Session Information
Session Type: Poster Session B
Session Time: 10:30AM-12:30PM
Background/Purpose: The transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) is a critical driver of osteoarthritis (OA) pain. RTX-GRT7039 is an investigational medicinal product containing the active pharmacological agent, resiniferatoxin (RTX), a potent agonist of TRPV1 and a direct-acting neuronal analgesic that selectively targets and deactivates TRPV1-expressing nociceptors.
The aim of this trial was to evaluate the efficacy and safety of a single intra-articular (IA) injection of RTX-GRT7039 in knee OA.
Methods: This phase II RCT (P03, Part 2) enrolled patients with a baseline VAS pain score >40mm (0-100mm) on motion for average joint pain in the target knee during the last 2 days, with or without analgesic medication, and Kellgren-Lawrence Grade 2-4.
Forty patients (25 females, 15 males; mean age of 65.5 years) were randomized and treated with RTX-GRT7039 2 mg [n=11] or 4 mg [n=10; all RTX-GRT7039 doses are presented as equivalent to Euphorbia resinifera latex in the injectate solution] administered consecutively (within 1 minute) to IA local anesthetic (LA; ropivacaine, 5mL, 0.5%); or RTX-GRT7039 4 mg [n=5] or 8 mg [n=7] or placebo [N=7] administered 15 minutes after IA ropivacaine. The primary endpoint (VAS scores for pain on motion) was captured at 3 and 6 months. Pharmacokinetic (PK) samples were collected for up to 2 hours post- RTX-GRT7039 [n=5], 2 mg or placebo [n=1] and were analyzed using a LC-MS/MS method (LLOQ = 50pg/mL). VAS pain scores for the assessment of procedural-related pain were captured for up to 3 hours post injection.
