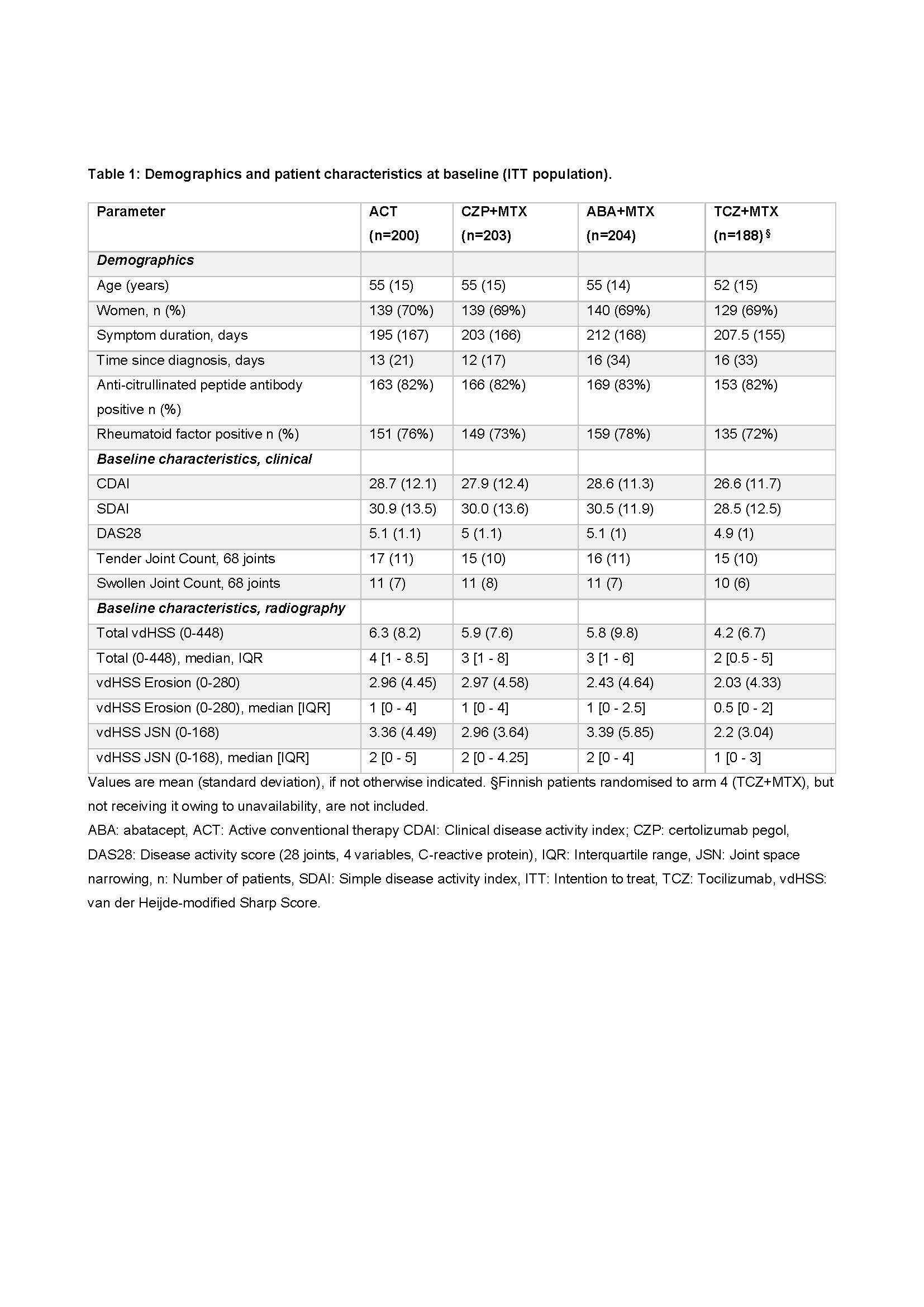
Results: 812 pts were randomized. Table 1 shows baseline data.
