Session Information
Date: Tuesday, November 10, 2015
Title: Rheumatoid Arthritis - Human Etiology and Pathogenesis Poster III
Session Type: ACR Poster Session C
Session Time: 9:00AM-11:00AM
Background/Purpose: Anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPAs)
are specific to rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and are associated with disease
severity. Although ACPAs are associated with disease progression, mechanisms driving
this relationship are not well understood. The objective of this study was develop
an in vitro model incorporating bovine bone chips and micro-CT (µ-CT) to
investigate the effects of ACPA on bone remodeling.
Methods: PBMCs were isolated from the blood of
normal controls. Osteoclasts (OCs) were generated by culture in α-MEM
media containing 1% penicillin/streptomycin and 10% heat inactivated FBS along
with RANKL (1 ng/ml) and MCSF (10 ng/ml) for 14 days. Sera from ACPA positive RA
patients was obtained and IgG was isolated using Staph Protein G columns. Antibody
to citrullinated type II human collagen (Cit-C-II) was purified using CNBR
Sepharose beads coupled with Cit-C-II. F(ab’)2 and Fc fragments were generated
using pepsin columns and were added to differentiated OCs in the presence and
absence of C-II and Cit-C-II and incubated with bone chips for 3 days (n=3
chips/group). Bone chips were then scanned with µ-CT for bone mineral density (BMD)
and pit volume (PV). Bone specific alkaline phosphatase (BAP) and cathepsin-K
(CTPK) were measured on media using ELISA. BAP/CTPK ratios served as the
primary measure of bone turnover.
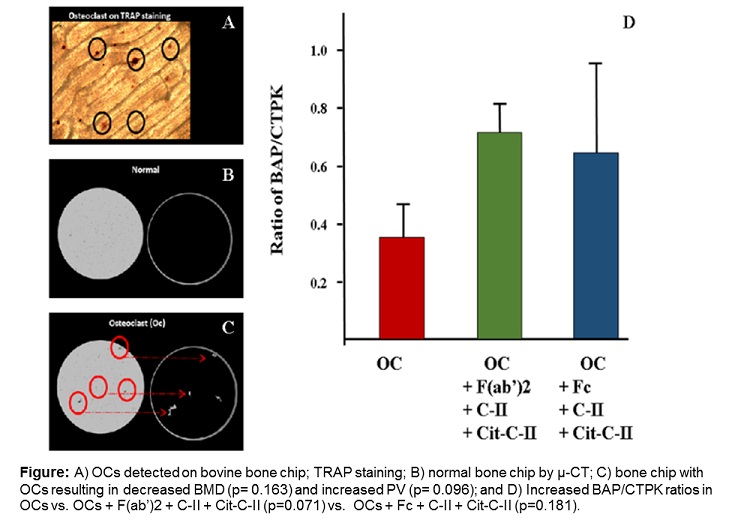
Results: Activated OCs in the absence of ACPA
increased PV and decreased BMD (Figure), although these differences did not
reach significance. Compared to OCs stimulated with F(ab’)2 + C-II + Cit-C-II,
the substitution of Fc fragments for F(ab’)2 led to significant increases in
BAP (4.24 vs. 1.89 ng/ml, p=0.006) and CTPK (7.07 vs. 2.83 ng/ml, p = 0.011);
BAP/CTPK ratio was higher, but not significantly, in OCs incubated
simultaneously with Fc and F(ab’)2 antibodies along with C-II and Cit-C-II as
compared to OCs alone (Figure; p= 0.181 and p= 0.071, respectively). Across
groups, BAP values were positively correlated with PV (r= 0.52, p=0.015). Addition
of the F(ab’)2 or Fc fragments led to a numeric increase in PV and decreased BMD,
although differences compared to OCs alone did not reach significance.
Conclusion: The differential effects of Fc and
F(ab’)2 fragments of anti-Cit-C-II antibody along C-II and Cit-C-II antigens suggests
that the action on bone could be mediated by both the type of antibody fragments
and the amount and type of antigen present. Additional studies with a larger
number of samples will be needed to perform more robust statistical comparisons
including the evaluation of alternative doses and different ACPA. This novel
model, incorporating bovine bone chips with µ-CT, appears to be a practical and
reproducible approach for studying the osteoimmunology of ACPA and citrullinated
antigens.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sethi MK, Dusad A, Hollins A, Hunter CD, Duryee MJ, Mikuls TR, Thiele GM, Gravallese EM. An in Vitro Bovine Bone Chip Model with Micro-CT: A Model for the Assessment of Autoantibody Mediated Bone Resorption [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015; 67 (suppl 10). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-in-vitro-bovine-bone-chip-model-with-micro-ct-a-model-for-the-assessment-of-autoantibody-mediated-bone-resorption/. Accessed .« Back to 2015 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-in-vitro-bovine-bone-chip-model-with-micro-ct-a-model-for-the-assessment-of-autoantibody-mediated-bone-resorption/