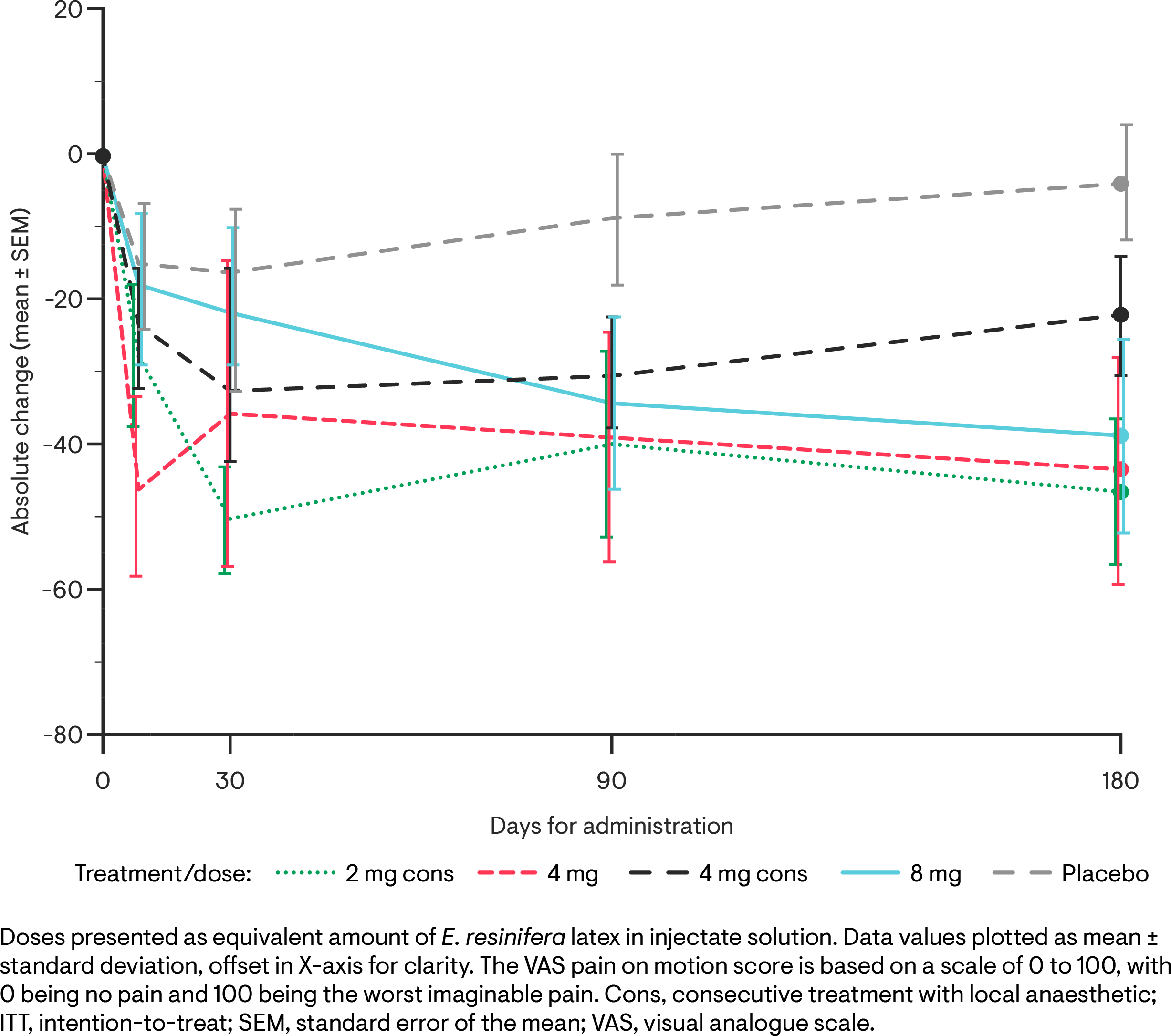
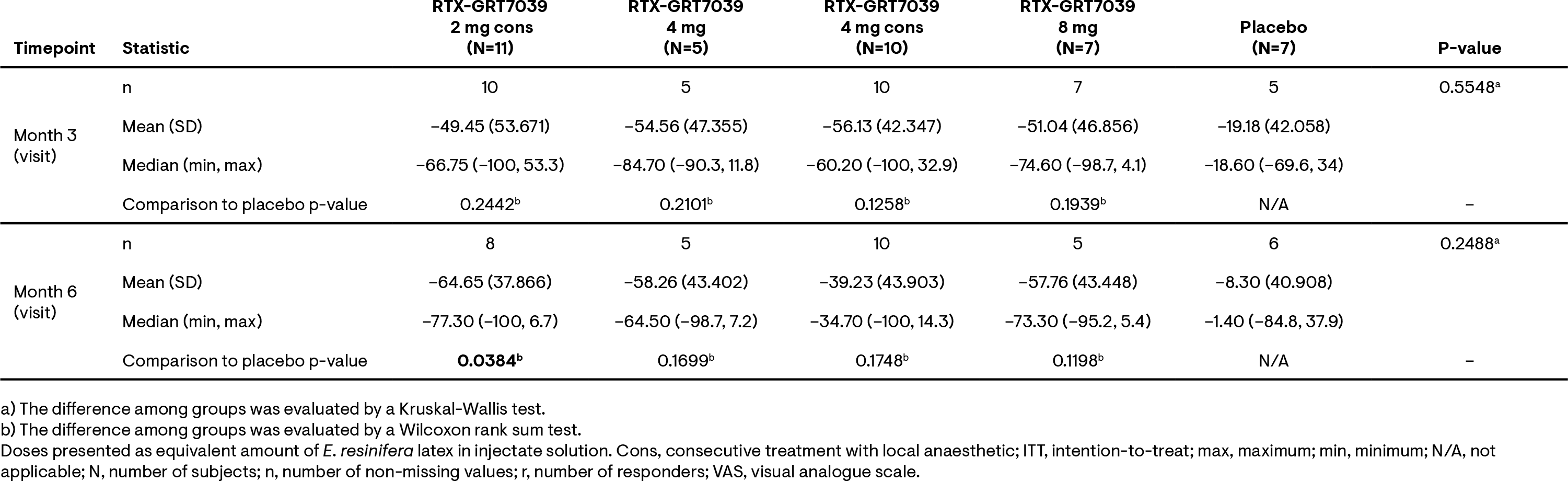
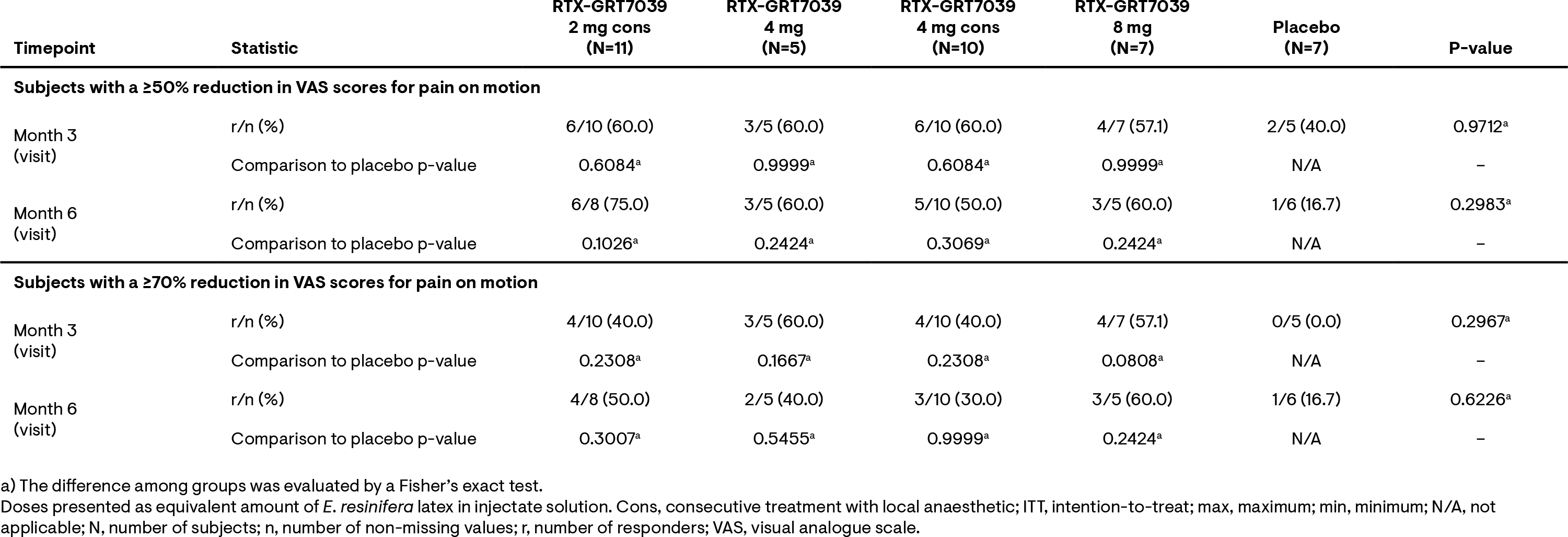
Results: For all treatment groups, mean absolute VAS pain scores for pain on motion experienced over the last 2 days in the treated knee decreased rapidly from baseline (Figure 1). At 3 and 6 months, mean percentage change from baseline in VAS pain scores were greater for the RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups than for placebo (Tables 1). Responder analyses revealed a higher percentage of subjects with ≥50% or ≥70% reduction in VAS scores for pain on motion across all RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups compared to placebo (Table 2). RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups showed a greater reduction in WOMAC total score than the placebo group; consistent changes were generally observed across the WOMAC pain, function and stiffness subscale scores. All samples analyzed for PK were below the LLOQ. Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) were comparable across all treatment groups; the majority were of mild or moderate intensity. The most frequent TEAEs were arthralgia and headache. Two serious AEs (lumbar spinal stenosis and knee arthroplasty) were reported in the group receiving