Session Information
Session Type: Abstract Session
Session Time: 9:15AM-9:30AM
Background/Purpose: ANCA-associated vasculitis (AAV) is characterized by fluctuating levels of disease activity. Randomized controlled trials (RCTs) in AAV have used multiple instruments to define active disease or remission as a dichotomous outcome. However, no formal criteria exist to measure treatment response in AAV. This Delphi exercise aimed to reach consensus about which measures are considered by patients and physicians to be most important when assessing treatment response in RCTs in AAV.
Methods: An international 3-round online Delphi exercise was conducted in English. Survey participants included experts in AAV and patients with AAV. Items in the Delphi were based on a systematic literature review of outcome measures in RCTs in AAV, and suggestions from a Steering Committee comprised of vasculitis experts and patients with AAV.
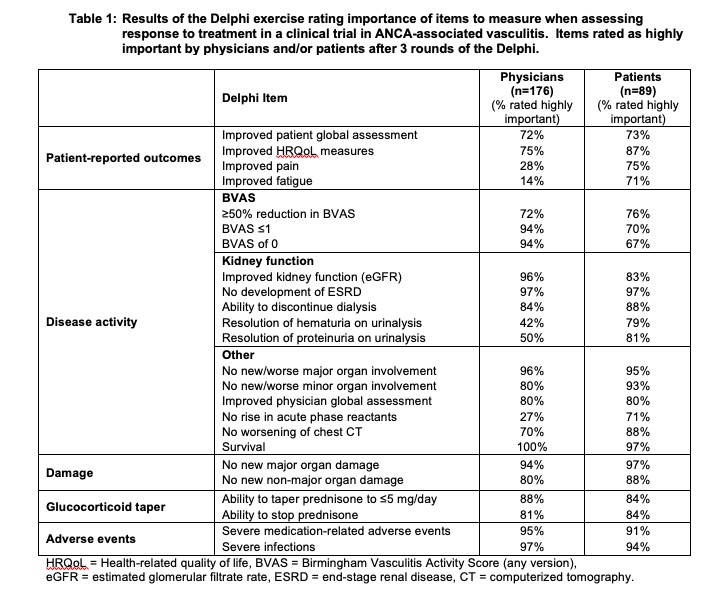
Survey participants were asked to rate (on a scale of 1-9) the importance of each item when assessing response to treatment (improvement) in a RCT in AAV. Items scored 7-9 by ≥70% participants were considered to be highly important, and items scored 1-3 by ≥70% participants were considered to be of limited importance.
Results: 265 participants completed three rounds of the Delphi, including 176 physicians with expertise in AAV and 89 patients with AAV. Physicians were from six continents; the majority from Europe [n=81 (46%)] or North America [n=50 (28%)]. Most physicians specialized in rheumatology [n=105 (60%)] or nephrology [n=50 (28%)]. All physicians were in practice for at least 2 years (two-thirds >10 years) and responsible for managing ≥30 patients with AAV; over half of the physicians managed >75 patients with AAV. Patients with AAV were from four continents, with most located in North America [n=63 (71%)] or Europe [n=23 (26%)] with a diagnosis of GPA [n=71 (80%)] or MPA [n=16 (18%)]. The majority of patients with AAV were female [n=61 (69%)], ages 50-79 years [n=67 (75%)], were diagnosed in the past 10 years [n= 62 (70%)], and were currently on treatment [n=61 (69%)].
The most highly rated items of response (Table 1) involved disease activity [reduction in BVAS, extent of organ involvement, and physician global assessment] and patient-reported outcomes [patient global assessment and health-related quality of life]. Achievement of BVAS ≤1 and BVAS of 0 were highly rated more often by physicians than by patients. Pain and fatigue were highly rated by patients, but not by physicians. Changes on urinalysis and acute phase reactants were highly rated only by patients. Additional items related to organ damage, glucocorticoid tapering, and treatment-related adverse events were highly rated by both patients and physicians. There were no items rated of limited importance by both patients and physicians.
Conclusion: In this Delphi exercise, there was consensus between international experts in AAV and patients with AAV on many items considered important to measure when assessing treatment response in RCTs in AAV. There were also some items rated as highly important by only experts or only patients. These data provide insights into how to evaluate this complex form of vasculitis and will inform the next steps in the development of treatment response criteria in AAV.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Quinn K, Monti S, Lanier G, Bjork Viðarsdóttir M, Christensen R, Jayne D, Langford C, Mahr A, Pagnoux C, Tomasson G, Merkel P. An International Delphi Exercise to Identify Items of Importance for Measuring Response to Treatment for ANCA-associated Vasculitis [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021; 73 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-international-delphi-exercise-to-identify-items-of-importance-for-measuring-response-to-treatment-for-anca-associated-vasculitis/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2021
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-international-delphi-exercise-to-identify-items-of-importance-for-measuring-response-to-treatment-for-anca-associated-vasculitis/