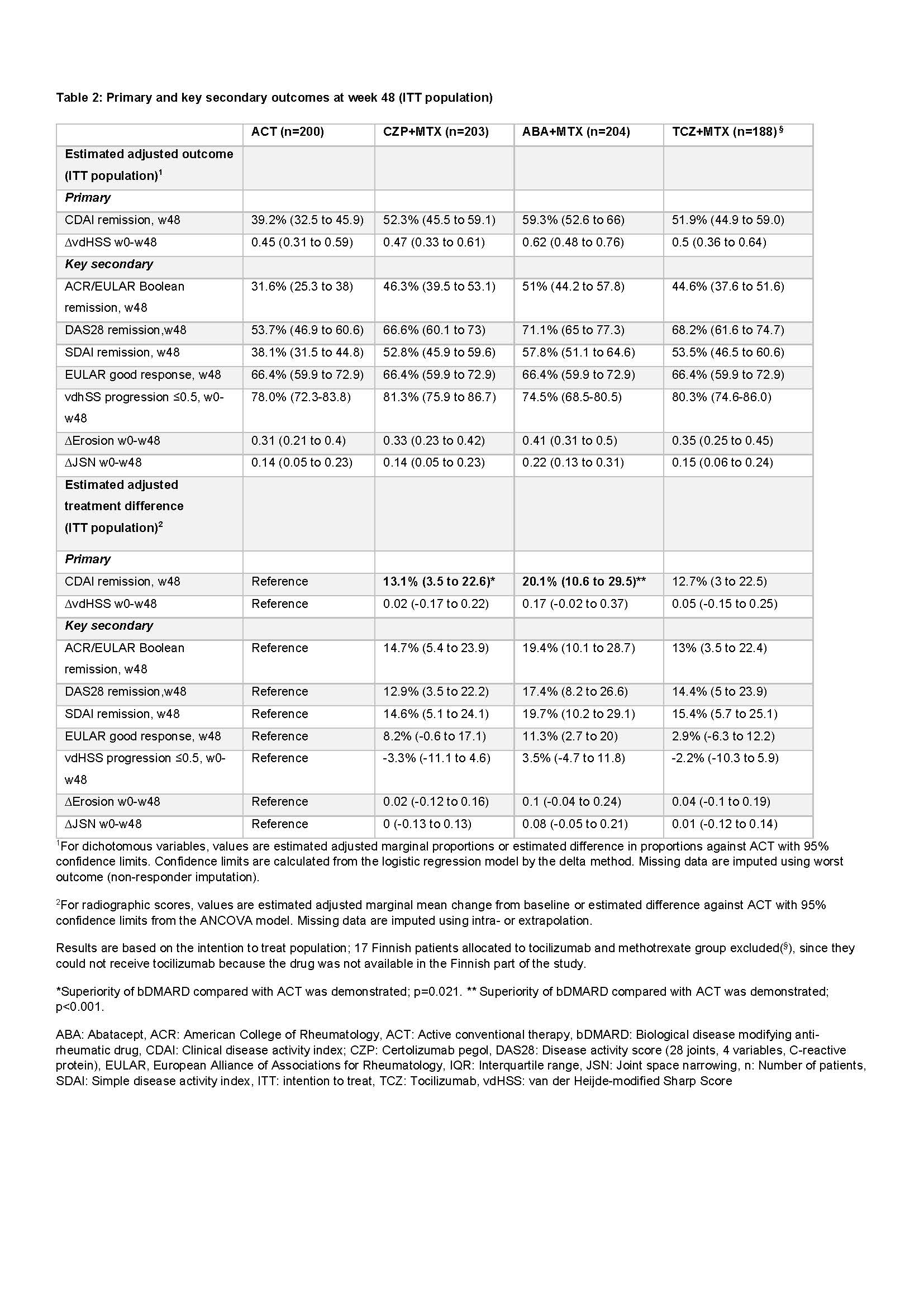
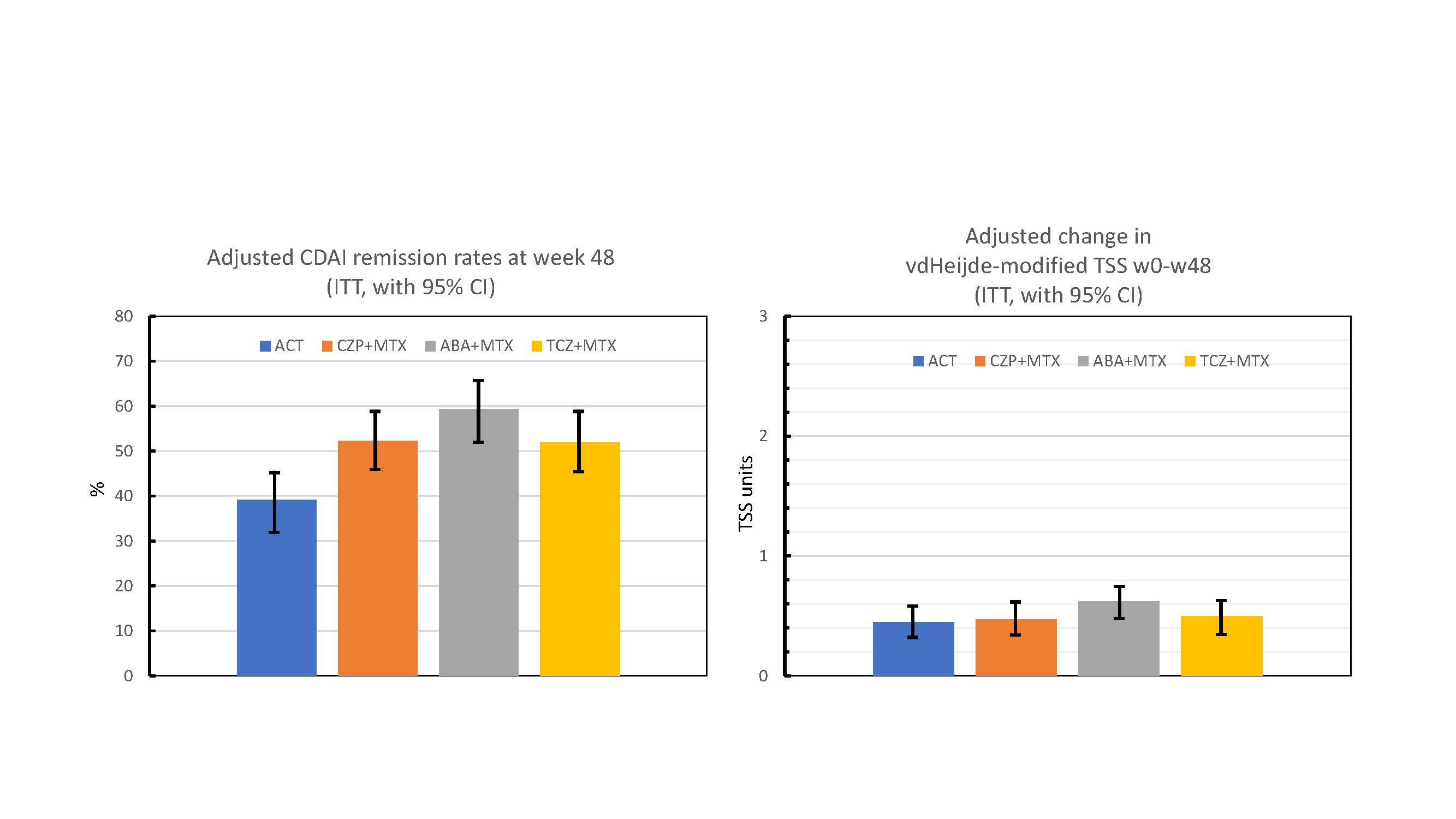
Adjusted CDAI remission rates at w48 were: 59.3% (for ABA), 52.3% (CZP), 51.9% (TCZ) and 39.2% (ACT), with the null hypothesis formally rejected for ACT vs ABA (adjusted difference +20.1%; adjusted p< 0.001) and ACT vs CZP (+13.1; p=0.021), but not for ACT vs TCZ (+12.7; p=0.030). For key secondary clinical outcomes improved clinical outcomes in bDMARD groups compared to ACT were consistently found (Table 2).
Adjusted estimated mean ∆vdHSSw0-w48 was 0.62 (ABA), 0.47 (CZP), 0.50 (TCZ) and 0.45 (ACT), i.e consistently low. None of the radiographic null hypotheses were rejected (Table 2).
Safety profiles were as previously reported. The total number of serious adverse events (% patients with ≥1 event) were: ABA 21 (8.3%), CZP 28 (12.4%), TCZ 20 (9.2%) and ACT 23 (10.7%).
Conclusion: Compared with ACT (csDMARD+glucocorticoids), statistically significant superiority regarding CDAI remission rates was demonstrated for ABA+MTX and CZP+MTX, and not for TCZ+MTX. Radiographic progression was low, without significant differences between treatments.
References: 1. Hetland et al. BMJ 2020; 371:m4328