RTX-GRT7039 2 mg immediately after LA; neither considered related to RTX-GRT7039. Procedural-related pain intensity was higher in RTX-GRT7039 treatment groups than for placebo, generally peaking at around 0.5 h post injection and resolving by 1.5-3 h.
Conclusion: This early phase trial indicates that RTX-GRT7039 has the potential to provide meaningful and sustained analgesia for patients with KOA pain. Injection site pain was expected but transient. In this study, RTX-GRT7039 was found to have a good safety profile and to have been well tolerated over the dose range evaluated.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ostenfeld T, Ivanicius S, Stancik R, Conaghan P. An Evaluation of the Efficacy, Pharmacokinetics and Safety, of the Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) Agonist RTX-GRT7039 – a Placebo-controlled Study in Patients with Osteoarthritis Knee Pain [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2024; 76 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-evaluation-of-the-efficacy-pharmacokinetics-and-safety-of-the-transient-receptor-potential-vanilloid-1-trpv1-agonist-rtx-grt7039-a-placebo-controlled-study-in-patients-with-osteoarthr/. Accessed .« Back to ACR Convergence 2024
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-evaluation-of-the-efficacy-pharmacokinetics-and-safety-of-the-transient-receptor-potential-vanilloid-1-trpv1-agonist-rtx-grt7039-a-placebo-controlled-study-in-patients-with-osteoarthr/