Session Information
Date: Tuesday, October 23, 2018
Title: 5T106 ACR Abstract: Measures of Healthcare Quality I: QI in RA (2856–2861)
Session Type: ACR Concurrent Abstract Session
Session Time: 4:30PM-6:00PM
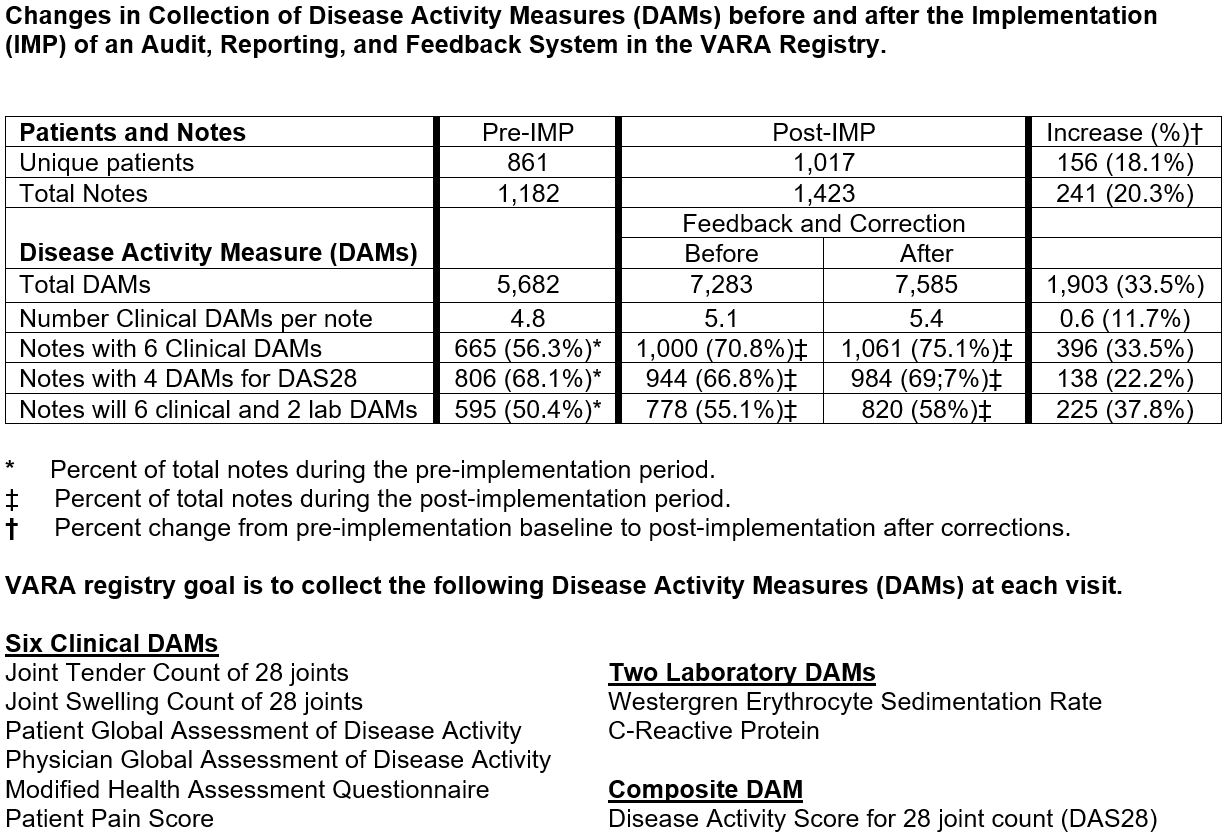
Background/Purpose: The Veterans Affairs (VA) Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) (VARA) registry is an observational cohort study of US Veterans with RA at 11 VA Medical Centers. VARA investigators capture clinical and laboratory disease activity measures (DAMs) during clinic visits via standardized templates in the electronic health record (EHR). Six clinical (tender/swollen joints, patient/provider global, MD-HAQ, pain) and 2 laboratory (ESR, CRP) DAMs are extracted post-visit using natural language processing (NLP). An audit and reporting system was developed to identify and report incomplete DAM collection and provide a method for entering missing data, when available. We report the impact of this system on the quantity and quality of DAMs collected.
Methods: After March 2017, VARA site investigators were provided monthly reports of incomplete / missing DAMs for the prior month. Review of clinic notes was used to identify data that was not captured by NLP because of modification of EHR templates or data entry errors. Updated and/or corrected data were entered into the EHR via note addendums and then automatically re-extracted by NLP to complete the capture of DAM data. DAMs collection from October 1, 2016 to March 31, 2017 (pre-implementation – Pre-IMP) was compared to collection from October 1, 2017 to March 31, 2018 (post-implementation – Post-IMP) before and after investigators received monthly reports.
Results: During the pre-IMP period, there were 1,182 notes with DAMs collected on 861 unique patients compared to 1,423 notes on 1,017 unique patients in the post-IMP period–an increase of 156 (18%) unique patients and 241 (20%) notes. The quantity of DAMs collected increased from 5,682 to 7,585, a 34% increase. During this timeframe enrollment in the VARA registry increased by only 4%. The quality of DAMs collected was measured by completeness of notes containing DAMs which also increased with corrections, as demonstrated by an increase in the average number of DAMs collected per note rising from 4.8 to 5.4 and proportion of notes achieving the goal of 6 clinical DAMs increasing from 56% to 75%. There were 170 notes identified with deficiencies and with monthly feedback 302 DAMs that were original missing added to the database. Similar quantity and quality/completeness improvements were seen in notes with all clinical and laboratory DAMs and the ability to calculate DAS28 (see Table).
Conclusion: An audit, reporting, and efficient data collection system improved both the quantity and quality of DAMs collected in this national observational study. The improvement in the collection of DAMs in RA patients will further enhance the feasibility of conducting epidemiologic and outcomes studies of RA and provide higher quality longitudinal data to enhance the care of RA patients via expanded use of HER.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cannon GW, Rogas J, Bell N, Baker J, Kerr GS, Gaffo A, Richards JS, Barton J, Schwab P, Mikuls TR, Singh N, Caplan L, Lazaro D, Reimold A, Sauer B. An Electronic Audit, Reporting, and Data Correction System Improves the Quantity and Quality of Observational Data Collected for US Veterans Enrolled in the Veterans Affairs Rheumatoid Arthritis Registry [abstract]. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2018; 70 (suppl 9). https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-electronic-audit-reporting-and-data-correction-system-improves-the-quantity-and-quality-of-observational-data-collected-for-us-veterans-enrolled-in-the-veterans-affairs-rheumatoid-arthritis-regis/. Accessed .« Back to 2018 ACR/ARHP Annual Meeting
ACR Meeting Abstracts - https://acrabstracts.org/abstract/an-electronic-audit-reporting-and-data-correction-system-improves-the-quantity-and-quality-of-observational-data-collected-for-us-veterans-enrolled-in-the-veterans-affairs-rheumatoid-arthritis-regis/