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ostergaard M, van Vollenhoven R, Rudin A, Hetland M, Heiberg M, Nordström D, Nurmohamed M, Gudbjornsson B, Ørnbjerg L, Bøyesen P, Olsen I, Lend K, Hørslev-Petersen K, Uhlig T, Sokka-Isler T, Grondal G, Krabbe S, Lindqvist J, Gjertsson I, Glinatsi D, Kapetanovic M, Aga A, Faustini F, Parmanne P, Lorenzen T, Giovanni C, Back J, Hendricks O, Vedder D, Rannio T, Grenholm E, Ljoså M, Brodin E, Lindegaard H, Söderbergh A, Rizk M, Hermansson E, Larsson P, Uhrenholt L, Just S, Stevens D, Bay Laurberg T, Bakland G, Haavardsholm E, Lampa J. An Investigator-initiated Multicenter Randomized Study in Early Rheumatoid Arthritis of Active Conventional Therapy versus Three Biological Treatments: 48 Week Clinical and Radiographic Results of the NORD-STAR Trial [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-investigator-initiated-multicenter-randomized-study-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-of-active-conventional-therapy-versus-three-biological-treatments-48-week-clinical-and-radiographic-results-of-the/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-investigator-initiated-multicenter-randomized-study-in-early-rheumatoid-arthritis-of-active-conventional-therapy-versus-three-biological-treatments-48-week-clinical-and-radiographic-results-of-the/